
Making Learning Inclusive with the Power of Web Accessibility Solutions
Summarize with:
The traditional mode of education follows a one-size-fits-all approach. However, this approach has excluded many learners from organized education. For instance, approximately 240 million children worldwide have some form of disability. The education system is not equipped to deliver web accessibility and inclusive education in a format that accommodates students with disabilities.
However, digital transformation in the EdTech sector is disrupting this status quo. By making learning an accessible user experience, educators will be relevant to more students. Adopting web accessibility solutions is helping educators offer an agile, inclusive experience.
According to estimates from the World Health Organization, 16% of the global population, or 1.3 billion people, live with a major handicap. Approximately one in four people, or 27% of them, have a disability, according to the CDC.
Collaborating with accessibility experts can significantly boost your EdTech content strategy. This approach expands the reach of your educational materials while ensuring they meet international accessibility standards. It promotes equity, enabling all learners to engage with your offerings.
This blog will explore the benefits of partnering with accessibility companies to enhance your EdTech content strategy, how they can add value, the best ways to implement them, and more.
Table of Contents:
- What are Web Accessibility Solutions?
- Web Accessibility Standards in Education
- Understanding Accessibility in EdTech
- The Importance of Accessibility in Education
- Key Pillars for Accessibility in Higher Education
- What are the Problems People Face with Online Course Accessibility?
- How to Promote eLearning Accessibility in Higher Ed?
- Best Practices for Implementing Accessibility in EdTech
- How Born Accessible Learning Materials Benefit Students and Educators Alike?
- Top 5 Strategies for Building Accessible Learning Materials
- Accessibility Tools and Technologies in Educational Publishing
- Conclusion
What are Web Accessibility Solutions?
Web accessibility solutions refer to tech-enabled solutions that help make websites, apps, and other tools more accessible for learners with a diverse range of needs.
For instance, learners with disabilities may have speech, visual, motor, cognitive, auditory, and neurological challenges. Adopting web accessibility solutions helps learners overcome these barriers and makes the entire learning process inclusive, interactive, and engaging.
Thus, learning becomes an equal opportunity. Many learners excluded from the traditional education system can now access high-quality educational tools and platforms.
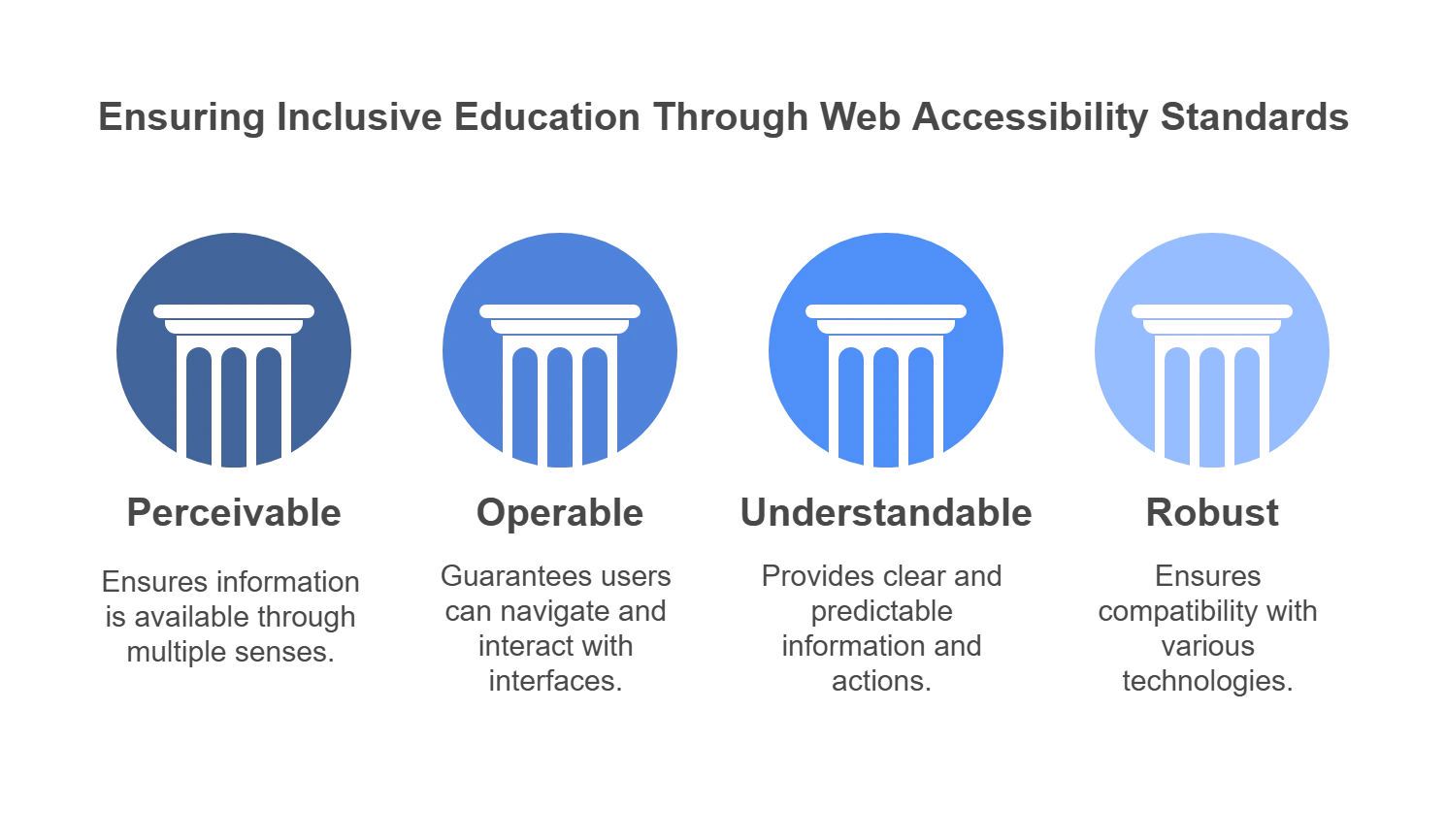
Web Accessibility Standards in Education
WCAG, or Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, is a set of internationally recognized digital accessibility standard guidelines that can be broadly combined under four principles.
These guidelines are encompassed by the acronym POUR, representing four fundamental principles: Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust.
1. Perceivable
We can generally perceive or interact with web content through our eyesight, our auditory senses, and, in certain cases, even our touch.
For web content to be perceivable, it has to be presented in such a way that even if the user lacks one of the senses, there is an alternative perceivable way available by which the content can be understood. For example, videos must have captions, images must have alt text, audio must have transcripts, etc.
2. Operable
We have to understand that many people are impaired by certain physical movabilities, like those with motor disabilities, arthritis, etc. They often face difficulty using a mouse. They tend to use keyboards more easily. So, a web-accessible website will be one that can be navigated even by using only a keyboard. Also, certain content comes with a time limit.
Accessibility ensures that the content or instruction stays on the screen for a longer period of time so that users can interact or respond without rushing.
3. Understandable
An understandable website is one whose content can easily be understood, irrespective of abilities.
Also, the website should be clutter-free and easily navigable. Font size and color should be consistent; graphs and charts should be properly used to summarize content; the reading level should be basic for generic websites, etc.
4. Robust
This is to ensure that the website is as compatible as possible with all kinds of devices, browsers, OSs, and even future updates. Keeping in mind the elderly, the portal should be functional even on certain outdated OSs and browsers.
Understanding Accessibility in EdTech
Accessibility in EdTech is all about ensuring everyone can learn and grow, no matter what.
It’s about creating a space where no one is left behind. Imagine a world where every student, no matter their abilities, can fully engage with the educational content and reach their full potential. That’s what accessibility is all about.
Accessibility involves designing and delivering educational materials that work for everyone—those with visual, hearing, cognitive, or physical differences. It’s about providing alternative ways for people to access the information and interact with the content. The goal is to create a level playing field where every learner has the chance to succeed.
It ensures that the playground of learning is accessible and inclusive for everyone. It’s about creating an environment where everyone feels welcomed, empowered, and able to thrive.
The Importance of Accessibility in Education
When EdTech solutions are accessible, doors open for students who might otherwise face insurmountable obstacles on their journey to educational success. Accessible EdTech-ready students for more inclusive work where they can contribute their unique experiences and perspectives to make meaningful contributions.
Accessibility extends beyond the law; it represents a moral imperative for today’s diversified learning environment. Make sure online learning platforms, resources, and tools are usable by all learners is essential to modern education.
In doing so, institutions not only follow accessibility regulations but also create an inclusive atmosphere. This gives students from diverse backgrounds a sense of belonging, which is also more conducive to participating in varied academic segments.
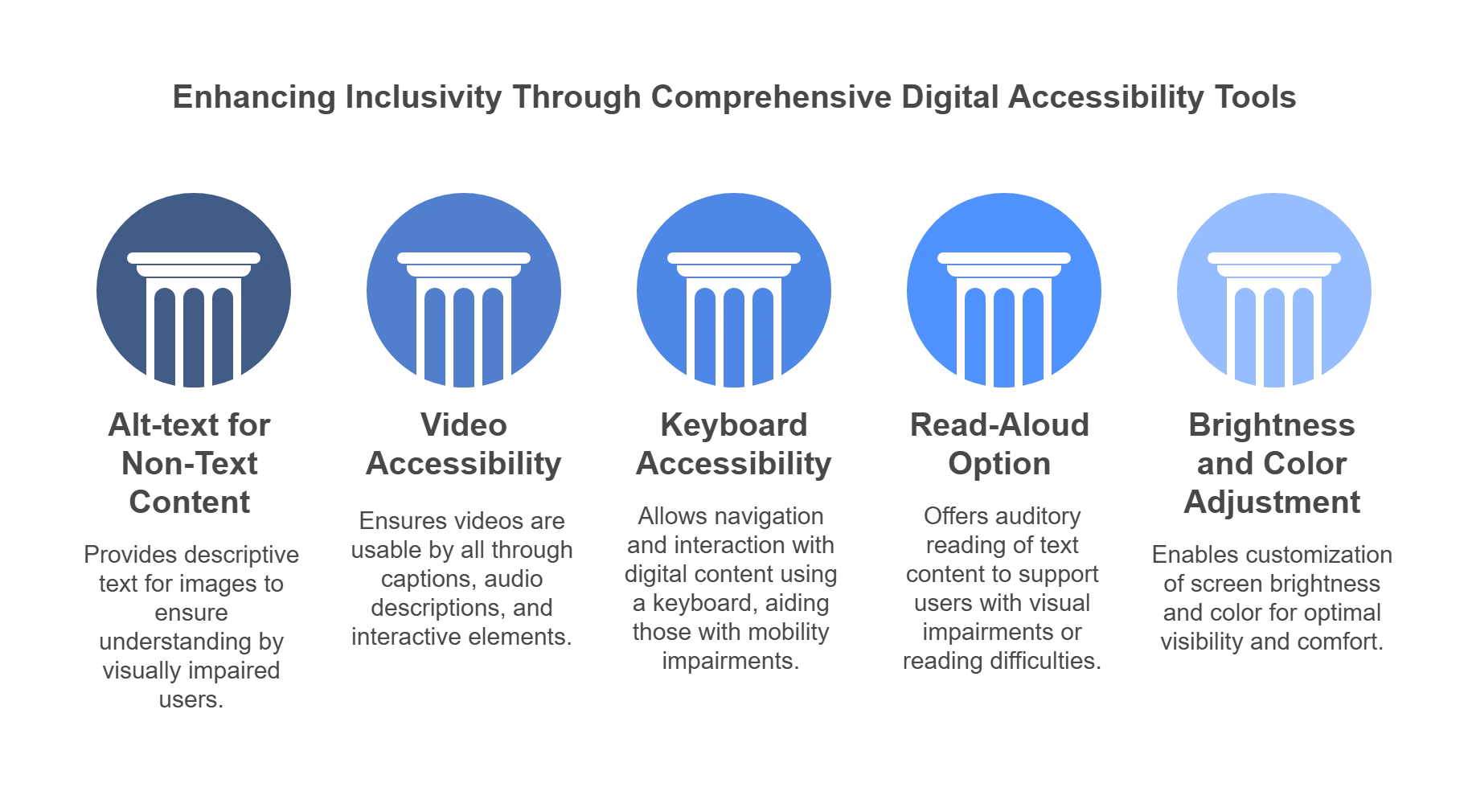
Key Pillars for Accessibility in Higher Education
A snapshot of essential features for enhancing inclusiveness and accessibility in higher education:
1. Alt-text for Non-Text Content
Alt-text or alternative text is a feature that comprises writing text to describe any non-textile content. Such content includes videos, photographs, GIFs, and other types of visual content. These descriptors play an important role in helping learners with visual challenges decipher non-text content.
2. Ensure Video Accessibility
With the rise in popularity of video content, custom EdTech accessibility solutions must include accessible video content that supports learners with a wide range of challenges:
- For instance, videos must have captions in relevant languages, and video pages must feature transcripts of the content.
- The font size and display of captions must be adjusted group based on the learner’s preferences.
- The nonvisual aspects of the video must also be described in detail.
- The video player must have a screen reader so that all the text can be read out loud.
3. Keyboard Accessibility
Not all learners can use a mouse. Friends educators must use assistive technology to ensure that all actions can be executed only with the help of the keyboard.
4. Provide Read-Aloud Option
eBooks, blogs, and other text-based content must have a read-aloud option. Learners with visual themes can listen to the content and access it easily.
5. Adjustment of Brightness and Colours
Learners must be able to adjust the brightness and color scheme of the content as per their specific needs.
6. Adjustment of Font Size and Style
They must also increase or decrease font size and change the phone style to make it let it go and easy to read.
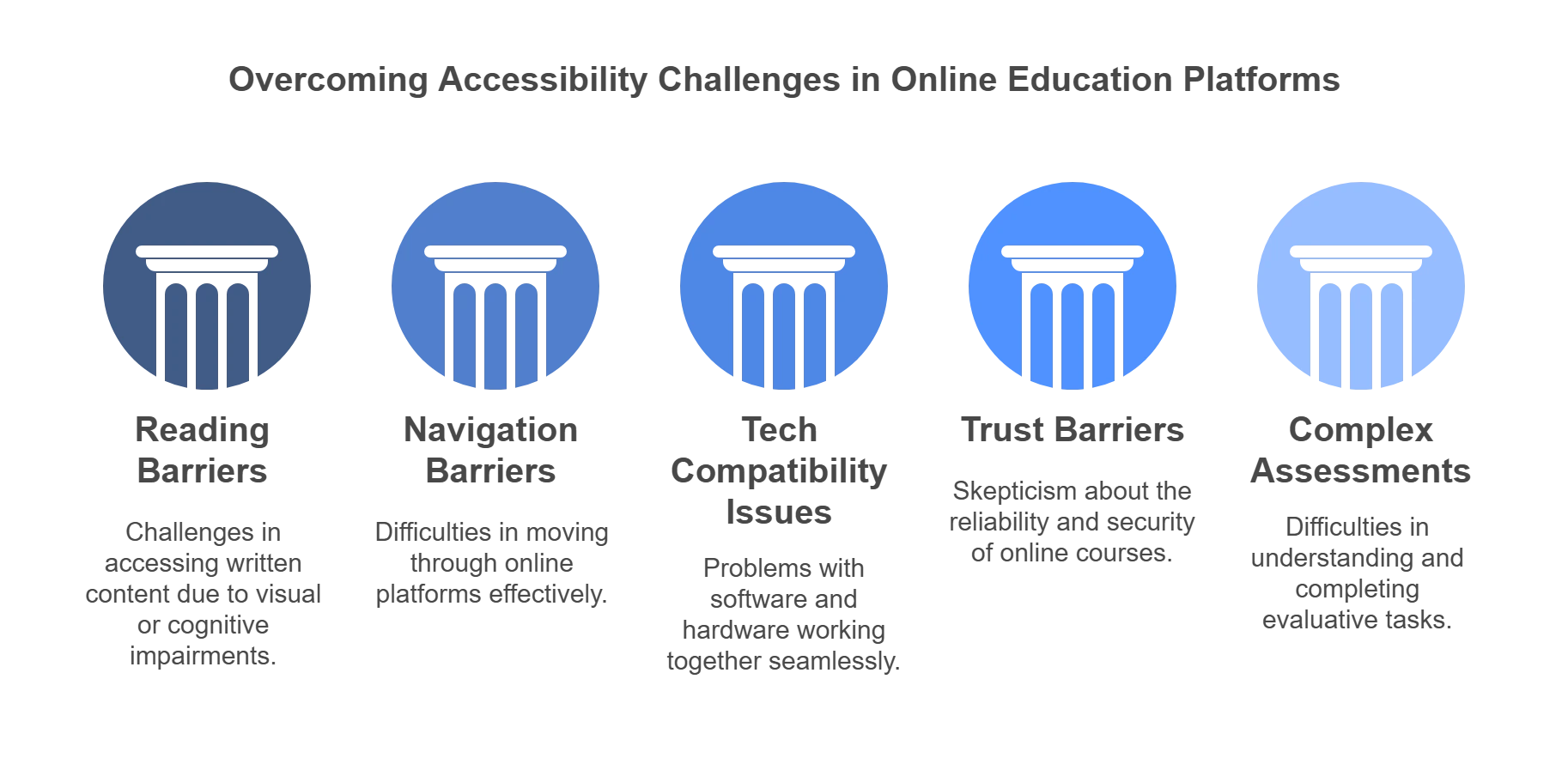
What are the Problems People Face with Online Course Accessibility?
With more and more people turning to online education, especially post-COVID, it is even more important now that the platforms are made web-accessible. Otherwise, several barriers might affect the users’ experience while accessing the course.
Let us look at some of the common reasons:
1. Reading Barriers
This involves selecting an inappropriate font, changing the text size, or contrasting the text’s color with the background. For example, we need to ensure that someone with color blindness can read the content as easily as others or that someone with an eye infection or partial visibility impairments doesn’t face problems reading the fonts due to their smaller size.
2. Navigation Barriers
The interface of an online course should be designed with easy navigation in mind. This includes logical organization, clear headings, and keyboard-friendly controls, ensuring that all students can navigate the course content seamlessly.
3. Tech Compatibility Issues
Considering the compatibility of online courses with various assistive technologies is crucial. From screen readers to speech recognition software, compatibility ensures that technical barriers do not hinder the learning experience.
4. Trust Barriers
Videos, distracting visual carousels, or flashing images impair concentration and may even cause seizures. This can create trust barriers for students, especially those with attention-related challenges. Designing courses that prioritize a focused and distraction-free environment is essential to fostering a trustworthy learning experience.
5. Complex Assessments
Assessments should be designed with flexibility in mind, e.g., providing alternative exam formats. It should ensure that assessments are designed to measure knowledge rather than a student’s ability to navigate inaccessible formats.
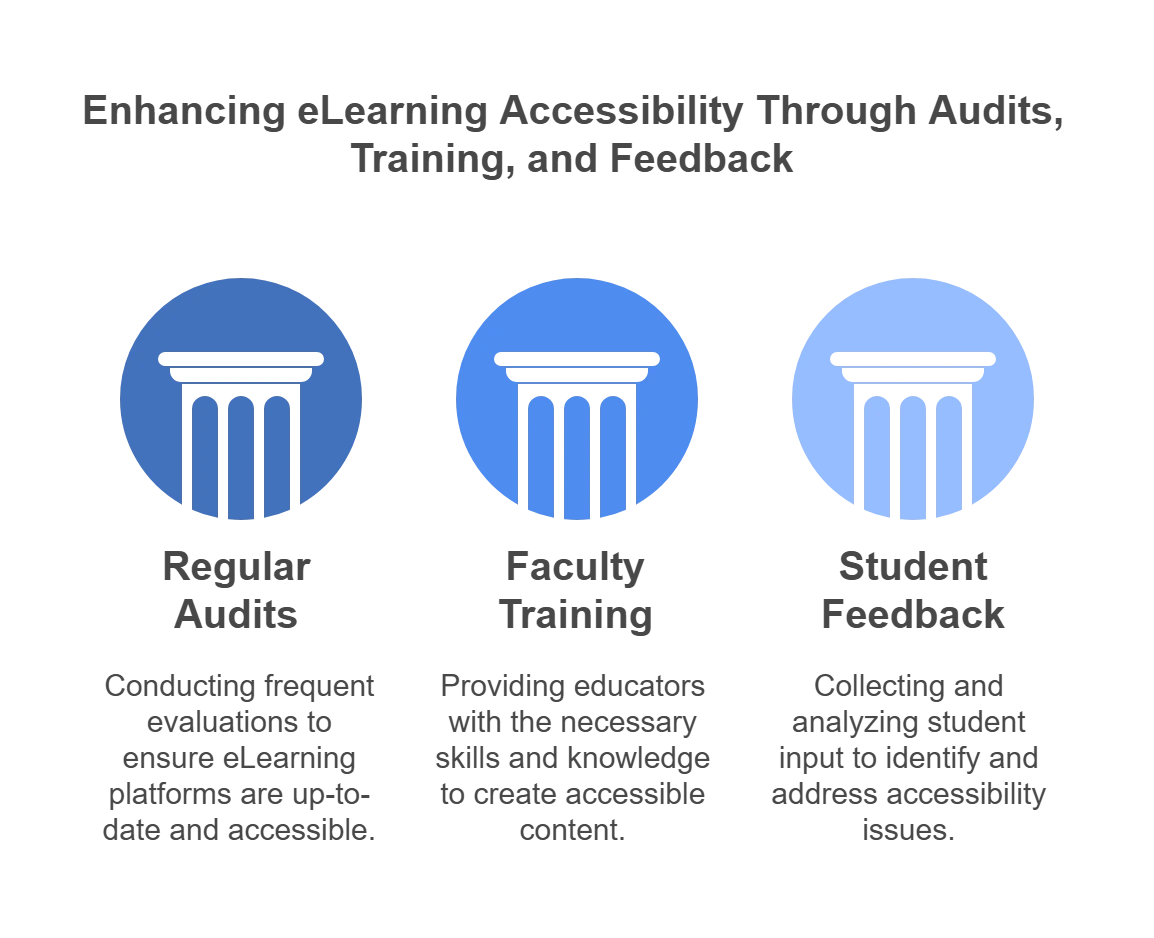
How to Promote eLearning Accessibility in Higher Ed?
Universities and colleges must stay proactive in ensuring that their platforms evolve with the latest web accessibility standards in education. Let us look at some of the steps they can take.
1. Regular Audits and Updates
Periodic accessibility audits are essential for colleges and universities. It’s crucial to assess websites and portals for compliance with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Any identified discrepancies should be promptly addressed and updated on the portal to maintain a high accessibility standard.
2. Faculty Training
Promoting awareness of accessibility among faculty and staff is important. By providing comprehensive training to faculty members, they can gain proficiency in the principles of web accessibility.
This knowledge empowers them to create inclusive content right from the outset. Not only does this approach contribute to a more accessible learning environment, but it also proves to be a strategic investment, saving both time and resources in the long run.
3. Student Feedback
Engage with a diverse group of students with disabilities within your institute to understand their challenges. Inquire about their perspectives on potential solutions and action plans to alleviate these challenges.
Incorporate all viable feedback into your system, ensuring a responsive and inclusive approach to address the specific needs of your student community.
Best Practices for Implementing Accessibility in EdTech
Implementing accessibility in educational technology effectively involves a set of best practices that can ensure all learners benefit from equal access to educational opportunities. Expert accessibility consultants recommend the following strategies:
1. Start with an Accessibility Audit
Conduct an accessibility audit of existing educational materials and technologies to discover potential barriers to access. This baseline review will consider different content and digital platforms to develop a holistic enhancement plan.
2. Implement Universal Design for Learning (UDL)
Elements of UDL must be incorporated to develop instructional material appropriate for all groups of learners. UDL aims to offer multiple representations, actions, and expressions, as well as varied manners of engagement, for diversified learning.
3. Embed Accessibility from the Design Stage
Incorporate features that ensure accessibility at the inception of content development. This covers selecting accessible color contrasts and the appropriate text sizes, as well as ensuring that all media, such as videos, images, or audio, have appropriate alternatives like captions, audio descriptions, and alt text.
4. Offer Training on Accessibility
Train your development team and educators in using accessibility tools and best practices. Continuous training ensures that staff can effectively implement and maintain accessibility standards.
5. Use Accessibility Technology
When considering implementing sophisticated technology tools, ensure they support varied learning requirements, such as screen readers, speech-to-text applications, and adaptive hardware. It is important to have the latest technology since development does not halt for better practices.
6. Regularly Update and Test for Compliance
Update your educational resources to comply with the latest guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. Regular testing on real users, especially people with disabilities, can help you get real feedback and valuable suggestions for improving the system.
How Do Born Accessible Learning Materials Benefit Students and Educators Alike?
Web accessibility is crucial for both educators and students, offering substantial benefits that span across educational experiences. It not only facilitates equal access to online content and resources for students with disabilities but also promotes an inclusive learning atmosphere for all students. This approach enables full online learning participation, enhancing engagement and academic performance.
For students, born-accessible learning materials grant equal access to information, ensuring they can fully engage with online learning materials and the community. It fosters an inclusive environment where every student can participate and collaborate regardless of ability.
Accessibility features like text-to-speech and screen readers allow a customizable learning experience catering to individual needs and preferences. This boosts engagement through clear navigation and interactive content and improves academic performance by making learning materials more accessible.
Furthermore, engaging with accessible technology enhances digital literacy skills and prepares students for future educational and career opportunities. It also cultivates empathy and inclusion, making students more aware of the diverse needs within their community.
Educators benefit from born-accessible learning materials by extending their reach to a more diverse audience, including those with disabilities. This inclusivity in teaching practices enhances the learning environment, promoting equity and diversity.
Knowledge of web accessibility principles contributes to professional development, ensuring educators can meet diverse learning needs. Compliance with legal standards like the WCAG reduces legal risks and underscores a commitment to accessible education.
Ultimately, prioritizing web accessibility encourages a culture of respect and inclusion, creating a supportive educational environment where all members feel valued and empowered to succeed.

Top 5 Strategies for Building Accessible Learning Materials
Creating educational services that are accessible to all can seem overwhelming, especially for those new to the concept of inclusivity in education.
Here are five key strategies we’ve found effective in making education accessible to everyone.
1. Gathering Student Insights
Listening to students is crucial in making education accessible. Their feedback provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of assistive technologies and highlights current accessibility challenges. By involving students in evaluating new technologies and discussing their experiences, educators can identify and implement necessary changes.
Collecting feedback through surveys and forms helps gather comprehensive data on the usability of software, tools, and learning materials, guiding educators toward making informed improvements.
2. Embracing Multilingual Support
A large segment of the world’s population does not speak English as a primary language, making translation tools crucial for education. Providing students with trustworthy translation technology allows them to grasp and interact fully with educational content.
This approach improves their learning journey and bolsters their trust in the integrity of the information provided. Selecting reliable translation resources is crucial to prevent misunderstandings.
3. Optimizing Digital Content
Accessible digital content begins with simple formatting modifications. Structuring text with distinct headings, selecting fonts that accommodate disabilities, maintaining a font size that is easy to read, and providing options to adjust the page content size are basic yet impactful measures to improve accessibility.
Guidance on selecting accessible fonts and designs friendly to dyslexic learners can help educators make their digital offerings more user-friendly for a broad audience, including those with various disabilities.
4. Implementing Text-to-Speech
Text-to-speech technologies are essential for rendering educational materials accessible to those with visual impairments or reading difficulties. This technology transforms written content into audible speech, facilitating an inclusive educational experience for individuals who struggle with conventional reading formats.
Beneficial for people with visual impairments, this solution also supports students with learning disabilities or limited reading proficiency, promoting a more inclusive and fair educational environment.
5. Evaluating Accessibility Tools
The current abundance of accessibility tools allows educators to customize educational settings to meet the needs of a diverse student body. Soliciting student feedback is crucial for highlighting the most beneficial tools to boost accessibility. Moreover, these tools also foster educational equity, with a vast majority of educators acknowledging their importance in comprehensively supporting and understanding the needs of all students.
By implementing these strategies, educators can create a more inclusive and accessible learning environment where every student has the opportunity to succeed.
Accessibility Tools and Technologies in Educational Publishing
In educational publishing, a range of tools and technologies play critical roles in enhancing content accessibility. Accessibility consultants often recommend several key solutions to ensure materials are universally accessible:
1. Screen Readers
These tools are used to read out text appearing on the screen for visually impaired users. They make the content of digital programs both perceivable and understandable.
2. Text-to-speech Software
This includes software programs like Natural Reader, which transform written text into spoken word and are designed for people with dyslexia or other reading challenges.
3. Captioning and Audio Description
Captioning and audio description services provided by companies like Amara and the Described and Captioned Media Program help make audiovisual content usable with assistance for people with hearing or visual impairments.
4. Accessible LMS
Learning Management Systems like Blackboard and Moodle have built-in accessible features, and anyone can use assistive technologies.
Conclusion
Today, digital transformation is revolutionizing the education sector. Schools and colleges are adopting digital tools to make education a more agile, mobile-friendly experience.
Another important consideration is to make education a more inclusive experience across all levels of education. Web accessibility solutions are a game-changer, making education relevant to a broader student demographic.
If your institution is looking to customize web accessibility solutions for your platform, consider leveraging the power of technology to make learning an inclusive experience. Hurix Digital has a deep understanding of accessibility and the tech expertise to customize the user experience to the real-time needs of learners.
Get in touch with us to start a conversation.
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 



