A Modern Educator’s Guide to Purposeful Curriculum Planning & Design
Summarize with:
Due to its current model, education is facing unprecedented challenges. The university must position itself with the changes in industries and the global economy brought about by technological innovations that shape students’ futures.
Regarding the gap, as noted by a study, 80% of employers believe that a graduate does not have the ability or skills needed in the working world. Thus, educational institutions need to rethink their curriculum planning by instilling critical thinking and problem-solving in this rapidly changing environment.
In this light, students are fully armed with knowledge and skills for the 21st century, and universities are embracing innovative teaching methodologies and experiential learning.
Keep reading to identify the changes, review the curriculum planning strategies, and learn how to design and implement one.
Table of Contents:
- The Changing Landscape of Education
- What is Social-Emotional Learning? Why is it Important?
- How to Integrate SEL into Curriculum Planning and Implementation?
- Define the SEL Vision, Mission, and Goals
- Adopt or Adapt an SEL Framework or Model
- Align the SEL Competencies and Standards with the Academic Content and Standards
- Design and Develop the SEL Curriculum and Instruction
- Implement and Monitor the SEL Curriculum and Instruction
- Evaluate and Improve the SEL Curriculum and Instruction
- How to Evaluate the Impact of SEL Curriculum on Students’ Outcomes?
- Implementing Project-Based Learning in Education
- How Can Students Engage in Project-Based Learning?
- Examples of Successful Project-Based Learning Activities
- How to Design and Implement a Future-Proof Curriculum?
- How to Prepare Students for an Interconnected World?
- Wrapping Up!
The Changing Landscape of Education
The world outside us is changing at unprecedented rates. Automation and AI are changing industries and the nature of the skills capable of leading to success in a labor market. Traditional or static curricula might prove unsuitable for equipping the students with the preparation to solve problems in the future, in all probability.
- Age of Automation and AI: It will change the world of work since much of it can be automated—repetitive jobs require higher-level thinking and problem-solving capabilities.
- Change of the Job Market: The job market is changing, and new jobs are emerging as others disappear. Hence, students will need to be flexible enough to learn new skills whenever this is necessary in their lives.
- Increase in Demand for Skills: In uncertain times, students enrolled in higher institutions need to be equipped to work in the future. This might include certain skills, such as creativity, critical thinking, effective communication, problem-solving abilities, or collaboration.
What is Social-Emotional Learning? Why is it Important?
Social-emotional learning (SEL) is the process of developing the skills, attitudes, and behaviors that enable students to understand and manage their emotions, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions.
SEL is based on the premise that learning is not only cognitive but also social and emotional, and that these domains are interrelated and influence each other.
SEL is important because it:
- Enhances students’ academic performance, motivation, and engagement
- Improves students’ mental health, well-being, and resilience
- Reduces students’ behavioral problems, such as aggression, bullying, and substance abuse
- Fosters students’ social skills, such as communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution
- Develops students’ character traits, such as empathy, respect, and responsibility
- Prepares students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, such as diversity, globalization, and technology
SEL is not a separate subject or program but a framework that can be integrated into the academic content and the school culture.
SEL skills and concepts can be taught in two ways:
- The first way is explicit, which means using direct instruction and modeling.
- The second way is implicit, which means creating a supportive and caring learning environment.
Both ways also provide opportunities for students to practice and apply the SEL skills and concepts in various contexts and situations.
Now, let’s dive into the details of curriculum planning, implementation, and evaluation.
How to Integrate SEL into Curriculum Planning and Implementation?
Here are some of the steps and considerations for integrating SEL into curriculum planning and implementation:
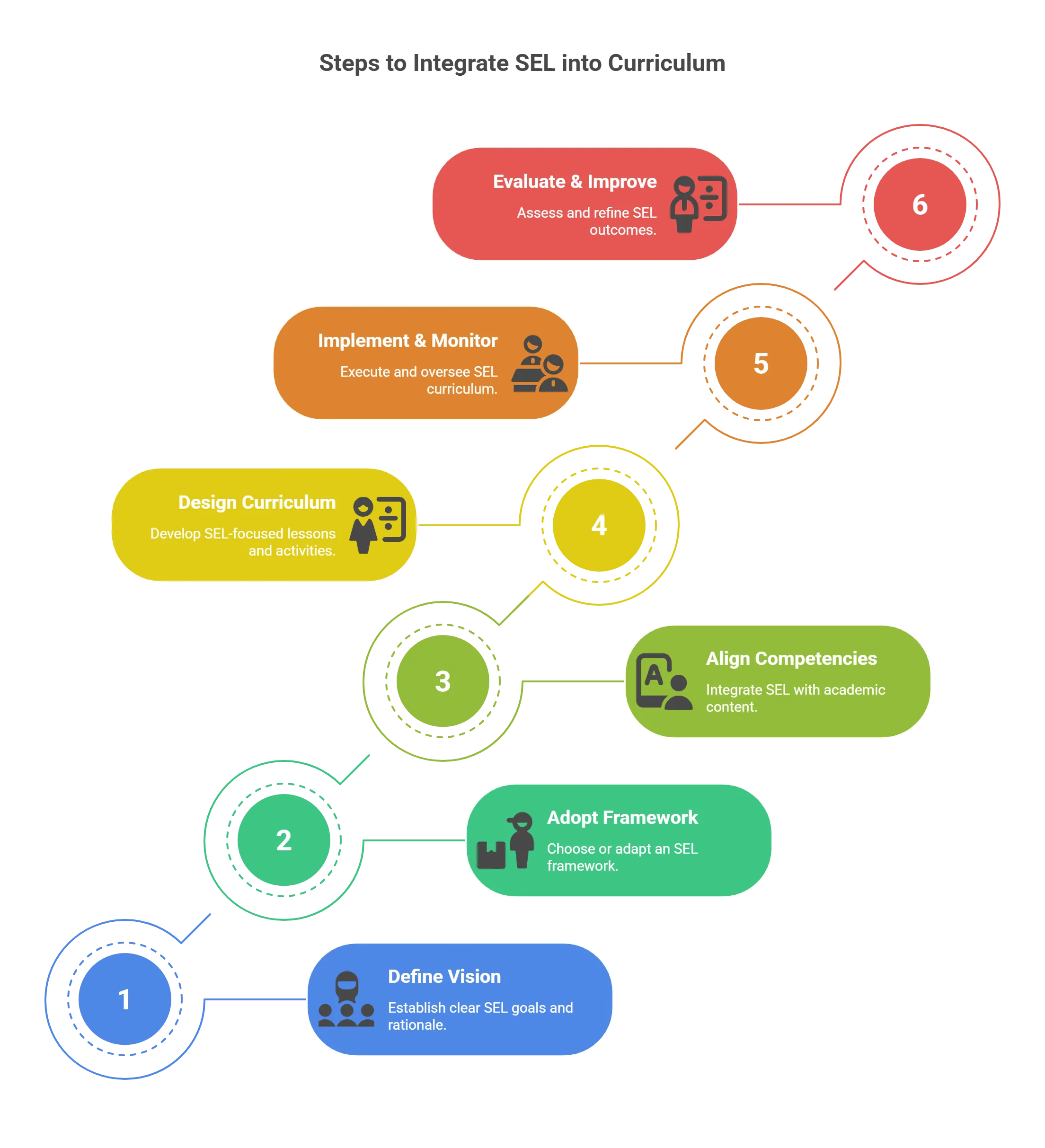
1. Define the SEL Vision, Mission, and Goals
The first step of SEL curriculum implementation is to establish a clear and shared vision, mission, and goals for SEL in the school or district.
This involves articulating the rationale, purpose, and expected outcomes of SEL and how they align with the academic and organizational goals. It also means engaging and communicating with the stakeholders and gaining their support and commitment to SEL.
2. Adopt or Adapt an SEL Framework or Model
It is then necessary to adopt or adapt an SEL framework or model that defines the SEL competencies and standards that students should learn.
Various SEL frameworks and models are available, such as the CASEL’s five core competencies of self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making, or the OECD’s four domains of cognitive, emotional, social, and metacognitive skills.
The chosen SEL framework or model should be relevant, comprehensive, and developmentally appropriate for the students and the context.
3. Align the SEL Competencies and Standards with the Academic Content and Standards
After adopting a framework, align the SEL competencies and standards with the academic content and standards, and identify the connections and opportunities for integration.
SEL competencies and standards are mapped to academic content and standards, to find areas where they overlap, complement, and enhance.
For example, math content can be integrated with the SEL competency of self-management by teaching students how to set goals, plan strategies, monitor progress, and regulate emotions.
4. Design and Develop the SEL Curriculum and Instruction
The next step is to design and develop the SEL curriculum and instruction, and incorporate the SEL competencies and standards into the academic content and instruction.
This means selecting and organizing the SEL content and activitie,s and choosing and implementing the SEL instructional strategies and methods.
For example, the SEL content and activities can include explicit lessons, discussions, role plays, educational games, projects, and reflections. On the other hand, the SEL instructional strategies and methods can include cooperative learning, inquiry-based learning, project-based learning, and problem-based learning.
5. Implement and Monitor the SEL Curriculum and Instruction
Institutions then need to implement and monitor the SEL curriculum and instruction and provide the necessary support and resources for the teachers and students.
Providing professional development and coaching for teachers, as well as creating a positive and supportive learning environment for students, are part of this process.
6. Evaluate and Improve the SEL Curriculum and Instruction
The final step is to evaluate and improve the SEL curriculum and instruction and measure the impact and outcomes of SEL on the students and the school. This involves using various SEL assessment and evaluation tools and methods, such as:
- Surveys
- Observations
- Interviews
- Portfolios
- Performance tasks
- Collecting and analyzing data on the students’ SEL skills, attitudes, behaviors, and academic performance
Furthermore, the data is used to revise and improve SEL curriculum and instruction and to share and celebrate SEL results and achievements.
How to Evaluate the Impact of SEL Curriculum on Students’ Outcomes?
There are different types of SEL assessment and evaluation tools and methods that you can use, depending on your purpose and context. Some of the common ones are:
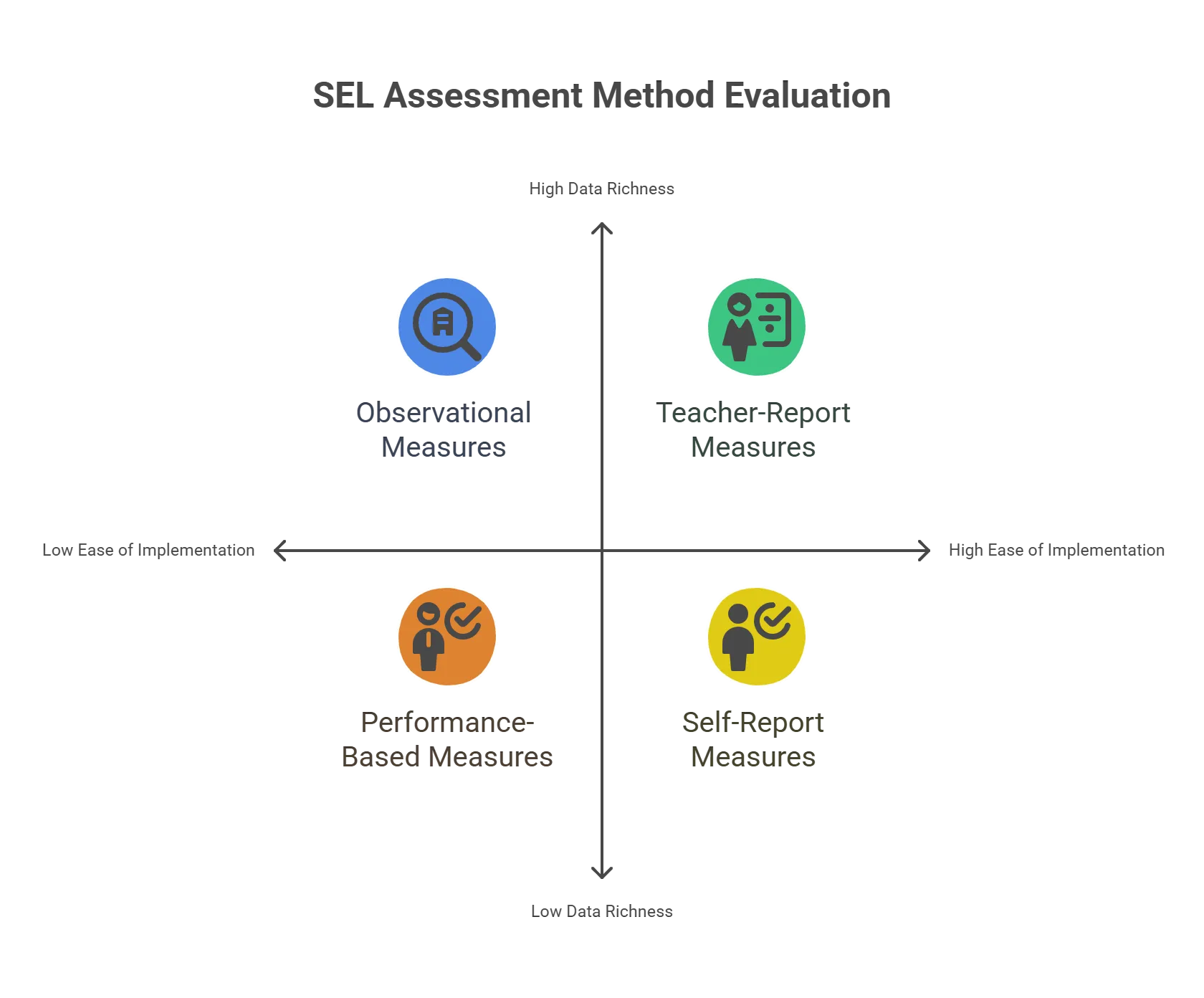
1. Self-Report Measures
These are surveys or questionnaires that ask students to rate their own SEL competencies, attitudes, and behaviors. Self-report measures are easy to administer and score, but they may be influenced by students’ social desirability, self-awareness, and honesty.
2. Teacher-Report Measures
These are surveys or questionnaires that ask teachers to rate their students’ SEL competencies, attitudes, and behaviors. Teacher-report measures can provide a more objective and comprehensive perspective, but they may be affected by teachers’ biases, expectations, and workload.
3. Performance-Based Measures
These are tasks or scenarios that require students to demonstrate their SEL competencies, such as recognizing emotions, solving problems, or collaborating with others.
Performance-based measures can capture students’ authentic and contextualized SEL skills, but they may be difficult to design, administer, and score.
4. Observational Measures
These are tools or protocols that allow observers to record and rate students’ SEL competencies, attitudes, and behaviors in natural or structured settings. Observational measures can provide rich and detailed data, but they may be time-consuming, subjective, and intrusive.
Implementing Project-Based Learning in Education
Here’s how you can implement project-based learning in education:
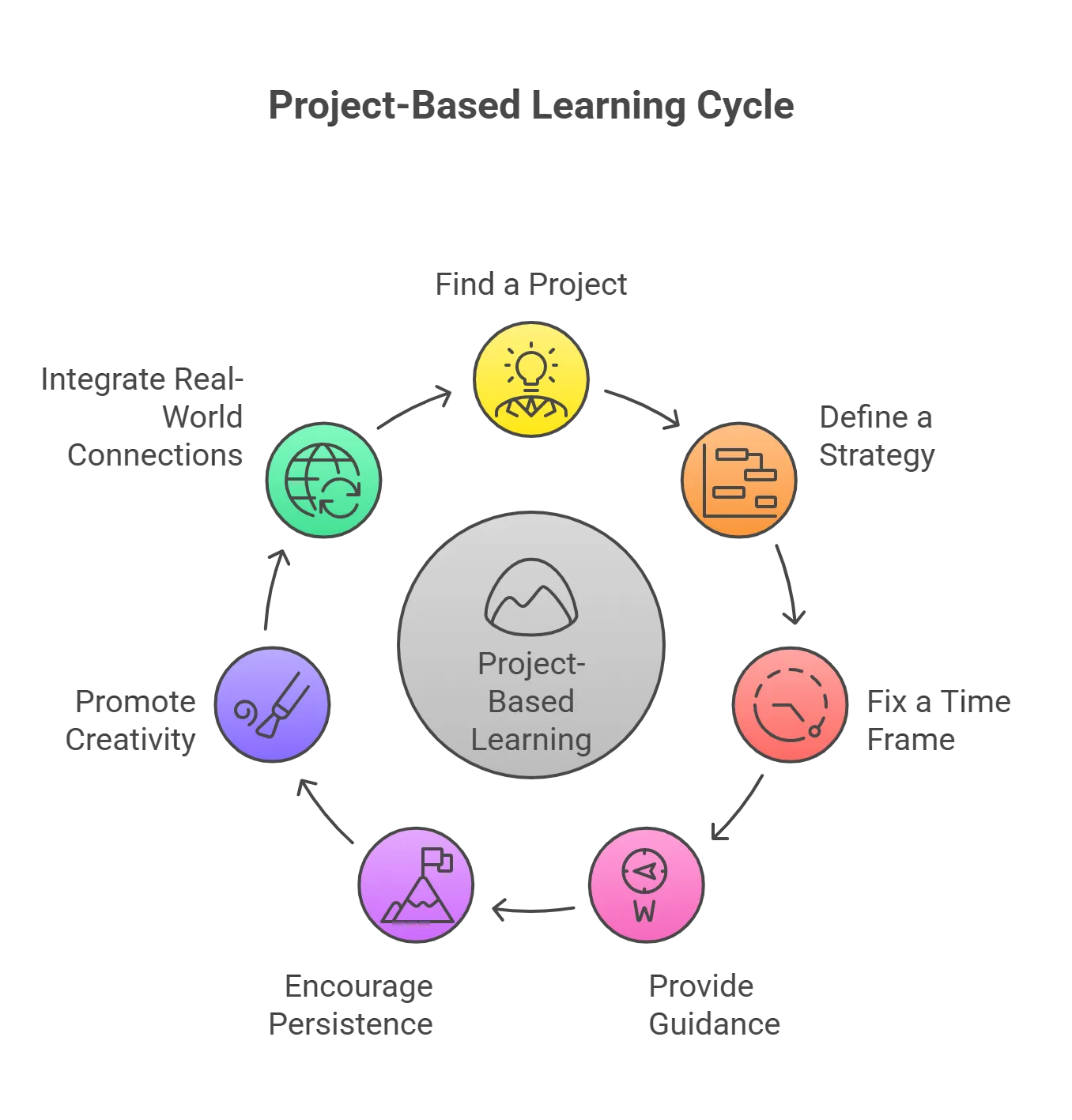
1. Find a Project to Work On
Inspiration can stem from real-world scenarios, igniting students’ curiosity and motivation. Consider diverse projects, such as planning a seminar or addressing a community issue. Encourage interdisciplinary exploration to deepen engagement and relevance.
2. Define a Strategy
Each project requires a thoughtful approach. Designate a project leader and delineate roles for each team member. Provide clear guidelines and activities, empowering students to navigate tasks effectively. Consider various strategies and outcomes to anticipate challenges and cultivate problem-solving skills.
3. Fix a Time Frame
Every project is a time-sensitive endeavor. The student must understand the relevance of a time period for project completion. All of the projects’ activities take a certain amount of time to complete. Every project must be well-structured while still being adaptable in terms of its timeline.
4. Provide Guidance and Monitoring
Often, project participants become stuck with a certain procedure, making it hard to move forward. In this scenario, they will require direction, which may be gained from various sources, including books, the Internet, and professionals in the subject.
While the project leader’s role in project monitoring is critical, the guide instructor also plays a role. So, make sure to provide ample support and guidance to students as they navigate project challenges.
5. Encourage Persistence
Encourage students to persevere through challenges and setbacks. Emphasize the importance of resilience and problem-solving skills in overcoming obstacles and achieving project goals.
6. Promote Creative Exploration
Encourage students to think outside the box and explore creative solutions to project challenges. Foster an environment where experimentation and innovation are celebrated, allowing students to unleash their creativity and develop unique approaches to problem-solving.
This way, you can eventually transform curriculum planning, engaging students in authentic inquiry and real-world experiences through Project-Based Learning (PBL).
7. Integrate Real-World Connections
Connect projects to real-world contexts to enhance relevance and authenticity. Encourage students to explore how their project impacts the broader community or addresses global issues, fostering a sense of purpose and civic responsibility. By grounding projects in real-world applications, students develop a deeper understanding of the significance of their learning.
How Can Students Engage in Project-Based Learning?
Here are some ways students can engage in project-based learning:
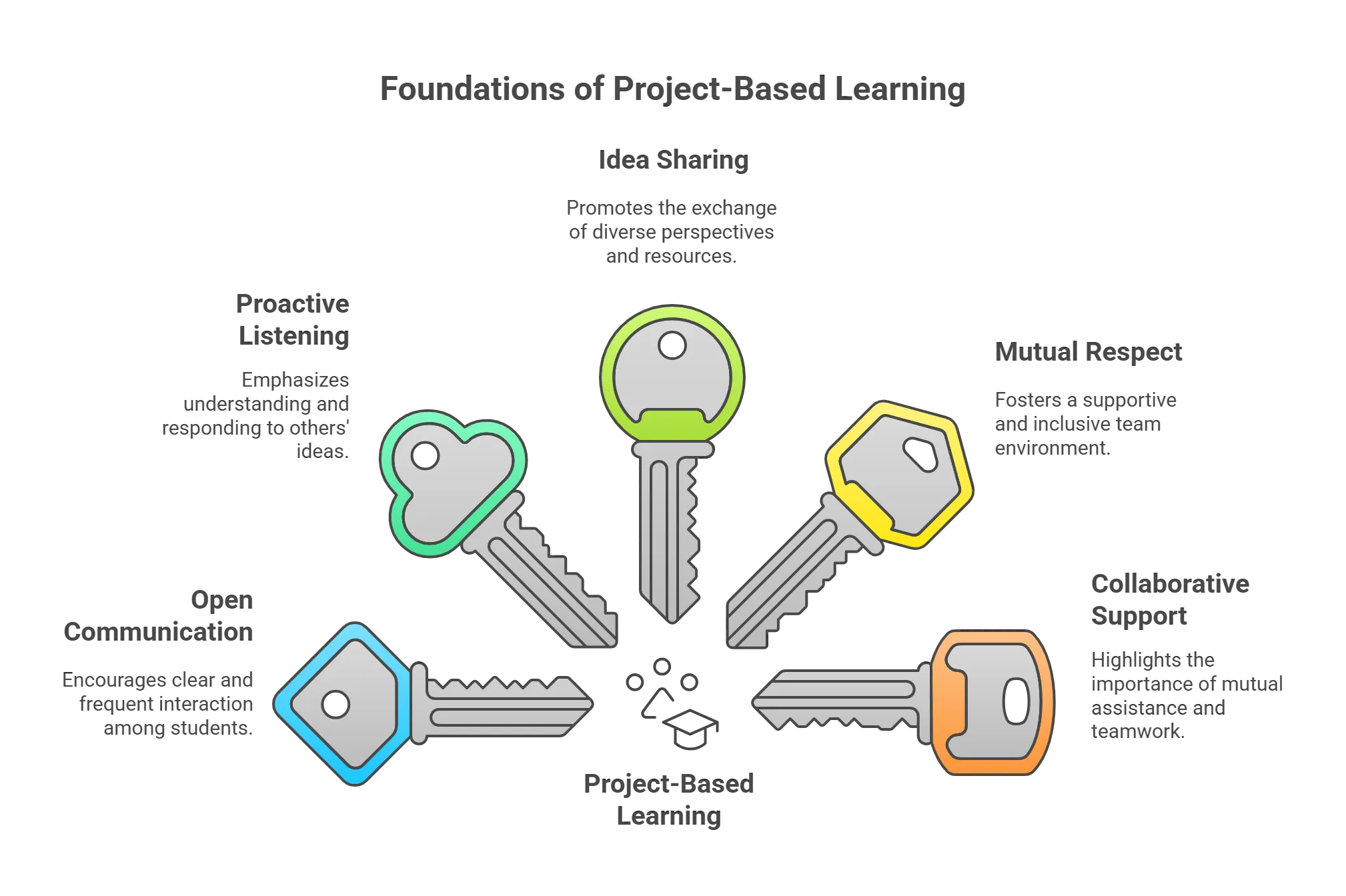
1. Open Communication with Others
Encourage students to maintain open lines of communication with their peers throughout the project. Whether through emails, phone calls, or in-person meetings, effective communication ensures seamless collaboration and problem-solving within the team.
2. Becoming a Proactive Listener
While working on a project together, it is vital to comprehend the thoughts of others. Team members who listen to each other in group meetings and follow agreed-upon measures can achieve this.
3. Sharing Ideas and Insights
Collaboration flourishes when students freely exchange ideas, images, and resources. Encourage students to contribute their unique perspectives and expertise to the project, enriching the collective knowledge pool and enhancing creativity.
4. Demonstrating Respect for Teammates
Cultivate a culture of respect and appreciation for every team member’s contributions. Encourage students to value and acknowledge each other’s opinions and ideas, fostering a supportive and inclusive team environment.
5. Offering Assistance and Support
Encourage students to lend a helping hand to their peers whenever needed. Collaboration often requires seeking assistance from both team members and external resources, highlighting the importance of collective effort and mutual support.
In a nutshell, open communication, proactive listening, idea sharing, mutual respect, and collaborative support are key pillars that empower students to succeed in project-based learning experiences.
By following these guidelines, students can actively engage in project-based learning, fostering teamwork, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills while addressing real-world challenges.
Examples of Successful Project-Based Learning Activities
Here are a few examples of successful project-based learning activities.
- Community Service Assignments: Students recognize a community requirement or issue, research solutions, and take measures to address it. For instance, students may run a food drive, build a community center, or raise awareness about environmental problems.
- Historical Assessments: Students explore a historical event, period, or figure through assessment, analysis, and inventive expression. For example, students may reenact a key moment in history, make a documentary film, or plan a museum exhibit.
- STEM Challenges: Students engage in hands-on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) assignments that require problem-solving, experimentation, and collaboration. For example, students may plan and build a solar-powered car, develop a bridge utilizing only toothpicks and sticks, or make a model of a sustainable city.
- Entrepreneurship Undertakings: Students develop entrepreneurial aptitudes by creating and establishing their business ventures. For example, students may develop a product, perform market analysis, create a trade plan, and pitch their ideas to potential investors.
How to Design and Implement a Future-Proof Curriculum?
Design is only half the problem. The hard part of a future-proof curriculum is in its delivery.
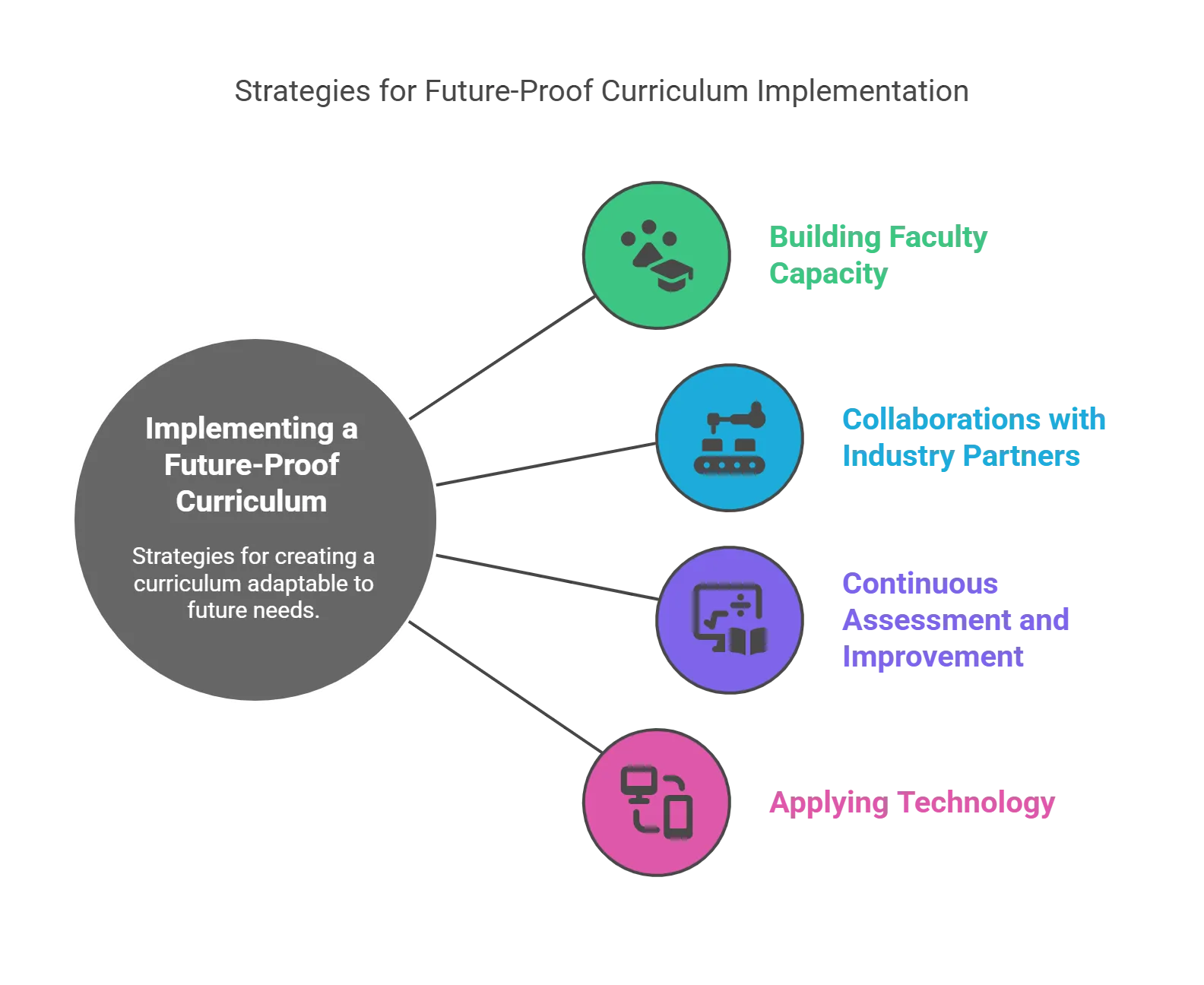
Here are some important strategies for implementing a future-focused curriculum planning:
1. Building Faculty Capacity
A future-proof curriculum requires a future-ready faculty. Investing in faculty development ensures that educators have the knowledge, skills, and mindset to deliver innovative and engaging learning experiences. It offers:
- Professional Development: Invest in continuing professional development programs and upgrade faculty with new teaching methods, contemporary technologies, and industry-specific updates.
- Mentoring and Coaching: Develop and facilitate mentoring programs to encourage faculty to easily transition into innovative pedagogy and learning design.
2. Collaborations with Industry Partners
Universities should consult with their industry partners about the latest trends and the skills they are looking for. This close collaboration could allow universities to align the curriculum according to industry needs and develop students into professionals.
- Industry Advisory Boards: An advisory board consists of industry leaders who will give insight into current and future industry needs.
- Internship and Co-op Programs: The institutes will be able to engage students with practical applications of concepts learned through internship and co-op programs and, hence, apply them directly in real-world settings.
- Joint Research Projects: Work on research projects in mutual collaboration with industry players in respective areas, leading to innovation and interchange of knowledge.
3. Continuous Assessment and Improvement
A future-proof curriculum will adapt to students’ and the labor market’s changing needs. For universities to be relevant, systems should be put in place to assess and improve the curriculum.
- Regular Review of Curriculum: Regularly review the curriculum to ascertain whether it is relevant and effective.
- Student Feedback Mechanisms: Student feedback in the form of questionnaires, focus groups, and exit interviews will help establish points of improvement.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Use data analytics to track student performance, detect trends, and inform curriculum development.
4. Applying Technology
Technology can transform the way a student learns. When technology is integrated into the curriculum, universities can provide interactive and engaging learning environments, preparing students for the technology world.
- Learning Online Platforms: Such platforms give flexibility and accessibility for all students.
- Utilization of Digitised Resources: Use digital tools and resources to give students and faculty all the needed digital tools for deeper learning and research.
- Data Analysis: Adopt data analytics to track student progress in studying, identify gaps in learning, and improve instruction.
Curriculum implementation of all these strategies would create a future-proof document in which students are prepared and capacitated to take hold and succeed in this highly changeable job market.
How to Prepare Students for an Interconnected World?
Preparing a curriculum that equips students to thrive in an interconnected world is not a cakewalk. You will have to take different steps to ensure they are ready to go out there and spread their wings.
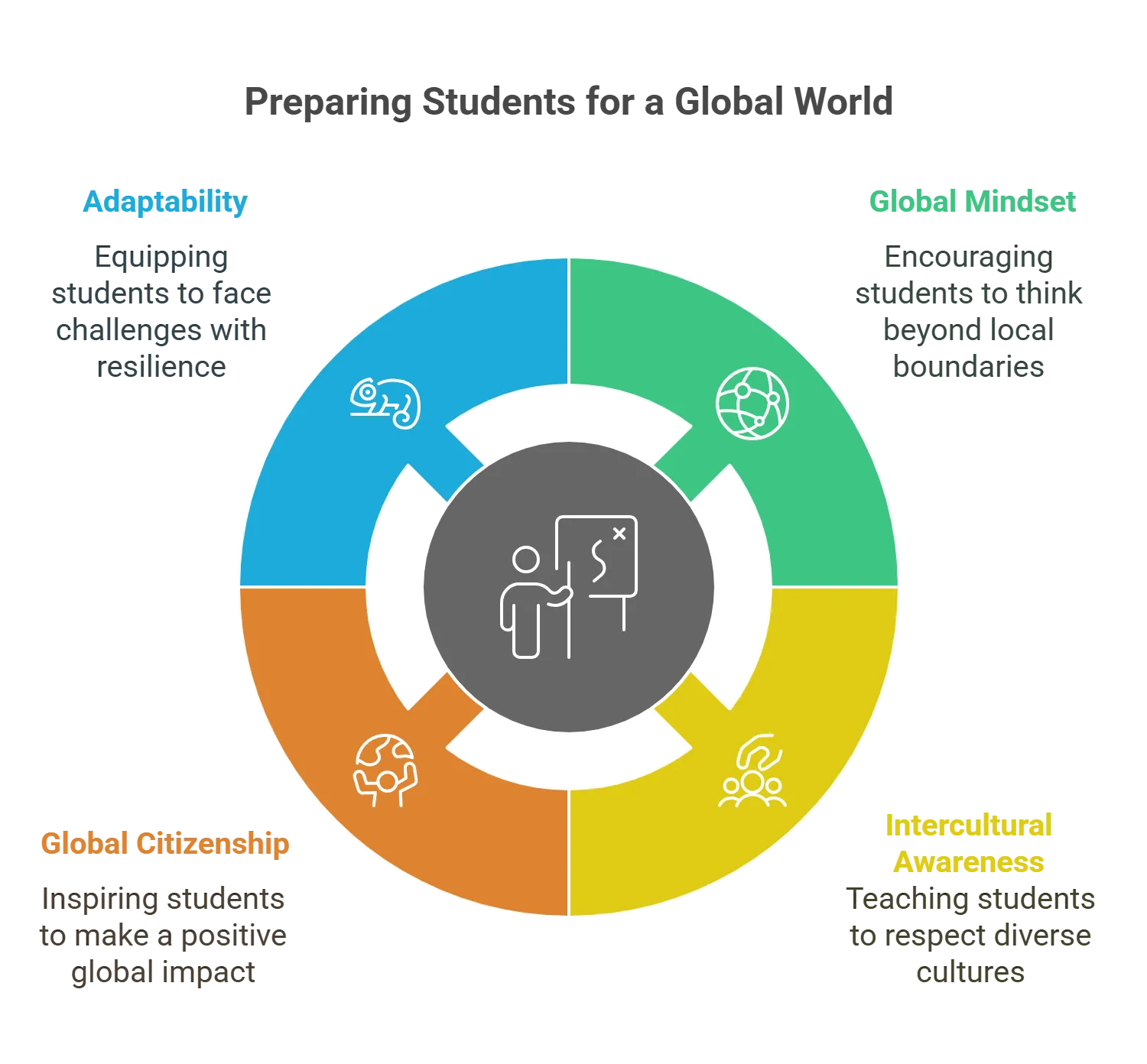
Here are a few things that you can do to prepare the students for an interconnected world.
1. Build a Global Mindset
While building a global mindset might sound generic and easy, it has different layers. When students are restricted to a particular geography, helping them gain perspective about the rest of the world is not easy. Therefore, it is important to expose the students to different learning experiences that will help them push their boundaries.
Curriculum planning can incorporate several global themes to help build a global mindset. You can try to add themes like social justice and human rights to make the students aware of global issues that might impact them directly or indirectly.
You must also actively use digital tools, enabling them to connect with subject matter experts who can broaden their horizons.
Another way to open their minds and bring in a fresh perspective is to ask them to learn a new language. Schools today have the resources to provide opportunities for students to travel abroad and witness different cultures and realities firsthand.
2. Bring in Intercultural Awareness
We live in a world where people come from different backgrounds and speak different languages. Hence, the education system needs to impart intercultural awareness among the students.
The curriculum should equip students to recognize and respect different cultures and communicate clearly and effectively with people from diverse backgrounds. They should also be taught concepts of equity and diversity to ensure they communicate effectively.
You can impart these values by celebrating different cultures through an array of activities. Schools today must focus on educating students about the uniqueness of different cultures so that they start respecting people for who they are.
Also, the new curriculum should address stereotypes and biases that are prevalent in young minds to ensure they understand better and respect diverse cultures and backgrounds.
3. Sense of Global Citizenship
It is very important to make the students understand that countries are just geographical boundaries. It is their responsibility to become better and more empathetic humans before they start prioritizing their country.
Here’s where global citizenship comes into the picture. It invites students to speak up, take charge, and make a positive impact. To foster the idea of global citizenship, it is important to assign them projects involving real-world problems. You must empower them to use their creative judgment and logical arguments to devise innovative and practical solutions.
Schools can network with multiple organizations that are working to bring positive change to the world. These organizations can offer a platform for students to share their views and collaborate with them to achieve the desired outcome.
Schools must come up with a program that encourages students to become global citizens and celebrate the impact that they create.
4. Making Them Adaptable
With the recent pandemic, global citizens have learned the hard way to adapt to a situation. Therefore, if you aim to bring global competence into the education system of today, it is important to teach your students to become adaptable. You must teach them how to be ready to face any kind of challenge that comes their off.
There are different ways of doing so. You can provide them with access to resources that will help them become adaptable. Students should have access to emotional self-management and other resources that help them build self-confidence.
Students are like clay, ready to be molded into different shapes and forms. As educators, it is our primary responsibility to help them with everything that will help them take their shape.
Check out EXCLUSIVE: Hurix Minibook: The Paradigm Shift in Higher Education with Curriculum Development
Wrapping Up!
Including student-friendly learning methods in curriculum planning might seem challenging at first because we tend to have a myopic view of things.
However, it is important to understand how students can contribute to a growing economy. Globally competent students are much more competent, and they know how to tackle the challenges thrown at them.
At Hurix Digital, we provide education solutions that help schools provide immersive learning experiences to their students. Our expertise in curriculum design can help you deliver engaging content to your students and change how education is perceived.
Our courseware development team focuses on crafting lasting learning experiences, making them suitable for students.
Get in touch with us to know more.
Summarize with:

Senior Vice President
A Business Development professional with >20 years of experience with strong capability to sell new solutions and develop new markets from scratch. New Market Entry Specialist with experience working in the largest emerging markets. Exceptional experience in conceptualizing, ideating and selling new learning technologies like VR AR, etc. across multiple industry verticals.
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 




