
Automation Testing Explained with Real World Examples and Use Cases
Summarize with:
Testing is an essential part of product development, one that helps guarantee the quality of the product. Software tests need to be repeated several times during the development cycle to ensure quality. For every release, the software must be tested on all operating systems and hardware configurations. The advantages of an automation framework in this process are substantial, enabling the delivery of high-quality products more quickly.
This guide will cover everything you need to know about automation testing, from its core concepts and benefits to its various types, challenges, and its role in modern development practices like DevOps.
Table of Contents:
- What is Automation Testing?
- Test Automation vs. Automated Testing: What’s the Difference?
- What are the Main Types of Automation Testing?
- Which Tests Should Be Automated?
- Top Benefits of Automation Testing
- When Do You Need Automation Testing? Key Scenarios
- When Should You Not Use Automation Testing?
- The Role of Test Automation in DevOps
- Challenges Faced In Automation Testing
- A Final Word
What is Automation Testing?
Automation testing, or test automation, refers to the use of specialized software tools and scripts to execute predefined test cases and automatically verify the outcomes. It involves creating and running scripts that simulate user interactions with an application or system under test. The primary goal is to improve testing efficiency, accuracy, and speed by automating repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks.
Using open-source or paid automated testing tools, you can test software applications quickly and efficiently, 24/7, without human intervention. Automated software testing can reveal memory contents, data tables, and file contents, helping to determine if the program is functioning as required. With an automation framework, teams can execute thousands of varied and lengthy test cases that are impossible in manual testing, increasing the depth of tests to improve overall software quality.
This process is highly advantageous as it performs the tasks of many manual testers and improves accuracy with little to no manual intervention. Because pre-written scripts are used, it ensures that software of a standard quality is released consistently.
Automation testing typically follows a testing framework approach. The most common ones include:
- Keyword-driven framework: Uses keywords to represent actions, making it easy for non-technical users to create tests.
- Data-driven framework: Separates test data from test scripts, allowing the same test to be run with different data sets.
- Linear scripting framework: A basic record-and-playback model.
- Modular testing framework: Divides the application into separate modules that are tested individually.
Test Automation vs. Automated Testing: What’s the Difference?
While often used interchangeably, “test automation” and “automated testing” have distinct meanings. Understanding the difference is key to implementing a successful quality assurance strategy.
Automated testing refers to the specific process of executing a predefined set of test cases using automation tools and scripts. It is the act of running an individual test or a suite of tests automatically to verify that the software functions as expected.
Test automation, also known as QA automation, is a much broader concept. It involves automating the entire testing process and life cycle. This starts from designing code scripts for tests and managing the varied testing needs of an organization, all the way to deploying error-free software products. It’s a comprehensive strategy that integrates automated testing into the software development lifecycle.
Professionals Involved
The skill sets required for each also differ.
- Automated Testing usually involves professionals with strong programming skills in languages like Python, Java, or Ruby to write the test scripts.
- Test Automation is a more comprehensive effort that involves a range of professionals:
- Developers: Help create new features for test cycles.
- Testers: Ensure the quality of tests and the overall product.
- DevOps Engineers: Automate the deployment of tests, ensuring end-to-end automation of the testing cycles.
In a mature test automation framework, the development and testing teams work together to build quality automated tests, while the DevOps team automates their deployment for continuous integration and delivery.
What are the Main Types of Automation Testing?
Automation testing is divided into several main categories, each with different applications.
1. Code Analysis
This includes various testing tools for static and dynamic analysis. These tools can check for everything from usability issues to security flaws. While a developer must write the initial code to execute these tests, the rest of the process can run without human intervention.
2. Unit Tests
When developing software, unit testing is conducted to verify each component or unit of code, such as functions or methods. This ensures that the smallest parts of the application work correctly before they are integrated. While developers can write these tests manually, automating them is a standard practice in modern software development.
3. Integration Tests
Often called end-to-end tests, integration tests are more complex. In this process, different modules or services of an application are combined and tested as a group. This assesses how efficiently the modules communicate and function together, identifying issues at their interfaces.
4. Automated Acceptance Tests
Similar to Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), AATs are often developed before new features are created. This process involves collaboration between business stakeholders, developers, and QA to establish clear standards for new features. These tests verify that the system meets the acceptance criteria and can be reused as regression tests in the future.
5. Smoke Tests
Smoke testing is a quick, preliminary test to determine if a new build is stable enough for further testing. If the build fails the smoke test, it’s considered “unstable” and returned to developers for fixing. This prevents the QA team from wasting time on a broken application.
Other common types of tests that can be automated include:
- Functional tests: Focus on the overall functionality of the system from a user’s perspective.
- Performance tests: Measure system performance, such as response time and throughput, under a specific load.
- Security tests: Identify and address security vulnerabilities in the system.
- Regression tests: Ensure that new code changes have not unintentionally broken existing functionality.
Test automation frameworks and tools like JUnit, TestNG, Selenium, Appium, and Cucumber are commonly used to perform these tests.
Which Tests Should Be Automated?
Not every test is a good candidate for automation. It’s crucial to prioritize which tests to automate to get the best return on investment. Here are the types of tests that benefit most from automation:
- Repetitive and monotonous tests: Tests that are run frequently, such as regression suites, are prime candidates for automation to save time and reduce human error.
- Tests prone to human error: For complex and tedious tasks, automation ensures consistency and precision.
- Tests requiring numerous data sets: Data-driven tests, where the same function is tested with multiple inputs, are much more efficient when automated.
- Tests that are impossible to perform manually: Load and performance testing, which involves simulating thousands of concurrent users, can only be done through automation.
- Time-consuming manual tests: If a test takes a long time to execute manually, automating it can free up valuable resources.
- Tests across various platforms: Testing an application on different browsers, devices, and operating systems is much faster and more reliable with automation.
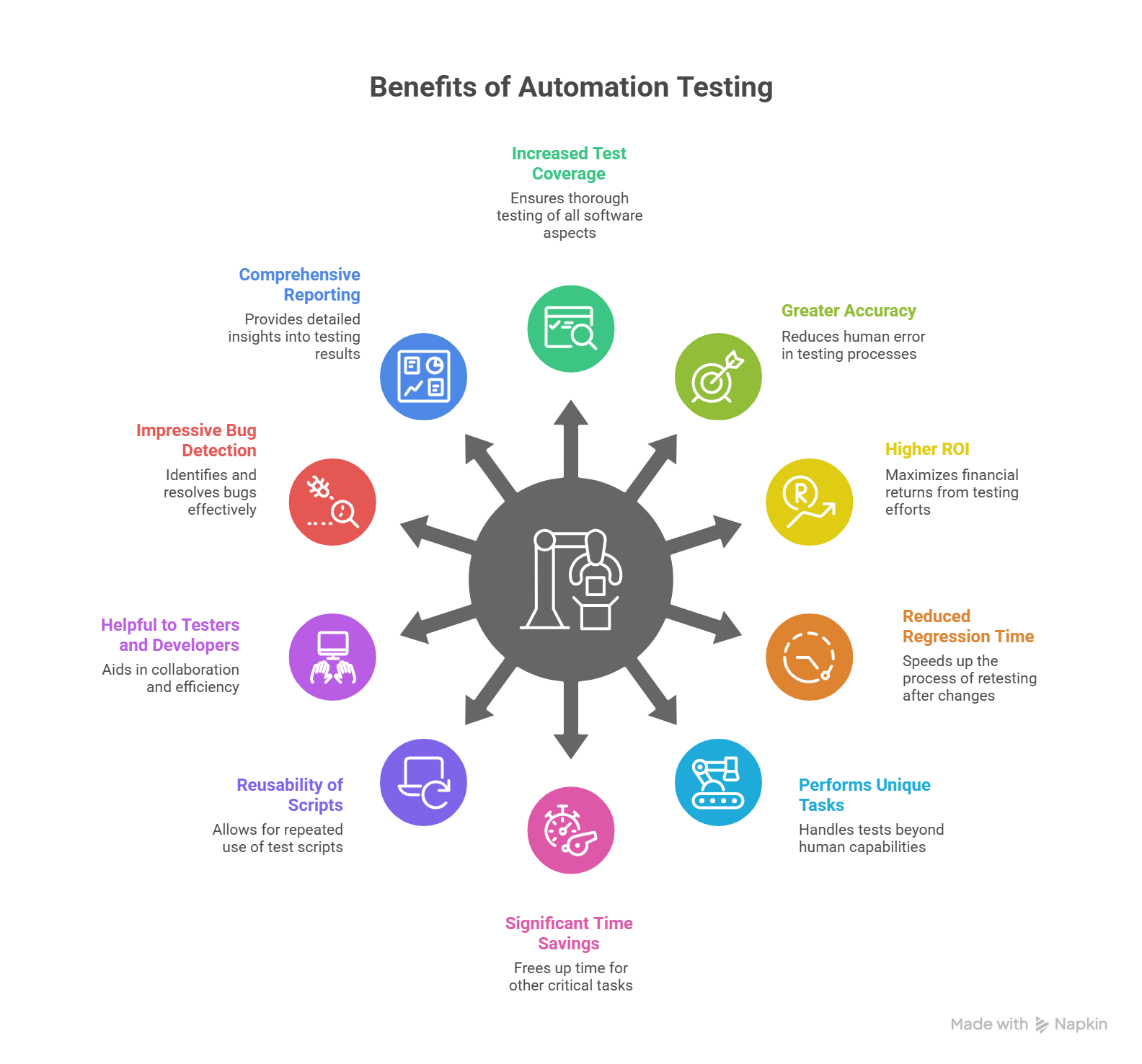
Top Benefits of Automation Testing
Automation technology is being used by SaaS companies all over the world because it offers several advantages.
1. Increased Test Coverage
More scripts can be tested simultaneously, increasing overall test coverage. Automated software testing can enhance software quality by expanding the range and thoroughness of tests. It enables the execution of lengthy tests, often avoided in manual testing, which can run unattended on multiple computers with diverse configurations.
2. Greater Accuracy
Continuous manual testing increases the chances of errors. In automated testing, repetitive tests are performed with the same precision every time, eliminating human mistakes and ensuring reliable results.
3. Higher Return on Investment
With automated testing, test cases run faster, and bugs are identified early in the development cycle. Despite high initial setup costs, once the framework is in place, there is a significant reduction in overall costs and a high return on investment.
4. Reduced Regression Testing Time
Automated regression tests free manual testers from running monotonous test suites. This allows the QA team to focus on more complex, value-added tasks like exploratory testing.
5. Performs Tasks That Manual Testers Cannot
Certain tests, such as controlled web application performance tests with thousands of virtual users, can only be simulated with automated testing.
6. Significant Time Savings
Automation testing saves significant time by executing tests faster than manual testing. As tests can run 24/7 without intervention, the development and testing cycles are drastically shortened.
7. Reusability of Test Scripts
In automated testing, the same script can be reused across different tests with minor changes. This reusability facilitates the testing process, and scripts can be stored for repeating tests whenever needed.
8. Helpful to Testers and Developers
Tests can run automatically whenever the source code changes, immediately notifying the team of any issues. This provides fast feedback to both testers and developers, enabling them to fix bugs quickly.
9. Impressive Bug Detection
One of the primary reasons to test a product is to find bugs. Automation simplifies this process by analyzing a broader test coverage than a human can in a short time, leading to more effective bug detection.
10. Comprehensive Reporting
Automation testing tools deliver detailed reports for every executed test case. These reports, often including visual logs like screenshots and videos, provide information on executed scripts, reported bugs, and how they were fixed, eliminating the need for manual documentation.
11. Better Utilization of Manpower
Since QA automation executes repetitive test cases, experienced QA team members can be reassigned to projects requiring strategic thinking and exploratory testing. This shift leads to higher job satisfaction and better retention rates.
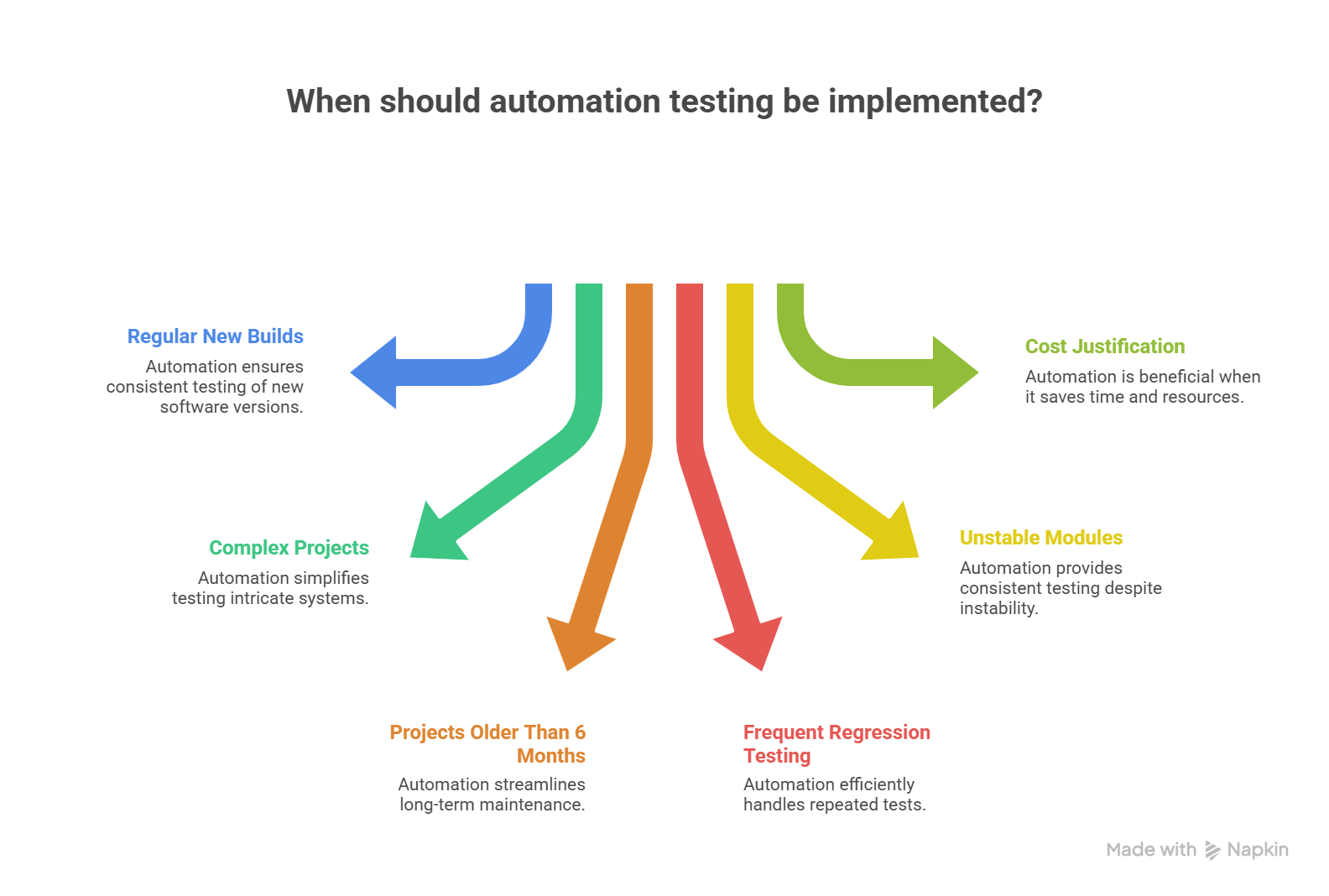
When Do You Need Automation Testing? Key Scenarios
While the benefits are clear, the decision to automate should be strategic. Here are six key scenarios where automation testing is necessary.
1. Testing New Builds Regularly
If you have a new build to test every week, automation is the best way to get it done quickly and accurately. Manual testing would be too slow to verify that all features are working as expected on each release. Automation allows testers to run a full suite of tests repeatedly and quickly.
2. Dealing With Complicated Projects
For products with a complex user experience or dependencies on many other systems, manual testing quickly becomes unwieldy. Automation is a great way to test complicated processes because it allows you to design tests that can be run multiple times without any change in how they work.
3. Projects Older Than 6 Months
The longer a project exists, the larger and more complex its codebase becomes, making it harder to track all edge cases. Unit tests may not be comprehensive enough to catch new bugs, especially those caused by external dependencies. Starting automated testing early is crucial, but for older projects, it’s essential for maintenance and stability.
4. Frequent Regression Testing
If your project requires frequent regression testing, automation is the best bet. Automated tests can be run automatically on your build server, in parallel, and even on the cloud. This provides fast feedback on code changes and ensures new features don’t break existing ones.
5. Unstable Test Modules and Repeated Scenarios
If a test module is unstable or a scenario needs to be tested repeatedly, automation is the solution. For example, testing a mobile app’s video recording function hundreds of times a day is only feasible through automation.
6. When the Outcome Justifies the Cost
Test automation requires an investment. It makes the most sense for large, long-term projects where the software requires multiple rounds of testing over an extended period. The long-term ROI from time savings and improved quality will justify the initial cost.
When Should You Not Use Automation Testing?
There are certain situations where automated testing may not be the best option:
- The application has a short lifespan: Automated testing requires a significant investment of time and resources to set up, so it may not be cost-effective for applications with a short lifespan or those expected to change frequently.
- The application has a low level of complexity: If the application is relatively simple, manual testing may be more efficient.
- The application has a high degree of unpredictability: Applications that involve real-time, unpredictable user interactions may be difficult to automate effectively.
- The application requires significant human interaction: Applications that rely on human intuition, such as those involving image and video recognition or usability testing, are better suited for manual testing.
- The application is in early development stages: Automated tests are best for later stages of development when the application is more stable. In early stages, when requirements and design are in flux, manual testing is more flexible.
The Role of Test Automation in DevOps
In a DevOps environment, the goal is to deliver applications and services faster than traditional approaches. This focus on speed and agility is achieved through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), where automation is key.
Test automation and DevOps go hand-in-hand. By incorporating automated testing into the CI/CD pipeline, teams can:
- Deliver products quickly: Automated tests provide fast feedback, enabling quicker releases of reliable, bug-free products.
- Ensure software stability: Continuous testing is vital to ensure that constant upgrades and new versions do not introduce glitches, keeping the software stable.
- Simplify the testing process: By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks with the right test automation tools, teams increase efficiency and reduce human error.
- Improve collaboration: Test automation fosters collaboration between development, operations, and QA teams, which is crucial for effectiveness within the release pipeline.
- Enhance quality: By automating tests, organizations achieve consistent and reliable results. Catching critical bugs early reduces the risk of releasing flawed software.
Challenges Faced In Automation Testing
Despite its benefits, implementing automation testing is not without its challenges.
- Network Issues: A stable network connection is necessary to smoothly access third-party services and databases. Network instability can cause tests to fail.
- High Initial Cost: The cost of automation tools and setting up the initial framework can be too high for some organizations. Even open-source alternatives involve significant training and maintenance costs.
- Testing Accuracy: Communication is key. If teams work with outdated information, it can lead to false test outputs and wasted effort.
- Choosing the Right Tools: Selecting the appropriate automation tools for a project can be challenging and requires careful evaluation.
- Requires Skilled Professionals: Writing and maintaining automated test scripts requires a team with strong technical and programming skills.
A Final Word
With increasingly complex applications and businesses demanding faster releases of high-quality products, the advantages of an automation framework are clear. Automating the testing process is an effective strategy that improves both efficiency and coverage, leading to better products and greater customer satisfaction. If you want to deliver robust software quickly while making the best use of your team’s talent, embracing automation testing is no longer an option—it’s a necessity.
At Hurix Digital, we provide QA services with a test automation framework built in-house. Our team of QA professionals uses various testing techniques and follows the best industry standards and practices. If you are looking for an automation testing service, get in touch with us.
Summarize with:

Vice President & SBU Head –
Delivery at Hurix Technology, based in Mumbai. With extensive experience leading delivery and technology teams, he excels at scaling operations, optimizing workflows, and ensuring top-tier service quality. Ravi drives cross-functional collaboration to deliver robust digital learning solutions and client satisfaction
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 



