A Provost’s Playbook for Curriculum Design & Compliance
Summarize with:
As a Provost, you are at the helm of curriculum alignment, a pivotal responsibility that shapes your institution’s future and reinforces its reputation. Meeting compliance standards and securing accreditation are not just formalities—they are critical commitments to delivering quality education that impacts students’ lives.
In short, achieving compliance is not just about ticking off items on a checklist; it is a promise to advance the cause of academia while preserving—no, expanding—the respect that this body earns in society. This alignment ensures that education is purposeful and practical and prepares one for careers in today’s fast-paced and changing world.
Moreover, aligning curriculum with institutional goals and effectiveness requirements does more than ensure compliance. It transforms educational approaches, fosters critical learning, and empowers students to excel.
Yet, curriculum design and compliance can be complex. This guide offers essential tools, actionable insights, and strategies to simplify the process and bolster your institution’s strengths. Together, let’s aim to meet standards and set new ones, ensuring your institution thrives and delivers on its promises.
Table of Contents:
- What Does Accreditation Mean for Your Institution?
- What is Curriculum Alignment?
- Why Compliance is Key in Curriculum Design?
- The Power of Curriculum Design: Understanding Its Significance
- Transforming Education: A Guide to Future-Ready Curriculum Design
- Core Components of a Compliance-Aligned Curriculum
- Actionable Strategies to Align Curriculum with Compliance
- 4 Best Practices for Sustaining Institutional Accreditation
- 11 Steps to Physical Education Curriculum Design
- Set the Context and Tone for Curriculum Design
- Critically Analyze Various Physical Education Curricula
- Develop Clarity on Physical Literacy and Its Importance
- Set Goals Based on Grade-Level Outcomes
- Map the Curriculum Units after Triaging Outcomes
- Select Unit Activities
- Fix the Periods Per Unit Per Grade
- Consider Playground and Physical Activity Facilities Availability
- Finalize the Evaluation Criteria
- Keep Deliberating Over the Curriculum Map
- Develop a Robust Quality Assurance Plan
- Final Thoughts
What Does Accreditation Mean for Your Institution?
Accreditation signals that an institution adheres to high standards in curriculum design and faculty qualifications. It can also significantly impact enrollment and federal funding eligibility.
Key Accreditation Standards for Curriculum Design
- Institutional Standards: Ensure alignment with national and international benchmarks.
- Rigorous Academic Standards: Ensure course rigor matches academic expectations and enhances critical thinking.
- Measurable Learning Outcomes: Define and evaluate specific learning outcomes to meet institutional effectiveness standards.
Accreditation is not a one-time achievement. It requires constant alignment with compliance standards when seeking reaccreditation and as an ongoing institutional practice.
What is Curriculum Alignment?
Curriculum alignment ensures that what is taught in each course supports the institution’s mission and meets accreditation standards.
It refers to strategically matching course content and teaching methods with learning outcomes. This alignment must demonstrate relevance and readiness for today’s workforce for institutional accreditation.
An aligned curriculum ensures every course module and objective supports compliance standards. It reflects the quality of education and prepares students for future challenges.
Why Compliance is Key in Curriculum Design?
Adherence to curriculum design is important for the preservation of accreditation and the respectability of an institution.
Accreditation bodies set standards to ensure educational quality, covering curriculum, faculty qualifications, and student outcomes. Non-compliance can result in penalties, loss of funding, or even accreditation, severely affecting the institution’s stability and reputation.
Once again, the significance of accreditation is clear regarding access to funds to support education. For example, federal student aid is available only if enrolled in an accredited institution. This has implications for student numbers and their reach.
Adhering to compliance standards shows a commitment to quality education and building trust with students, parents, and employers. It also assures prospective students that programs meet rigorous standards, preparing them for successful careers.
The Power of Curriculum Design: Understanding Its Significance
Do you ever wonder about the seamless flow of knowledge in a functional learning program? How do institutes create courses that captivate students? Moreover, how do they adapt to their changing needs and foster meaningful growth?
The answer lies in effective curriculum design.
It is the deliberate planning of educational content, activities, and reviews to achieve specific outcomes. It is not a one-time activity but a continuous cycle of reflection and improvement.
Designing a purposeful curriculum is significant because it:
- Considers diverse interests, backgrounds, and societal standards to create a resonating learning experience.
- Shapes the course content, learning objectives, and instructional strategies that seamlessly intertwine.
- Influences the quality and effectiveness of education and enhances learning outcomes.
- Adapts to the student’s evolving needs, ensuring teaching remains relevant and impactful.
Now that you understand the importance of an effective curriculum let’s move on to designing one.
Transforming Education: A Guide to Future-Ready Curriculum Design
Curriculum design is the skeleton for the future of education. It inspires the learner and prepares him for 21st-century challenges. A properly constructed, engaging, and effective curriculum enables educators to succeed in their learning ventures. The book comprehensively details curriculum design development, assessment, and implementation.
Educators know these pillars on a deep level so that they can design interesting, challenging, and appropriately contexted learning experiences for their learners. With innovation at the forefront and an up-to-date understanding of what’s new in education technology, these educators are empowered to curate curricula that are workable for learners while helping to generate positive results.
As stated earlier, curriculum design shapes course content and influences education quality. It involves three main pillars: development, evaluation, and implementation. By understanding these categories, you can create engaging and interactive curricula.
So, let’s take a closer look at each of them.
1. Curriculum Development: Building the Foundation
Curriculum development lays the foundation for the entire process. In this phase, you can define the learning objectives, select appropriate content, and design instructional strategies. Consider learners’ needs, societal demands, and emerging trends to develop a relevant curriculum.
This step tries to identify the gaps and opportunities for learning and define the scope of your curriculum. Here are some curriculum development best practices:
- Know your learners’ background, prior knowledge, and any specific challenges they may face.
- Gather data through surveys, interviews, or focus groups to understand learners’ skills and attitudes. This will help identify gaps between their current abilities and desired learning outcomes.
Setting clear and measurable learning objectives is an important step in curriculum development. Here’s how you can frame your objectives using the SMART criteria:
- Specific: Form clear objectives that use action verbs to describe observable behaviors.
- Measurable: Design quantifiable goals with measurable criteria for assessing progress and achievement.
- Achievable: Form challenging but realistic and achievable goals that inspire your students.
- Relevant: Create learning objectives according to field standards and stakeholders’ expectations.
- Time-Bound: Set clear time frames for your curriculum to be reasonable. Plus, split all your goals into smaller and manageable milestones.
Break down the silos! Interdisciplinary learning prepares students for the complex challenges of the future. Here’s how you can execute this step:
- Logically categorize the content. Use foundational concepts as a starter and gradually build up toward more advanced topics.
- Focus on developing critical thinking, communication, and problem-solving skills necessary for success in the 21st century.
- Add interactive and practical elements to create an immersive learning experience. Augment your digital learning curriculum with case studies, group projects, and real-world examples.
2. Curriculum Evaluation: Ensuring Continuous Improvement
The second phase of curriculum design begins with collecting relevant data for the curriculum. The data is then studied to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement.
Here’s how you can ensure its efficacy and make data-driven decisions:
Since such an undertaking can only be meaningful, it necessitates moving away from old-fashioned summative assessment strategies and towards continuous assessment approaches to ensure that learning becomes constantly flowing and effective. Integrating formative assessments within the curriculum offers students an evaluation process and opportunities for regular feedback.
The feedback received at the right time would mean personalized learning. You can find places where students are getting tough and concentrate your support there. With constant tracking of student learning, you can take decisive steps to alter your teaching plan so that all students can succeed.
Student voice and perspective should be the priority in making curricula truly effective. Active solicitation of student feedback can provide insight into students’ learning experiences and identify areas for improvement. Regular surveys, interviews, or focus groups allow students to voice their thoughts, opinions, and suggestions.
Such feedback will inform curriculum decisions so that the content is relevant, engaging, and interesting to students. It is also possible to create a more positive and productive learning environment by giving students a voice in their education.
Educators and subject matter experts must collaborate to produce the most effective curriculum. You can share ideas, best practices, and resources by working together.
Working with colleagues refreshes your perspective on what you will be teaching. You realize some areas in which you can improve or innovate in the curriculum. A subject matter expert may give insight into current research and industrial trends, keeping your curriculum relevant and in line with the times. You then create high-quality curricula that inspire learners and engage them.
3. Curriculum Implementation: Bringing Learning to Life
It is the last stage of the design process. It involves delivering the curriculum, monitoring student progress, and making necessary adjustments.
The following approaches can support effective curriculum implementation:
Make learning fun and exciting! Using gamification can boost learner outcomes by up to 35%. So, blend game-based and experiential learning techniques to create memorable experiences.
Cultivate problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity in your classroom. Remember, an interactive approach will make your curriculum stand out.
Connect education with the actual world! This approach enhances student engagement and develops their social and civic responsibility.
- Engage with the local community to provide students with authentic learning experiences.
- Partner with businesses and community leaders to bring real-world scenarios into the classroom.
Core Components of a Compliance-Aligned Curriculum
A compliance-aligned curriculum establishes a framework that balances institutional goals with regulatory compliance. Below are the key elements:
1. Clear Learning Objectives
Define measurable objectives for every course. For instance, rather than a broad goal like “understand environmental science,” use specific outcomes like “analyze the impact of global warming on ecosystems.” This approach meets compliance requirements by providing tangible learning outcomes.
2. Industry-Relevant Content
Courses must reflect current trends and industry demands. In a recent survey, 86% of U.S. employers valued candidates with practical, industry-aligned education. Regular updates to course content keep it relevant and compliant with accreditation standards.
3. Reliable Assessment Methods
Use assessments that evaluate students’ knowledge consistently. Consider using formative assessments, such as quizzes and feedback forms, to monitor student progress. Summative assessments, like projects and final exams, validate overall course understanding.
Rigorous and fair assessment strategies reinforce credibility and compliance. They demonstrate a measurable level of academic excellence.
4. Transparent Documentation
Maintain thorough records of feedback loops and assessment results. Compliance requires that curriculum changes and their justifications are documented transparently.
This provides evidence of compliance standards in practice and builds accountability, a cornerstone of institutional accreditation.
Actionable Strategies to Align Curriculum with Compliance
To effectively align curriculum with compliance, institutions must adopt proactive, structured strategies that enhance curriculum quality and ensure adherence to standards.
Here are some actionable strategies:
1. Implement Regular Curriculum Audits
Audits allow you to identify outdated content and address gaps in your curriculum. Conduct curriculum audits annually and involve diverse stakeholders like faculty and accreditation experts.
- Are learning outcomes measurable and relevant?
- Is the course content current and aligned with compliance standards?
- Do assessments measure the intended learning outcomes effectively?
2. Engage Stakeholders in Curriculum Development
Collaboration with faculty, industry professionals, and students offers a broad perspective on curriculum effectiveness.
- Host regular meetings to review curriculum relevance.
- Invite industry professionals to provide insights.
- Gather student feedback to align with student needs and expectations.
3. Utilize Data Analytics
Tools like dashboards and predictive analytics help monitor trends and identify areas for improvement. For example, tracking student outcomes in courses with high failure rates can reveal areas needing adjustment.
Analytics help improve curriculum design and provide measurable results to accreditation bodies.
- Student retention rates
- Graduation rates
- Course pass/fail rates
4. Continuous Professional Development
Offer faculty training on compliance standards and emerging teaching methodologies. When faculty are well-versed in regulatory requirements, they can design courses that meet compliance goals, ensuring consistent curriculum quality.
- Assessment methods and alignment with learning outcomes
- Updating curriculum to meet industry standards
- Compliance with federal and regional regulations
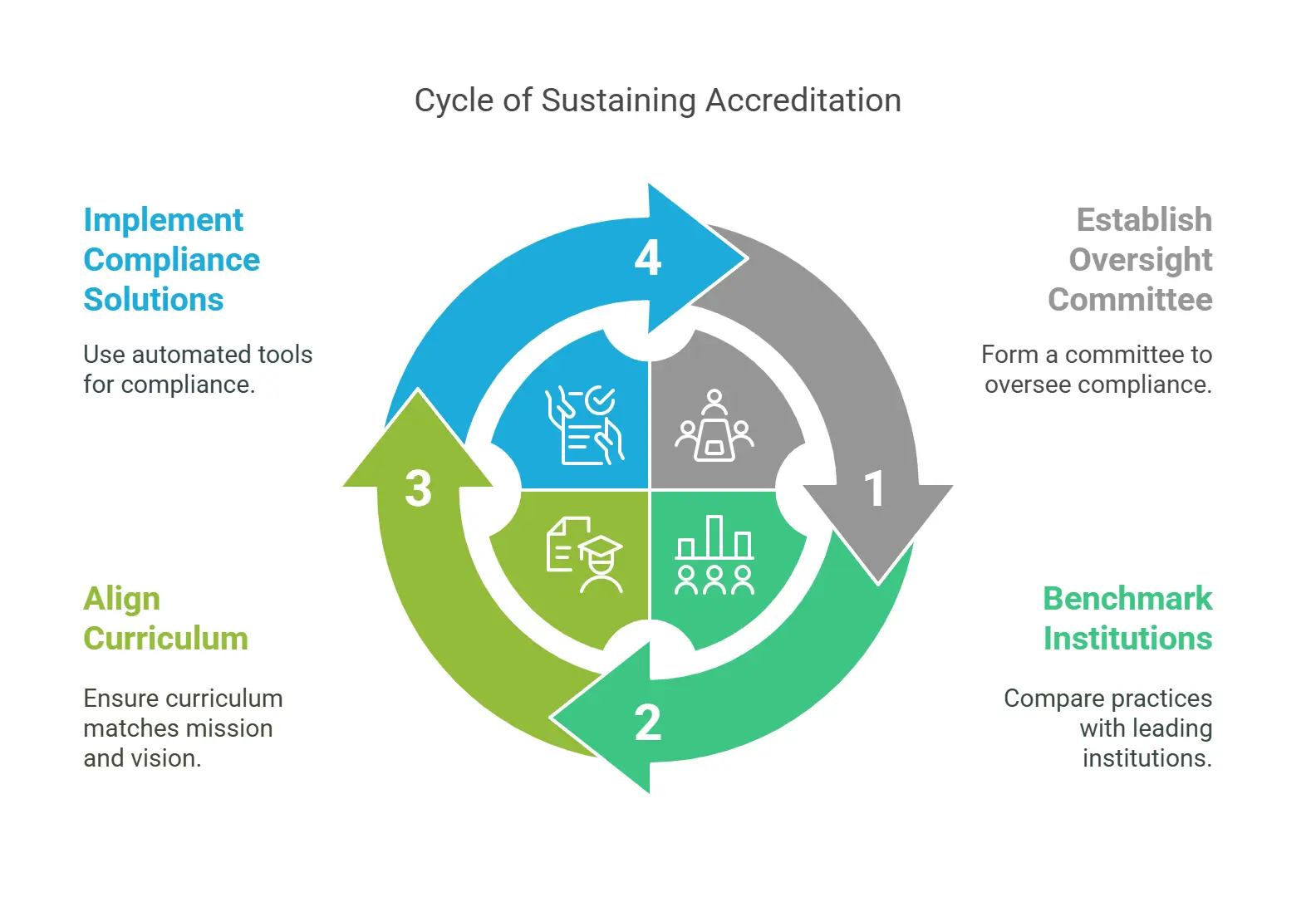
4 Best Practices for Sustaining Institutional Accreditation
Adopting sustainable practices that foster ongoing compliance and quality improvement is essential to maintaining institutional accreditation effectively. Below are key strategies to achieve this:
1. Create a Compliance Oversight Committee
A compliance-focused committee can regularly review and update curriculum alignment, track new regulations, and support faculty in meeting compliance standards. The committee should consist of representatives from various departments for balanced oversight.
2. Benchmark Against Leading Institutions
Compare your curriculum against those of peer institutions. For instance, benchmarking against Ivy League standards can reveal areas for improvement and establish a high bar for institutional effectiveness.
3. Align Curriculum with Institutional Mission and Vision
Accrediting bodies often assess how well the curriculum supports the institution’s strategic objectives. Ensure each course module reflects your institution’s goals and mission. This alignment makes it easier to meet accreditation expectations.
4. Implement Automated Compliance Solutions
Technological advancements are making compliance easier. Automated solutions track curriculum changes, provide reminders for audits, and create detailed reports for accreditation.
Platforms that monitor and report curriculum compliance allow for efficient updates and record-keeping, easing accreditation reviews.
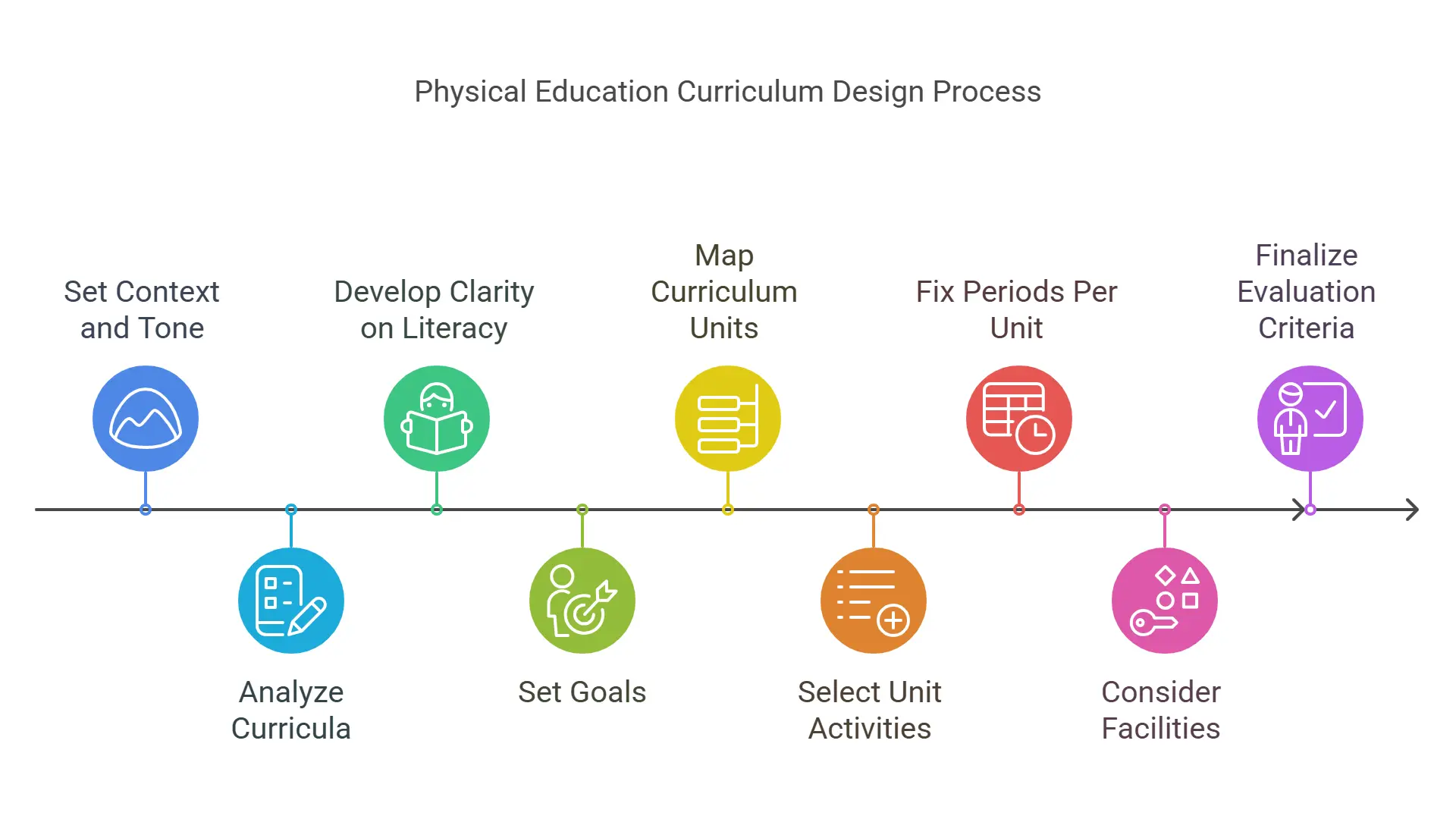
11 Steps to Physical Education Curriculum Design
Curriculum development in physical education is a methodical process that must be executed prudently to optimize outcomes. The key 11 steps in this direction have been discussed below to make the strategic process easier.
1. Set the Context and Tone for Curriculum Design
At the outset, it is critical to:
- Deliberate over the personalities of your students
- Understand the motivations and attitudes that underline the requirements of learners
- Conduct student surveys to learn about their expectations
- Brainstorm collectively with veterans in curriculum design
These will offer you actionable insights into the perspectives of those for whom the curriculum in physical education is to be developed.
2. Critically Analyze Various Physical Education Curricula
Next, an expert team of teachers from across the globe from across the globe should be constituted to explore various effective curriculum models in physical education. For this:
- Develop an understanding of qualitative physical education guidelines set down by UNESCO
- Cull and analyze prime aspects of selected curricula to figure out the reasons for their overwhelming success
- Gain clarification on national and regional guidelines and policies for curriculum designing for identification of priorities for goal setting
- Build a checklist of goals that would be accomplished through your curriculum
3. Develop Clarity on Physical Literacy and Its Importance
The goal-setting process is incomplete without an appreciation of the vital role of physical literacy. A thorough comprehension of physical literacy needs to be developed:
- To instill in students self-assurance for embracing physical activity as life’s integral aspect
- To incorporate chapters that can promote the students’ abilities for developing movement patterns and skills for different durations and intensities
- To chalk out ways to develop physical competence to facilitate students’ participation in a broad array of physical activities in different settings
- To work out ways to inculcate key qualities for influencing movement so that students can appreciate the advantages of an active lifestyle
- To engage students in a range of personally challenging and effective activities regularly
An infographic can be created with key physical literacy points for identifying steps to evaluate them.
4. Set Goals Based on Grade-Level Outcomes
Once clarity on physical literacy has been developed, it is time to reflect on how the curriculum will develop grade-wise. For this, comprehensive grade-level outcome mapping is needed to transition the curriculum from one class to another seamlessly.
Concurrently, the curriculum must phase-wise build the skills and understanding in students needed to appreciate the value of physical education and adapt accordingly.
5. Map the Curriculum Units after Triaging Outcomes
After defining the standard goals, it’s time to map the curriculum. Start with the youngest learning grade in school and factor in the grade-level outcomes to develop unique course content for each grade.
Assess and organize the outcomes in associated blocks. Cross-check if some blocks have more content than others. Balance the same to create engaging unit blocks.
6. Select Unit Activities
After sorting all outcomes for a grade in unit blocks, you have to ascertain which activities will be included for respective units to empower students to achieve the expected results.
- Define the challenges to which students are subjected so that they can apply the acquired knowledge and skills to surmount them tactically.
- Write down different challenges and match them with the sports or physical activities that can help combat those challenges.
- Use your professional acumen, experience, and judgment to select relevant activities.
7. Fix the Periods Per Unit Per Grade
After selecting activities, estimate the number of physical education periods each grade will have in an academic year. Based on this, decide the number of periods to allocate for each unit so students can comfortably reach the desired outcomes. Assign a relative weight to each outcome to determine the time needed to achieve it. Keep refining and improving the time set for each unit.
Consider the learning content students have been exposed to in previous academic years to ascertain the number of periods to assign for a unit.
8. Consider Playground and Physical Activity Facilities Availability
The pace of curriculum progress should be synced with the availability of physical activity facilities like gym, playground, etc. Check whether certain classes of different grades are overlapping. Plan the unit progress accordingly.
9. Finalize the Evaluation Criteria
The efficacy of the curriculum is reflected in the learners’ performance in the evaluative assessments. You need a good framework to inspect learners’ progress and judge their growing aptitude in field and classroom-level exercises.
- Finalize a range of questions for each grade, focusing on evaluating the practical aspect of learning.
- Develop a visual learning journey that will capture key milestones in physical education design and learning.
- Determine the frequency of assessments so that students get enough time to reorient themselves to the changing needs of the curriculum.
10. Keep Deliberating Over the Curriculum Map
Keep reflecting on each unit of the curriculum map while teaching to scope out avenues for revising the same. This will help you incorporate new physical activities in place of obsolete ones. Your understanding of the time devoted to each unit will also grow. Revise the curriculum accordingly before the start of the next session.
11. Develop a Robust Quality Assurance Plan
Developing a systematic process for periodically reviewing the quality of the curriculum is the concluding step in curriculum design. Set an interval to review the provisions of physical education to ensure that the efficiency and quality of the course align with evolving student needs and contemporary teaching standards.
- A self-evaluation team can carry out the quality check within the school or by external assessors.
- Quality audits should be conducted, and teachers’ efficacy as guides or torchbearers for learners must be checked.
- A set of key performance indicators can be finalized to gain valuable insights into the curriculum’s challenges, opportunities, strengths, and weaknesses.
The content, teaching mechanism, and evaluation methods can be revised based on this.
Final Thoughts
Designing a holistic curriculum in 2025 can be pretty challenging. However, adopting these best practices for curriculum development can help your students prepare for the future. Do you want help with curriculum design but don’t know where to begin?
Go for platforms like Hurix Digital, which provides innovative services that can prepare your students for the dynamic world ahead. Our solutions include a personalized learning platform and a digital learning curriculum.
So, are you ready to stay ahead and embrace the future of education? Get help from our team to explore our comprehensive curriculum design solutions.
Summarize with:

Senior Vice President
A Business Development professional with >20 years of experience with strong capability to sell new solutions and develop new markets from scratch. New Market Entry Specialist with experience working in the largest emerging markets. Exceptional experience in conceptualizing, ideating and selling new learning technologies like VR AR, etc. across multiple industry verticals.
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful