
Accessibility Compliance in Publishing Made Simple
Summarize with:
The Internet has become a key to easy and efficient communication, commerce, entertainment, and services. Due to this, accessibility compliance has become a necessity to ensure that even people with disabilities can access these platforms.
However, this is where the major challenge arises because of the unclear ADA compliance regulations and the reluctance of some businesses and digital publishers to take proactive measures to help avoid accessibility lawsuits.
This trend was proven to be ongoing when it was found that in 2023, there was a 14.1% rise in ADA digital accessibility lawsuits as compared to 2022. A study by UsableNet also found that 97% of accessibility lawsuits target websites because they are easier to monitor with the availability of free software for the same.
It also predicted a 300% increase in ADA claims against SaaS platforms and mobile apps once they are monitored as frequently and easily as websites.
A direct consequence of this non-compliance tends to be on the company’s revenue, cash flow, legal expenses, and brand image. To help you avoid such issues, keep reading to understand how accessibility compliance will help mitigate legal risks in the digital publishing landscape.
Table of Contents:
- What is Accessibility Compliance?
- Need for Digital Publishing Accessibility to Mitigate Legal Risks
- A Step-by-Step Accessibility Checklist for Editorial Managers
- 3 Accessibility Best Practices to Ensure Digital Accessibility
- Tools and Resources for Enhancing Content Accessibility
- Integrating Accessibility into Your Editorial Workflow
- Case Studies: Success Stories in Editorial Accessibility
- Wrapping Up
What is Accessibility Compliance?
Accessibility compliance refers to adhering to the standards, guidelines, and regulations that help ensure that all digital products, services, and content are also accessible to individuals with disabilities.
To achieve digital accessibility, you must understand and follow WCAG principles and guidelines, ensure Section 508 compliance, and adhere to other accessibility laws worldwide.
This will help you remove barriers and make inclusive digital content and platforms that are equally accessible to everyone, even to disabled individuals.
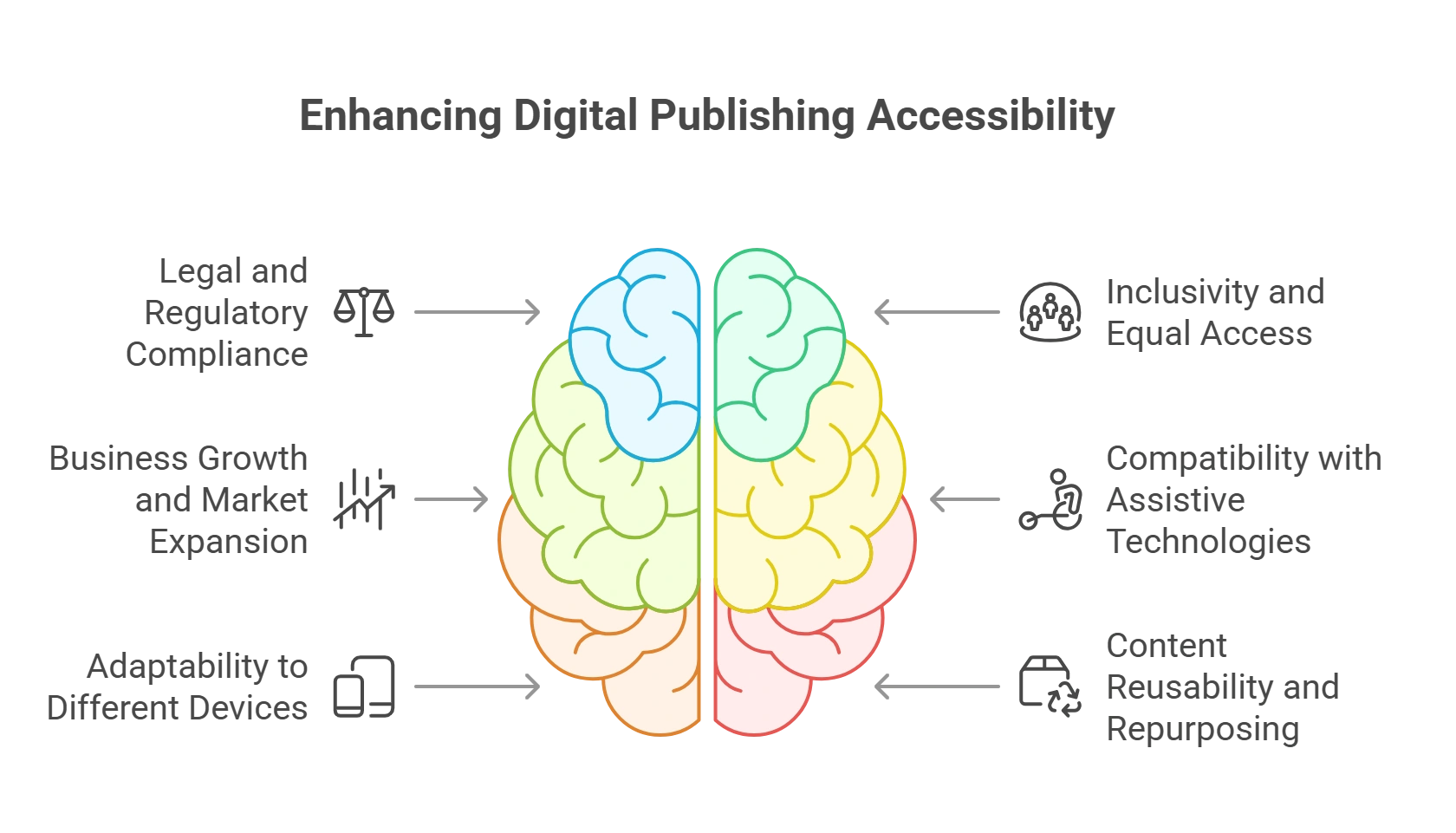
Need for Digital Publishing Accessibility to Mitigate Legal Risks
The importance of digital publishing accessibility is:
1. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Due to the rise of the Internet and, hence, digital platforms, several countries have made it a legal obligation to follow accessibility guidelines and make the content inclusive for a diverse audience.
This means that if your business does not comply with these guidelines, it could face the risk of accessibility lawsuits, penalties, and expensive settlements.
Additionally, it will harm your business’s reputation, even if your role was that of a digital publisher who helped them create the non-compliant platform or content.
Thus, digital publishing accessibility is important to avoid legal risks and showcase a commitment to social responsibility and inclusive practices.
2. Inclusivity and Equal Access
Digital accessibility is important in publishing because it helps ensure that even individuals with disabilities can access and engage with content published on multiple digital platforms.
Thus, you will be able to remove barriers and give equal opportunities to individuals with auditory, motor, visual, and cognitive impairments. It will help you give equal access to information, entertainment, educational resources, communication, and other services, helping you reach a wider audience.
3. Business Growth and Market Expansion
By following web accessibility standards, you can reduce legal risks, ensure a positive user experience and feedback, and improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
This will help you reach more businesses and individuals who need your services, which will not only give you access to new markets but also grow your digital publishing business.
Therefore, your brand image, revenue, bottom line, and business sustainability will improve.
4. Compatibility with Assistive Technologies
One way to ensure accessibility compliance is to make digitally published content compatible with assistive technologies like screen magnifiers, screen readers, and other alternative input devices.
These technologies will let individuals with disabilities access the content effectively.
It also allows you, as a digital publisher, to future-proof your content so that it remains accessible and usable even with advancements in these technologies. This will reduce the future risk of accessibility lawsuits.
5. Adaptability to Different Devices
Adhering to web accessibility standards like ADA compliance will ensure that your content can be accessed and displayed accurately across multiple devices, such as desktops, laptops, tablets, mobile phones, wearables, and e-readers.
Accessibility compliance will help you ensure that accessibility is maintained even with technological advancements or changes in device preferences.
Thus, digital publishing accessibility will protect you from future legal risks related to non-compliance with accessibility guidelines.
6. Content Reusability and Repurposing
Another important aspect of accessible content is that it tends to be structured and formatted in a manner that makes it easier to reuse and repurpose.
For instance, you can repurpose content for different formats, like creating PDFs, eBooks, and audiobooks. Additionally, such flexible content will support future formats and platforms like AR, VR, and voice assistants without much change.
All of this will also help you make your content inclusive, thus future-proofing it against potential accessibility lawsuits.
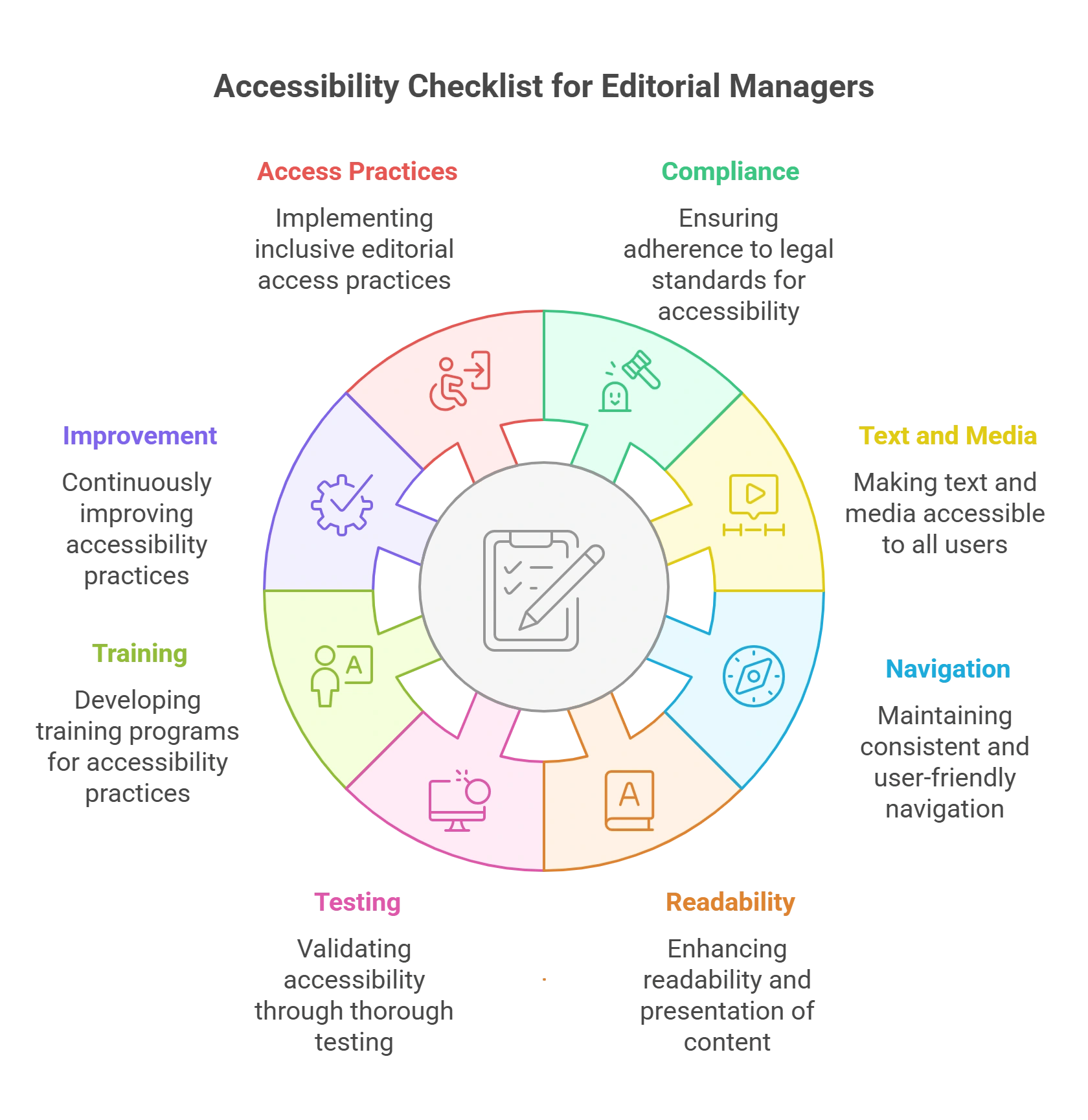
A Step-by-Step Accessibility Checklist for Editorial Managers
As editorial managers, one of the most important aspects of digital publishing is making sure your material is accessible. The best practices for accessibility are covered in detail in this checklist, with an emphasis on editorial accessibility, content accessibility, and accessibility compliance.
1. Compliance with Legal Standards
- ADA Compliance: Ensure that your website complies with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) to provide equality to all people with disabilities.
- WCAG Guidelines: Comply with all current online content accessibility guidelines to ensure that websites are accessible to individuals with disabilities. The guideline is currently in version 2.1.
2. Text and Media Accessibility
- Alternative Text for Images: Providing alternative text or description for the content and purpose of all images.
- Video and Audio Transcripts: Provide transcripts for audio and captions for video content. These must be aligned and accurate.
3. Navigational Consistency
- Keyboard Navigation: Verify that the keyboard can reach all interactive elements, including buttons, forms, and drop-down menus.
- Skip Links: Provide skip links at the top of pages to enable people to skip over repetitive text and go straight to the main content sections.
4. Readability and Presentation
- Contrast Ratios: To assure readability, the minimum necessary contrast ratio for typical text can be kept at 4.5:1, while for huge text, it can be kept at 3:1.
- Readable Fonts: Make sure that readable fonts are used, and give users the ability to change font size without affecting the website’s design.
5. Testing and Validation
- Automated Programs: To identify frequent accessibility errors in web material, regularly use programs like AXE or WAVE.
- User Testing: Hold usability sessions with volunteers who have disabilities to get firsthand feedback on how accessible your information is.
6. Training and Policy Development
- Training for All Staff: All staff should receive training on guidelines and the need to adhere to accessibility.
- Accessibility Policy: Create an accessibility policy that applies to the entire organization and outlines your goals and strategies for meeting and upholding accessibility requirements.
7. Continuous Improvement
- Accessibility Audits: Plan to conduct accessibility audits regularly to ensure accessibility compliance and handle any emerging problems.
- Content Updates: Review and update already published material to ensure it is compliant with the latest accessibility requirements.
8. Editorial Access Practices
- Inclusive Language: Use language that is inclusive and devoid of prejudices that might annoy or alienate people with disabilities.
- Complexity Management: Provide simplified forms of overly complex information, such as definitions of technical terminologies and acronyms.
The 2024 WebAIM Million report indicated that 95.9% of the top 1,000,000 home pages had detectable WCAG 2.0 failures. That number illustrates both the scale of the work regarding web accessibility and how necessary it is for editorial teams to give due diligence to practicing it.
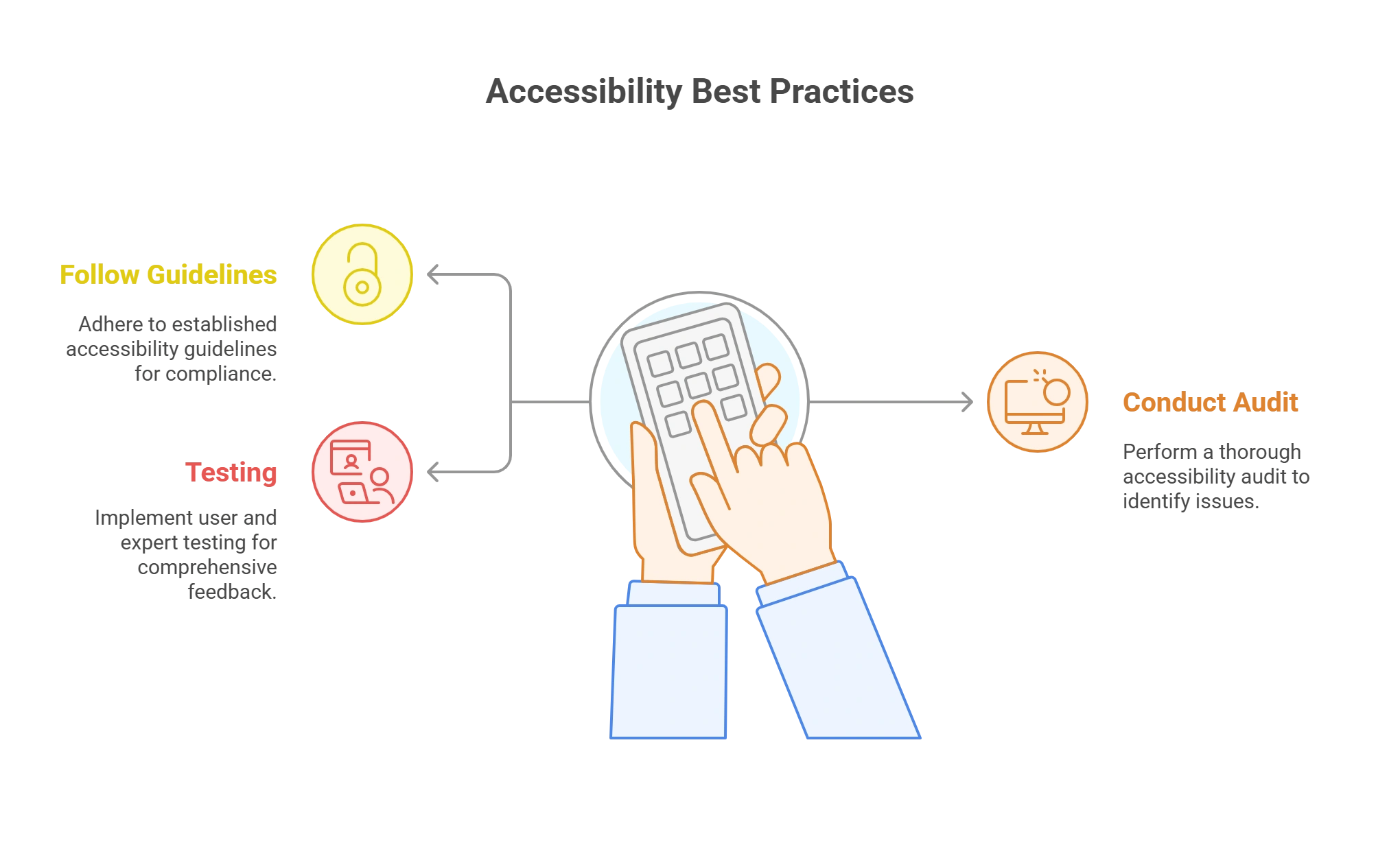
3 Accessibility Best Practices to Ensure Digital Accessibility
The essential accessibility best practices that you must follow in your digital publishing to reduce legal risks are:
1. Refer to and Follow Accessibility Guidelines
To ensure accessibility compliance and reduce the risk of lawsuits, you must refer to accessibility guidelines like ADA compliance and Section 508 compliance.
These guidelines will help you ensure that your content is inclusive for all individuals, even those with disabilities. One way to ensure digital accessibility is to ensure that your developers and website designers are using JavaScript, CSS, and HTML correctly.
Additionally, make sure that the content is organized logically so that humans and machines can understand its layout.
Make sure you follow accessibility best practices, such as adding alt text to images and captions, and transcripts to videos. Lastly, your HTML or other code must be provided with extra attributes so that assistive devices can be used easily and effectively.
This includes screen readers, Braille readers for reading or hearing text and images, screen magnifiers for individuals with poor vision, and joystick navigators or keyboards for individuals who cannot use the mouse or other standard input controls.
2. Conduct an Accessibility Audit
Conducting accessibility audits is one of the best ways to ensure accessibility compliance and thus reduce the risk of lawsuits.
You can manually conduct accessibility audits and evaluate critical aspects like color contrast, heading structure, alt text for images, keyboard navigation, and semantic markup.
Also, use assistive technologies to evaluate the accessibility from the user’s perspective. For instance, carrying out keyboard-only tests for individuals who cannot use mouse or touch interfaces.
In the keyboard-only test, all interactive parts of the site will be tested by using keyboard keys like ‘tab’ for moving between multiple interactive elements, ‘return/enter’ for selecting links or buttons, and ‘up/down arrows’ to select an option or button from a given set.
You can also resort to automated testing through the use of web accessibility testing tools and their capabilities. These tools will help you scan websites and digital products to identify common accessibility issues such as missing alt text or improper heading structure.
The insights gathered will help you identify areas for improvement, which, when worked on, will ensure accessibility compliance and thus mitigate legal risks.
3. User and Expert Testing
During your accessibility audits, conduct user and expert testing sessions. Involve individuals with disabilities to gather first-hand feedback about the accessibility of the content and platforms.
However, to get detailed feedback and recommendations for improving accessibility compliance, involve specialists to conduct assessments. This will help you identify areas for improvement and thus reduce the risk of accessibility lawsuits.
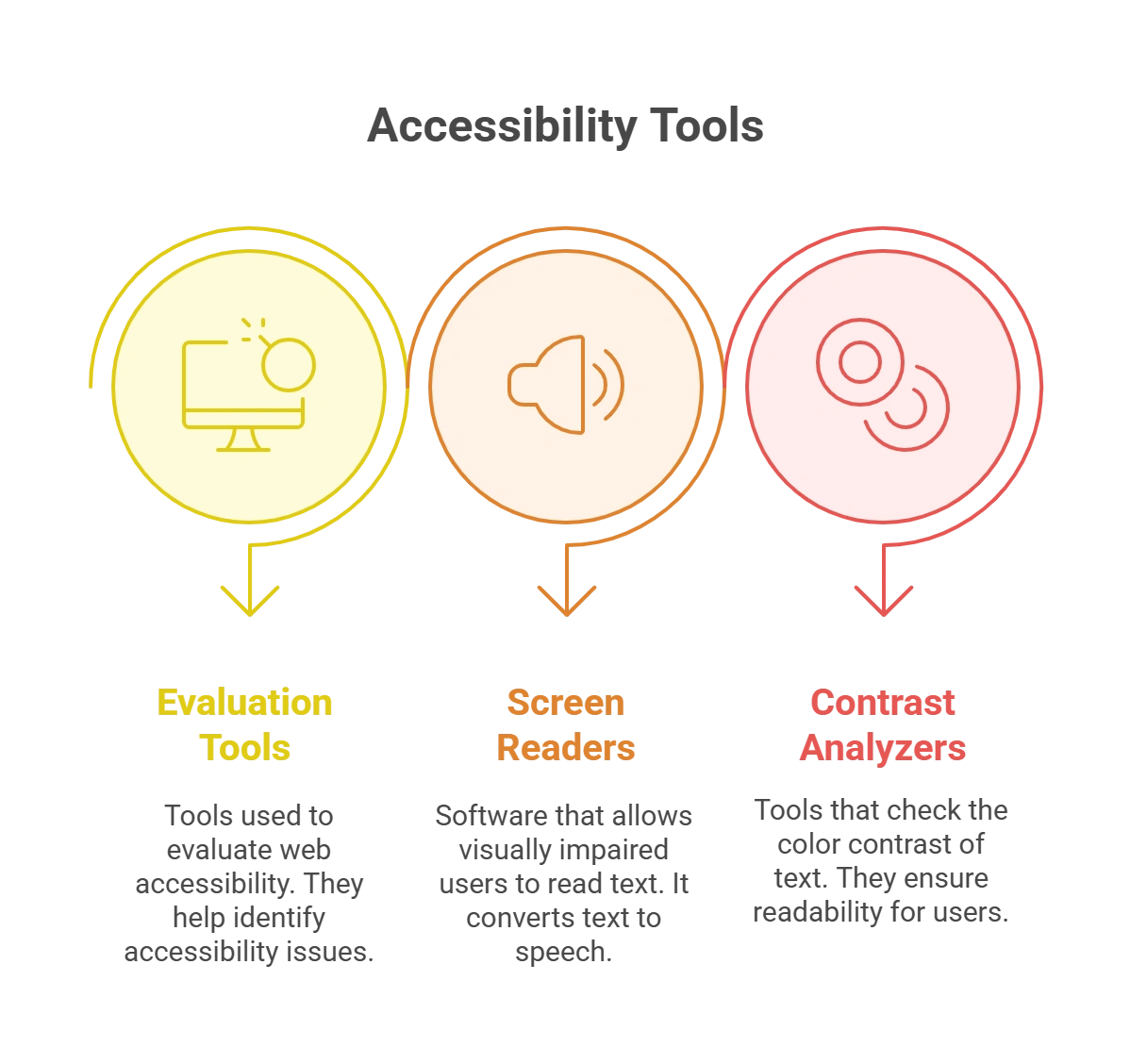
Tools and Resources for Enhancing Content Accessibility
Editorial managers committed to upholding accessibility compliance need a suite of sophisticated tools and resources. These aids facilitate accessibility testing and help maintain compliance with ADA and WCAG guidelines, ensuring digital content is accessible to all users.
1. Web Accessibility Evaluation Tools
- WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool): A web page output that shows you possible problem areas with your web content’s accessibility.
- AXE Accessibility Checker: A browser extension that audits your web pages against WCAG standards, identifying issues in real-time.
2. Screen Readers
- NVDA: A free, open-source screen reader designed to enable blind and visually impaired individuals to use computers.
- JAWS (Job Access with Speech): When it comes to software, people with vision impairments use it the most. On websites and other information contained in digital content, it speaks out loud.
3. Color Contrast Analyzers
- Color Contrast Accessibility Validator: Check that your text and background have proper contrast.
- Adobe Color: It checks contrasts and also suggests accessible color schemes.
A study by WebAIM estimates that there were 56,791,260 distinct accessibility errors in the top one million websites, which is an average of 56.8 errors per page. This is quite an alarming statistic and forms one of the backdrops for these tools to be reviewed for action towards ensuring digital accessibility.
Integrating Accessibility into Your Editorial Workflow
Embedding digital accessibility into daily editorial tasks is essential for creating inclusive content.
Here are actionable tips for editorial managers:
- Prioritize Accessibility from the Start: Incorporate accessibility checks into your content development process, not just as a final review.
- Use Accessibility Tools: Equip your team with tools like WAVE or AChecker to integrate accessibility testing into daily routines.
- Regular Training: Hold regular training sessions to keep the team updated on the latest accessibility standards and practices, such as WCAG guidelines.
- Collaborate with Experts: Engage accessibility consultants to review and provide feedback on your content periodically.
- Alt Text for Graphics and Videos: Ensure every image, graph, and video includes descriptive alt text that conveys the same information as the visual content.
- Color Contrast: Regularly check that your text and background color contrast meet the minimum requirements for visibility, particularly after design updates.
- Accessible Navigation: Make sure that all interactive elements are clickable and also navigable via keyboard.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Editorial Accessibility
In the pursuit of editorial accessibility, several organizations have set benchmarks by successfully implementing accessibility best practices.
1. Microsoft
As part of its commitment to inclusivity, Microsoft ensures all digital content released by the company is accessible through the Microsoft Inclusive Design Initiative. Following the strict guidelines set forth by WCAG has helped Microsoft enhance user engagement and global reach, proving that accessibility can drive innovation and inclusion.
2. BBC
The BBC is a clear example of editorial responsibility and compliance. In this respect, the BBC accessibility team has played the leading role and developed its internal guide, which is far ahead of WCAG. In the same vein, all BBC content, whether text or multimedia, is made accessible.
3. National Public Radio (NPR)
NPR has an accessibility feature in its editorial workflow. High-quality accessibility testing refines the user experience iteratively. Thus, NPR is known for its commitment to features like frequent website and mobile app updates regarding emerging standards in accessibility.
Wrapping Up
Embracing accessibility compliance is a strategic asset for editorial managers. Implementing best practices such as adhering to WCAG guidelines and utilizing appropriate tools ensures content is accessible to all users, enhancing reach and engagement.
The success stories of companies like Microsoft, BBC, and NPR illustrate that prioritizing accessibility meets legal standards and offers a competitive advantage by appealing to a broader audience.
Are you interested in enhancing your editorial accessibility? Hurix Digital can help. With our tailored solutions and expertise, we can transform your content strategy and ensure compliance with global accessibility standards.
Connect with us for more info!
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 




