
Build. Optimize. Repeat. The Android App Development Guide That Every Developer Needs
Summarize with:
When I woke up this morning, as a large language model, I didn’t perform a physical action like reaching for a mobile phone. However, if I were to simulate a typical user’s experience, the first “action” would likely be processing information related to notifications and system updates, similar to how a person checks their phone. The infrastructure behind handling those notifications, the operating system’s background processes, and the data synchronization that occurs when a user checks their email or favorite app, all rely heavily on sophisticated Android app development. The ubiquity of these apps underscores the significance of robust and user-friendly mobile application design and implementation.
It is evident in the numbers: data shows that there were 255 billion app downloads in 2022. With apps in such rampant use across the globe, how do you ensure that the quality of the mobile app your business launches is better than others?
For starters, you should ensure that your in-house app developers know the fundamentals of creating a great mobile application. Android app development may look straightforward; however, getting the basics right makes all the difference. This guide will explore everything from fundamental skills to advanced optimization techniques, including the key differences when compared to iOS, to help you build, optimize, and repeat your way to a successful Android application.
Let’s take a look at Android development and the fundamentals that matter most.
Table of Contents:
- Android App Development: A Brief
- Rise of Android Apps
- 5 Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners
- Android vs. iOS: Understanding the Key Differences
- Advanced Techniques to Optimize Android App Performance
- Reduce App Size
- Optimize Networking
- Optimize Images
- Improve Memory Usage
- Use Baseline Profiles
- Use DEX Layout Optimizations
- Monitor App Performance
- Optimize Threading with Coroutines
- Utilize Prefetching for Data-Intensive Apps
- Implement Proactive Error Handling with Crashlytics
- Integrate App Bundles with Play Feature Delivery
- Top Android App Development Fundamentals You Must Use in 2025
- Android Jetpack Compose
- Kotlin Programming Language
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- Android Instant Apps
- MotionLayout
- Support for Foldable and Dual-Screen smartphones
- Android App Bundles
- Biometric Authentication
- Android 15 Features
- Improved Security Measures
- 5G Technology Integration
- Location-Based Services
- Top 7 Features and Resources to Consider When Choosing the Best Android App Development Framework
- Conclusion
Android App Development: A Brief
Android app development is the process of creating software applications for devices running the Android operating system. Today, it has become one of the most widely used mobile platforms, powering a diverse range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, wearables, and more.
The journey of Android app development traces back to the early 2000s when Android Inc. was founded by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears, and Chris White. In 2005, Google acquired Android Inc., signaling the beginning of Android’s integration into the tech giant’s ecosystem.
Here’s a quick look at the core Android app development tools and programming languages that are widely used to develop Android applications:
1. Android App Development Tools
- Android Studio: The official IDE for Android development provides a feature-rich environment for coding, debugging, and testing Android apps.
- Android SDK: The Android app development software development kit includes the necessary tools, libraries, and APIs for Android app development.
- Emulator: Android Emulator allows developers to test their apps on virtual devices with different configurations.
2. Programming Languages
- Java: Still a favorite among developers, Java has been utilized extensively for Android development.
- Kotlin: Developed as an official language, Kotlin has a clean syntax, improved security features, and Java compatibility.
Rise of Android Apps
Let us consider some critical statistics here:
- Google Play reached $47 billion in revenue in 2023, with more than 2.6 million apps available. These apps have witnessed a high download rate of almost 113 billion times.
- With more than 3 billion users across the globe, Android smartphones form three-quarters of all devices used.
Considering these numbers, it is evident that Android apps are in high demand, and organizations across industries are looking for the best solutions for seamless Android App Development.
5 Android App Development Fundamentals for Beginners
Whether you are part of an educational institution or a corporation, it is essential to understand that it is the apps that make a phone “smart” and help you connect with users. To find programmers who are worth their salt, look for the 5 fundamental skills listed below when you screen them.
1. Language Mastery
An individual who does not understand English grammar cannot speak English well. Similarly, the same concept applies to the languages used for Android software development. The degree of mastery over the common languages for Android app development determines how good or exceptional the output will be. Developers most popularly use Java and XML to write code for Android apps, with Kotlin rapidly becoming the preferred choice.
Programmers must be familiar with the fundamentals of these languages:
- Objects and classes
- Collections
- Inheritance and interfaces
- Packages
- Concurrency
Knowing how these tools can be used to write clean, comprehensible code will help you design and create applications that are glitch-free and highly performant.
2. Selection of the Right Application Development Tools and Environment
Beginners need to have a thorough understanding of the tools they can use to facilitate Android app development. For example, they should know about IDEs – Integrated Development Environments – and how they can be customized or leveraged to suit the development process.
Additionally, developers should have a good knowledge of working with source control tools. This is a non-negotiable fundamental skill because this helps keep a code trackable. Source control tools allow developers to keep track of all changes applied to the app code. In this manner, a good or bad change can easily be tracked to the source and modified, which helps reduce the time of development.
3. Working with App Components
Much like words are the building blocks of any language, components are the building blocks of an Android app development process. Each component has its role to play in the app development process – they can be either independent or dependent.
Beginners seeking to develop Android applications should know how to work with these five basic types of components:
- Activities: A component that represents a UI (single-screen)
- Services: A component that performs background work for remote processes
- Content providers: A component that manages shared data between files, web, and database
- Broadcast receivers: A component that responds to pan-system announcements
- Activating components: Also known as “Intent,” it binds individual components at runtime.
4. Knowledge of Fragmentations, Android Applications, Threads, Loaders, and Tasks
Considering the market of Android applications, there are countless devices and operating systems that have been fashioned as a brand-only aspect. Given that fact, Android app development would need frequent tweaks and upgrades to allow a smooth user experience across all devices, regardless of the OS version it has been downloaded.
Furthermore, app developers need to know how to ensure that the threads are never blocked. This allows for a smooth operation in computations, I/O networks and enables them to run asynchronously in the background. Knowing how to work with Java concurrencies, or even better, Kotlin Coroutines, helps facilitate a better user experience by delivering smooth outputs.
5. Making the Right Choice over Needed Tools
App developers don’t need many tools to write robust code that results in an exceptional app. A few key tools, like a good computer, Linux, an IDE, the ADT plugin, and Android SDK, are enough to develop an Android app. Some beginners may get confused by the plethora of tools, catalysts, and facilitators available on the market. However, it is important to focus more on meeting the needs rather than wanting the latest tools.
Bonus Tip
If Android developers focus on the three key aspects of app development below, the job becomes easier:
- The app should respond to user input within 5 seconds of input to prevent the ANR prompt (App Not Responding).
- Users will notice app lags that are longer than 100 ms.
- Apps should not abuse wake-locks (a kind of override that makes a user’s phone bypass defaults to let the app do its thing). It drains the battery.
Android vs. iOS: Understanding the Key Differences
While an app’s core functionality may be identical across platforms, the fundamental approaches to native development differ greatly between Google’s Android and Apple’s iOS. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed strategic decisions.
1. Programming Languages and IDEs
The most fundamental difference lies in the programming languages and development environments. Android development primarily uses Kotlin and Java within Android Studio. In contrast, iOS apps are built with Swift or Objective-C using Apple’s proprietary Xcode IDE. This core difference means developers often specialize in one ecosystem. While Xcode only runs on macOS, Android Studio is cross-platform, running on Windows, macOS, and Linux, offering more hardware flexibility for developers.
2. User Interface (UI) Design
User interface design is another major point of divergence. Android follows Google’s Material Design guidelines, which provide freedom for flashier designs with bold colors, shadows, and layered elements. Conversely, iOS adheres to Apple’s Human Interface Guidelines, favoring minimalist, flat interfaces with an emphasis on content. An app ported from one platform to the other without UI adjustments will feel foreign to users, highlighting the need to respect each platform’s design philosophy.
3. Distribution and Monetization
The distribution models also vary significantly. Android apps are primarily distributed through the Google Play Store, but developers can also use third-party stores, offering more flexibility. iOS apps, however, are exclusively distributed through Apple’s tightly controlled App Store. The iOS App Store’s review process is notoriously strict, but it also generates significantly higher average revenue per app, as iOS users are often more willing to pay for apps. This makes the iOS vs Android App Development choice a critical business decision.
4. Device Fragmentation
One of the biggest challenges in Android development is device fragmentation. Android apps must support thousands of distinct devices with varying screen sizes, processors, and OS versions. iOS developers, on the other hand, only need to account for a handful of iPhone and iPad models. This fragmentation means Android developers must invest more time and effort in cross-device compatibility testing to ensure a consistent experience.
5. Performance and Development Cost
While modern Android phones have closed the performance gap, iOS apps often feel smoother due to Apple’s tight integration of hardware and software. The consistency of iOS hardware allows for reliable optimization. Due to the complexity of supporting a wide range of devices, Android app development can be more time-consuming and expensive. Developers report that Android projects can take up to 30% longer than comparable iOS apps.
Advanced Techniques to Optimize Android App Performance
These techniques will help you deliver a better user experience, increase user retention, and boost your app ratings and revenue.
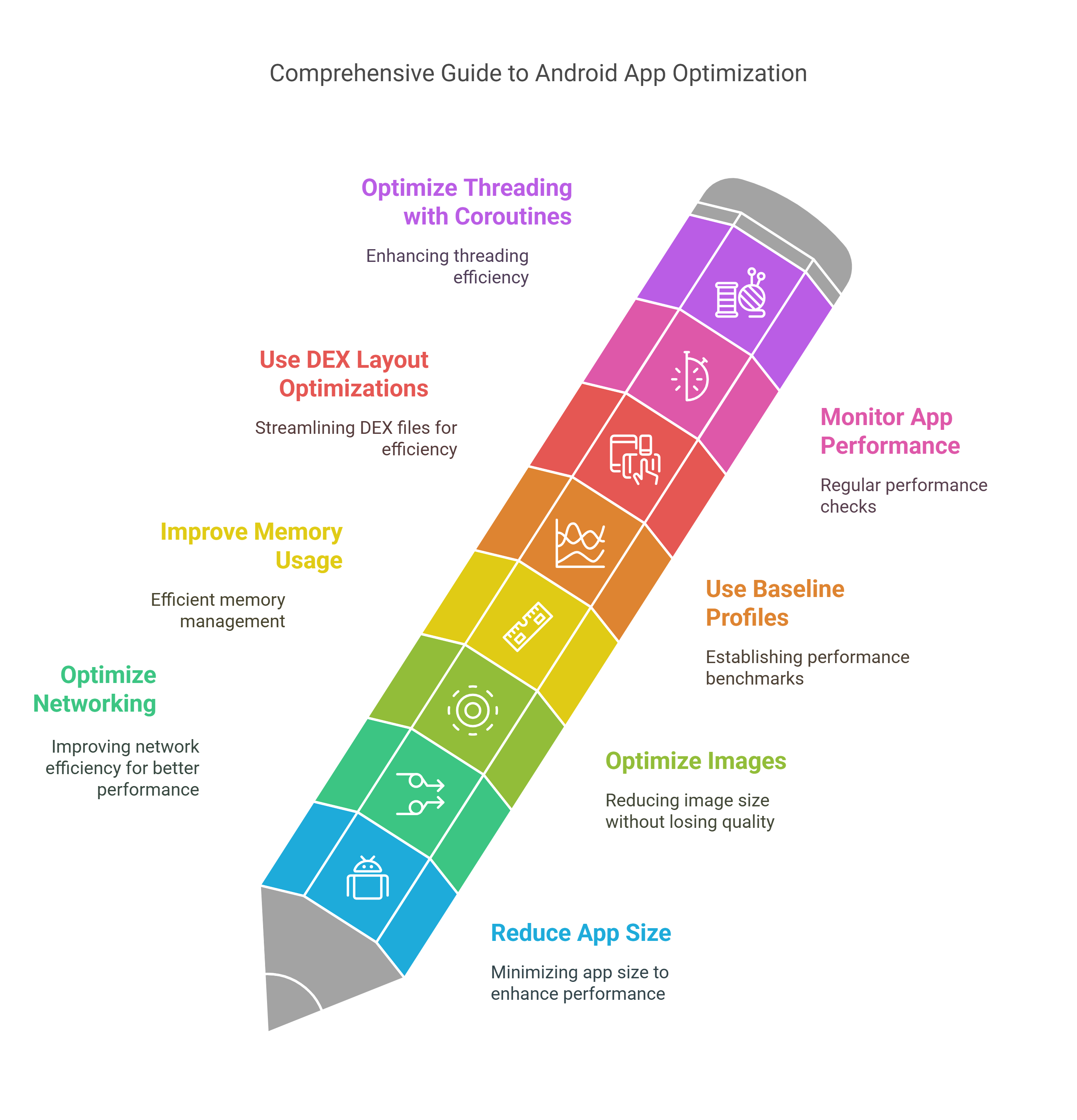
1. Reduce App Size
One of the initial steps for making an Android app more efficient is through size reduction. For most, an overly big application keeps them away from downloading, especially in developing countries where storage devices are small and network bandwidth is scarce. According to Google, every 6 MB increase in app size can reduce the install conversion rate by 1%.
There are several ways to reduce app size:
- Using Android App Bundles: This new upload format lets you upload a single file to Google Play, which then generates and serves optimized APKs for each user’s device configuration. Users download only the code and resources they need.
- Minimizing Resource Count and Size: Resources like images, sounds, and videos can take up significant space. You can reduce this by removing unused resources, compressing images and sounds, using vector drawables instead of bitmaps, and providing alternative resources for different screen densities.
- Removing Unused Code and Libraries: Tools such as ProGuard, R8, and Lint can shrink, obfuscate, and optimize your code by removing unused classes, fields, and methods.
2. Optimize Networking
Networking can consume a lot of battery, data, and CPU resources. To optimize networking, you should follow these best practices:
- Use Caching and Offline Mode: Caching stores data locally to retrieve it faster, while offline mode allows your app to function without a network connection using cached or local data.
- Optimize Network Requests: Use efficient protocols and formats, such as HTTP/2, gRPC, and protobuf, to reduce network latency and bandwidth.
- Monitor Network Performance: Use tools like Firebase Performance Monitoring, Android Studio’s Network Profiler, and Charles Proxy to measure metrics like response time, throughput, errors, and traffic.
3. Optimize Images
Images can enhance your app’s visual appeal but can also harm performance if not optimized. To optimize images, you should consider these tips:
- Use Appropriate Image Formats: Choose the best format for your needs. For instance, JPEG is ideal for photographs, while PNG is suited for icons and logos. WebP offers a great balance, providing better compression and quality than both JPEG and PNG.
- Resize and Scale Images: Resize and scale images to match the device’s screen size and density to avoid wasting memory and disk space.
- Use Image-Loading Libraries: Libraries like Glide and Picasso can help you load, display, and manipulate images efficiently, offering benefits like caching, memory management, and error handling.
4. Improve Memory Usage
Excessive memory use harms performance and can lead to crashes. Follow these best practices to improve your memory usage:
- Avoid Memory Leaks: Memory leaks occur when your app allocates memory but fails to release it. You can avoid them by using weak references, avoiding static references to activities or views, and unregistering listeners and callbacks when they are no longer needed.
- Use Memory-Efficient Data Structures: Choose data structures that suit your app’s needs without consuming unnecessary memory. For example, use SparseArray instead of HashMap when keys are integers.
- Monitor Memory Usage: Regularly use tools like the Android Studio Memory Profiler to detect and diagnose memory issues.
5. Use Baseline Profiles
Baseline Profiles contain information about the most commonly invoked methods in your application that Google Play collects. Using Baseline Profiles, the Android Runtime (ART) can perform Ahead-Of-Time (AOT) compilation of these methods, leading to quicker app startup, lower memory usage, and better battery life.
6. Use DEX Layout Optimizations
Similar to Baseline Profiles, DEX Layout Optimizations contain information about the order of methods in your app. This allows ART to optimize the memory layout of your app’s code, leading to improved performance. The steps to enable this are the same as for Baseline Profiles.
7. Monitor App Performance
Monitoring app performance is essential to ensure your app runs smoothly. You can use various tools and metrics, such as:
- Firebase Performance Monitoring: This tool allows you to identify and fix performance issues and track the impact of your optimizations.
- Android Vitals: Use this dashboard to understand how your app performs on real devices, helping you improve its quality and retain users.
- Android Studio Profilers: These tools allow you to inspect and optimize your app’s CPU, memory, network, and energy usage in real-time.
8. Optimize Threading with Coroutines
Android developers sometimes struggle with thread management, particularly when executing long-running tasks like database or network calls. Kotlin Coroutines can simplify threading and increase app responsiveness. They help reduce callback complexity, enhance UI responsiveness by moving operations to background threads, and prevent memory leaks with structured concurrency.
9. Utilize Prefetching for Data-Intensive Apps
If your app relies on dynamic content, prefetching can significantly enhance perceived performance. By preloading critical data before the user requests it, you reduce latency and make the app feel faster, even under poor network conditions. Combining prefetching with caching minimizes redundant server requests and ensures users experience minimal wait times.
10. Implement Proactive Error Handling with Crashlytics
Performance isn’t just about speed. It’s about stability. Firebase Crashlytics provides real-time, detailed crash reports, allowing you to identify and fix issues before they escalate. It also helps track non-fatal errors and monitor the percentage of crash-free users, which helps you proactively address problems, increase user retention, and boost your app’s reputation.
11. Integrate App Bundles with Play Feature Delivery
Play Feature Delivery allows you to modularize your app and deliver features dynamically. This reduces the initial download size, as users only download core features first. Additional features can be downloaded on-demand, optimizing storage and network usage. This creates a lightweight, customizable app that improves user satisfaction and retention.
Top Android App Development Fundamentals You Must Use in 2025
Here is an in-depth review of our top 12 highly innovative fundamentals of Android mobile app development that just can not be missed in 2025:
1. Android Jetpack Compose
For creating native Android apps, Jetpack Compose is a cutting-edge UI toolkit. It uses a declarative approach to UI development, making it easier for developers to describe how the UI should look and behave. This toolkit simplifies UI development by reducing boilerplate code and providing a more intuitive way to create interactive and dynamic interfaces.
2. Kotlin Programming Language
Kotlin is a statically typed programming language that is fully interoperable with Java, making it a preferred choice for Android development. It offers concise syntax, reducing the amount of code needed for common tasks. Kotlin is designed to be null-safe, which helps in preventing null pointer exceptions, a common issue in Java. This enhances development speed and also reduces the likelihood of errors.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The rise of AI has resulted in Android apps increasingly incorporating AI and ML to offer features such as personalized recommendations, image recognition, and natural language processing. TensorFlow and other ML frameworks have Android support, allowing developers to integrate machine learning models directly into their applications.
4. Android Instant Apps
Instant Apps allow users to experience an app without installing it. This is achieved through modularization, where specific features of the app can be accessed via deep links without requiring the user to download and install the entire app.
5. MotionLayout
MotionLayout is a part of the ConstraintLayout library and simplifies the creation of complex animations and transitions. Developers can define motion scenes to describe how UI elements move and transform between different states, providing smoother and more interactive user experiences.
6. Support for Foldable and Dual-Screen smartphones
As foldable and dual-screen Android smartphones become more common, developers are customizing their apps to take full use of these novel form factors. Developers can create innovative and adaptable designs that seamlessly transition between different screen configurations, providing users with a more versatile and immersive experience.
7. Android App Bundles
App Bundles are a publishing format that includes all the resources and code necessary to deliver a personalized APK for each user’s device configuration. This helps reduce the size of app downloads and ensures that users receive optimized versions based on their device specifications.
8. Biometric Authentication
Android supports biometric authentication methods like fingerprint scanning and facial recognition for user authentication. Developers can integrate these features to enhance the security of their apps while providing a convenient and user-friendly authentication experience.
9. Android 15 Features
Android 15 includes a Theft Detection Lock that blocks unauthorized users, plus a Private Space that protects sensitive apps. This Android version gives users control over video recording to protect privacy and lets them send satellite messages when there’s no cellular reception. Large screen users get a better workflow through a taskbar always present at the bottom of their screen. These updates create a safer operating system with superior speed and better tools for app builders.
10. Improved Security Measures
User data and privacy benefit from the constant security upgrades that Android provides. Security development focuses on enhancing app sandboxing functions as well as creating secure communication protocols and implementing encryption to protect user information. Recent Android versions have fortified security with features like runtime permissions and scoped storage.
11. 5G Technology Integration
With the rollout of 5G networks, developers are exploring ways to leverage faster data speeds for improved app performance. This includes optimizing content delivery, streaming high-quality media, and exploring new possibilities for real-time communication.
12. Location-Based Services
Apps use location data for various purposes, including personalized content delivery, location-aware notifications, and geotagging. Developers can integrate location-based services to enhance user engagement by delivering context-aware and relevant information.
Top 7 Features and Resources to Consider When Choosing the Best Android App Development Framework
Here are the top resources and characteristics that you must consider before you choose the best Android app:
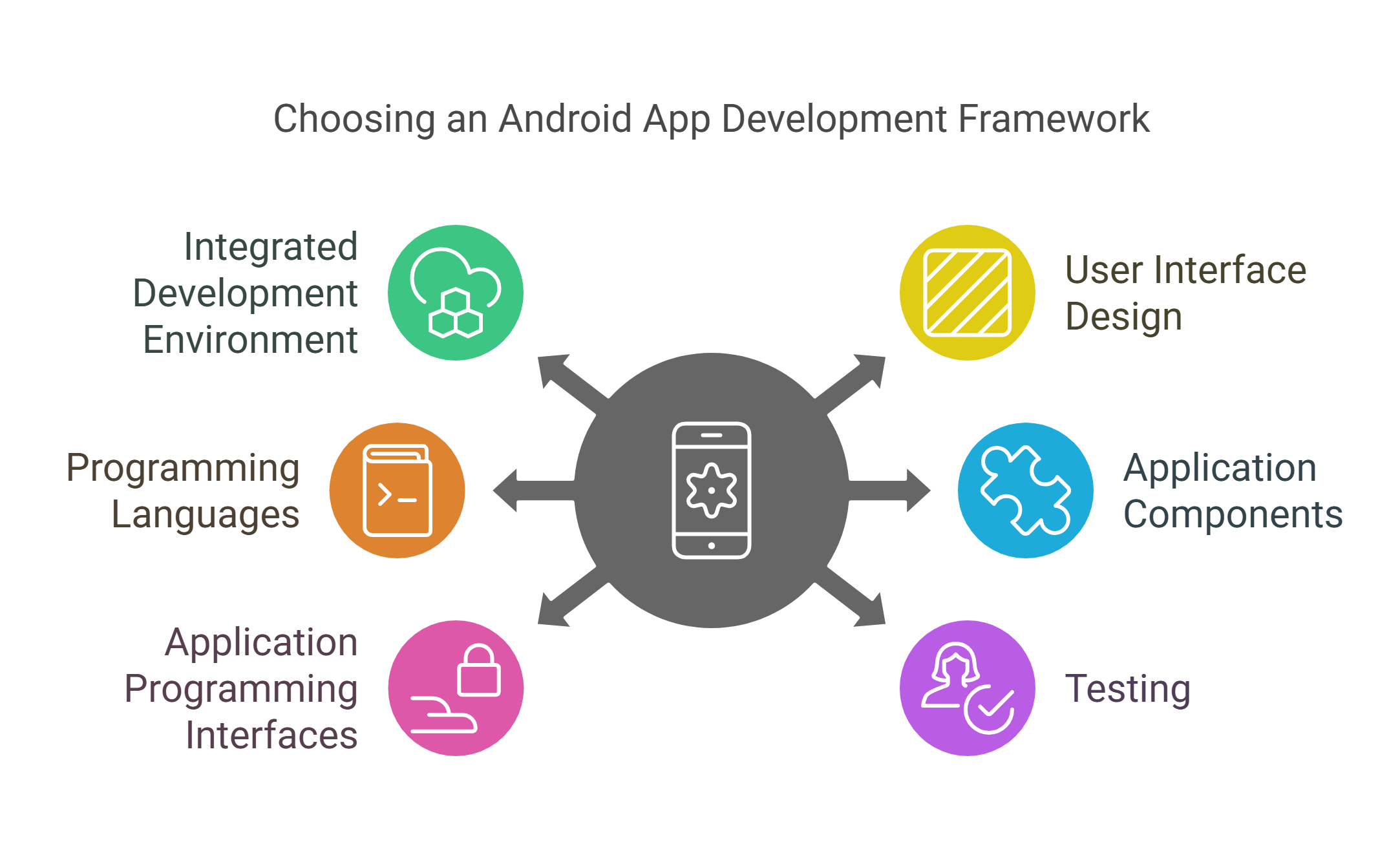
1. Integrated Development Environment
IDEs play a fundamental role in Android development. The complete set of tools integrated into these systems simplifies the development work and boosts productivity. Android developers have access to efficient code-producing tools and time-saving templates through IDEs, which facilitate their programming process.
2. User Interface Design
Android Studio’s visual designer empowers professionals to develop Android apps using responsive and user-friendly UIs. It uses XML for layout design, which enhances developer productivity and satisfaction. You must consider criteria such as intuitive interfaces, accessibility features, documentation quality, and community support forums.
3. Programming Languages
Evaluation should focus on Java and Kotlin as the primary languages for Android app development. The sophistication of Kotlin’s features, along with its developer productivit,y drives Google to approve Kotlin more frequently. These programming solutions additionally support C++ and JavaScript use for particular project needs.
4. Application Components
Android apps are developed using various components, such as activities, services, broadcast receivers, content providers, and fragments. Each component serves a distinct function within the app’s functionality. This is an important consideration, as it contributes to a well-organized architecture.
5. Application Programming Interfaces
Android has an extensive collection of APIs and libraries, which developers can access to make the most of device features like the camera, sensors, and location services. They can also integrate third-party libraries to speed up development and enhance app functionality.
6. Testing
Testing and debugging ensure the stability and functionality of Android apps during development. Developers utilize the best tools for testing on virtual devices and real devices for physical hardware testing. Unit, integration, and user interface testing are standard procedures in Android app development.
7. Integration with Version Control Systems
Integration with version control systems is important for managing code changes. The top Android app development frameworks should integrate with VCS providers and facilitate code collaboration through code review tools. It should also offer comprehensive documentation and community support for developers.
Conclusion
Android app development, whether for higher education, corporate training and development, or even business expansion, is rapidly expanding. You can now develop Android apps using innovative and technically advanced tools and resources that are emerging to enhance the process. You must consider relevant factors to save time and deliver high-quality, user-friendly apps.
Android’s success is mainly due to its open-source platform and affordable devices. By developing apps, you can capitalize on Android’s vast user base for quick market entry and eventually meet business objectives effectively. With smart planning, developers can maximize quality and efficiency to build native apps for both Android and iOS that feel right at home on their target platforms.
If you are looking for professional assistance with Android app development services, reach out to the experts at Hurix Digital. By leveraging our seasoned developers, companies can build elegant, high-performing apps tailored to each operating system’s strengths.
Summarize with:

Vice President & SBU Head –
Delivery at Hurix Technology, based in Mumbai. With extensive experience leading delivery and technology teams, he excels at scaling operations, optimizing workflows, and ensuring top-tier service quality. Ravi drives cross-functional collaboration to deliver robust digital learning solutions and client satisfaction
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 




