Internal Vs. External Enterprise Learning: What’s the Difference?
Summarize with:
Continuous learning has become essential to an organization’s success in the fast-paced environment of modern business. To enhance worker skills, foster creativity, and maintain a competitive edge, businesses invest actively in learning and development programs.
Nonetheless, there are two main methods in the field of corporate learning: internal and external. Comprehending the distinctions among these methodologies is crucial in developing effective learning strategies tailored to meet an organization’s specific needs.
Now, let’s examine the subtle differences between internal and external enterprise learning and how they affect employee development and organizational progress.
Table of Contents:
- Current Issues in Training and Development
- Tips to Address These Issues
- What’s the Difference Between Internal vs. External Enterprise Learning and Training?
- Moving Ahead
Current Issues in Training and Development
Numerous challenges hinder the effectiveness of corporate employee training programs offered by organizations across industries.
1. Standards & Quality
Traditional training methods, such as seminars or classroom lectures, are often standardized. Depending on the skills of individual facilitators, these sessions could work very well or completely fail to address the employees’ learning needs. Additionally, these methods are not in step with the rapidly evolving technology and market trends and often do not leverage the value technology can offer. This renders the training content obsolete by the time it reaches the employees.
The accelerated shift toward hybrid workplaces challenges organizations to deliver engaging and effective learning experiences in a virtual environment. Ensuring employees remain motivated and connected during remote training sessions has become another pressing concern.
2. Lack of Alignment
One of the most significant issues in training and development is the lack of alignment with business objectives. When training is not tailored to address specific skill gaps or organizational needs, it becomes an isolated activity that fails to impact the bottom line. Moreover, the absence of a clear and measurable training evaluation strategy leaves companies uncertain about the effectiveness of their training efforts.
3. Limited or No Hands-on Practice
Another challenge faced by corporate training programs is the lack of interactivity and hands-on learning experiences. Without practical application and reinforcement of newly acquired skills, employees may struggle to transfer knowledge to their job roles effectively.
Training programs that rely solely on passive learning through lectures or lengthy slide presentations do not engage learners effectively. Without active participation and opportunities for practice, employees may find it challenging to apply their knowledge when facing real challenges at work.
4. Ineffective Training Methods
Ineffective training methods can manifest in various ways, such as content overload, lack of real-world application, and monotonous delivery. When employees are bombarded with information, it causes cognitive overload, resulting in poor retention of crucial concepts.
5. Training and Development Problems and Solutions
To transform an ineffective training program into an impactful one, organizations must embrace modern solutions that address current challenges. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Needs Assessment: Conduct a thorough needs assessment to identify skill gaps and align training objectives with organizational goals. This process ensures that training efforts directly contribute to the company’s success.
- Interactive Learning: Incorporate interactive elements into training programs, such as simulations, gamification, and scenario-based learning. These approaches enhance engagement and promote practical application.
- Blended Learning: Combine online corporate training with in-person workshops or virtual instructor-led sessions. Blended learning allows for a more personalized experience and accommodates diverse learning preferences.
- Microlearning: Break down training content into bite-sized modules, making it easier for employees to digest and apply knowledge as needed. Microlearning fits well into busy schedules and encourages self-directed learning.
- Continuous Learning Culture: Foster a culture of continuous learning where employees are encouraged to seek opportunities for skill development beyond formal training programs. Encourage peer learning and knowledge sharing within the organization.
- Learning Analytics: Implement learning analytics to track the effectiveness of training initiatives continually. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make data-backed decisions, refine training strategies, and measure the return on investment (ROI) of training efforts.
Tips to Address These Issues
Here are some ways to tackle these issues efficiently:
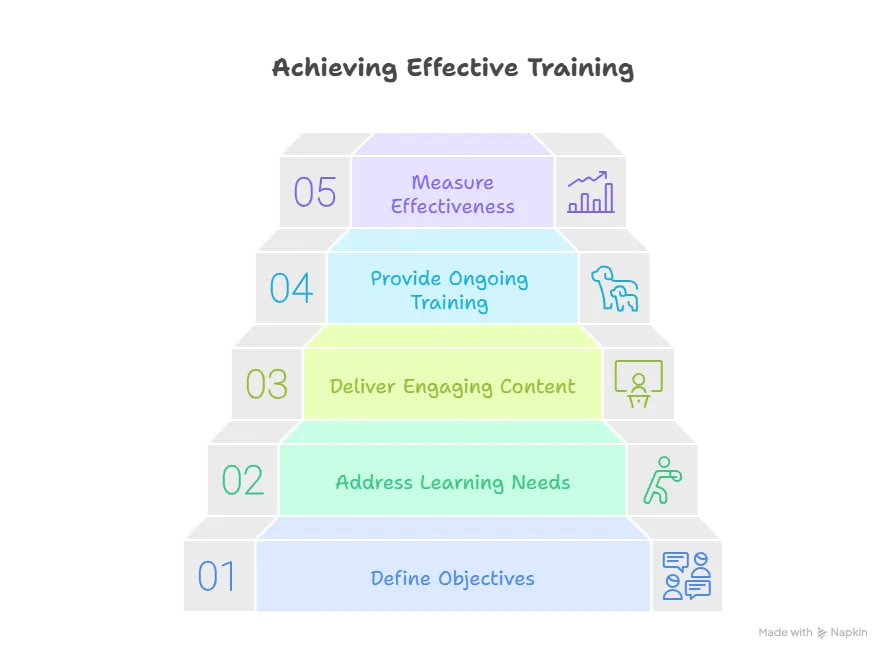
1. Define the Objectives
Collaborate with the functional leaders to understand the nature of their function and the performance gap they wish to close. This will help you define measurable training goals and objectives. The training goals and objectives must align with the organization’s overall strategy and be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Failure to define clear goals and objectives can lead to a lack of focus, confusion among employees, and a lack of motivation to participate in the training program.
2. Address the Diverse Learning Needs of Employees
Not all employees learn in the same way, and some may prefer hands-on training while others prefer to learn through self-paced online courses. Offer a range of training methods and modalities to cater to different needs and preferences.
3. Deliver Training Content that is Engaging and Relevant
Delivering training content that is engaging and relevant is crucial to the success of any training program. Training content that is dry, boring, or irrelevant to an employee’s job function is unlikely to be effective. Ensure that your training content is up-to-date, relevant to the job function, and delivered in an engaging way to capture the attention of employees.
4. Provide Consistent and Ongoing Training
Training is not a one-time event. It is an ongoing process that requires consistent and ongoing efforts. Provide consistent training to their employees to reinforce their knowledge and skills, and to keep them up-to-date with the latest industry trends and technologies.
5. Measure the Effectiveness of Training
Develop metrics to measure the impact of your training program on employee performance, productivity, and job satisfaction. Failure to measure the effectiveness of training can lead to a lack of accountability and a failure to identify areas for improvement.
What’s the Difference Between Internal vs. External Enterprise Learning and Training?
Training is an integral part of any organization’s functioning. An employee needs to be periodically subjected to skill development exercises to ensure that s/he can capably work on evolving systems driven by advanced technologies. This constitutes internal learning.
Businesses, however, are fast realizing that customers, key stakeholders, and others indirectly involved in organizational functions should also be trained with skills relevant to promoting organizational products. This extended or external enterprise learning is primarily concerned with training efficacy, quality of educational content, learning theories, and instructional design.
The goal is to manage the basic talents of trained professionals in alignment with organizational priorities to support optimum performance and facilitate compliance management.
It is vital to understand the key differences among the various enterprise learning strategies to create compelling training content that fulfills organizational objectives. As such, the major divergences between the learning approaches are explored below.
1. Content Assignment Methodology
In internal training, employees have limited choices. They are assigned learning content based on their roles, future growth requirements, strategic profile changes, and other organizational priorities. The learning management system automatically assigns content and showcases progress through its interface.
In extended learning, learners are allowed to pick up content that complements their interests and upskilling needs through search and other navigational features. The identification of relevant content is facilitated by suitable categorizations based on filters, recommendations, catalogs, tutors, learner ratings, feedback, etc.
2. Motivation for Subscribing to Training
Internal training is compulsory for employees. They have the professional obligation of taking and completing the assigned training to enhance their competencies. If anyone declines to complete training, s/he may be denied promotion, a pay hike, or even be fired.
The enterprise allows the voluntary participation of external partners in customized training modules developed exclusively for them. Often, they are requested to visit the learning management system to engage with relevant modules and complete the same.
Outsourced training solutions are deployed to psychologically motivate partners and offer them immersive learning experiences.
3. Content Type
The content for internal training can be devised by subject matter experts within the organization. Also, it can be sourced from renowned learning content developers and integrated with the organization’s training portal. Outsourced training benefits range from being cost-competitive to the availability of focused learning materials for all skill levels and industry niches.
The external enterprise learning content is bespoke and proprietary. This is because the strategic partners of an organization have to be engaged productively in a way that they can sync their efforts with the company’s business goals. For this reason, the content is tailored to focus on aspects that can help boost performance and expedite sales.
4. Complexity of Managing Roles
The content for employee skill development can cater to many professionals discharging similar or related job responsibilities in the organization. This implies that internal trainers have to focus on content access modalities and managing role-based training functionalities.
In contrast, the complexity of role management for external learners is higher. Such learners cannot be categorized based on roles, as the domains of their functionalities differ widely. This calls for crafting disparate and personalized learning experiences through unique configurations of brand-oriented business process overviews, workflow-related content, learning libraries, landing pages, training languages, third-party integrations, etc.
5. Integration Types
For internal training, content is deployed by integrating the employee profile-based user account with SAP-type enterprise resource planners or HR applications. The ERP software makes available information related to employees’ organizational hierarchy, manager, appraisal rating, identified opportunities for improvement, etc.
External training, driving educational programs, and measuring the enrichment levels of strategic partners are typically done through CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platforms. These include Zendesk, Zoho, Microsoft Dynamics, Salesflare, HubSpot, etc.
The partner’s attributes, such as education level, demographics, and areas of expertise, are gathered to create customized learning plans.
6. Notification Types
The enterprise training and learning platforms deployed for training employees come integrated with systems to automatically send text and email notifications to targeted employees. This implies that employees are informed in real time whenever a content assignment is done.
Further, notifications are sent for the successful completion of training, crossing of the completion deadline, reminding about the next training, etc.
In contrast, notifications to external enterprise training learners about training content are sent through email marketing platforms. The learning management system is integrated with one such platform. Emails are sent automatically in response to specific triggers from the system, such as user logging, frequency of visits during a particular period, completion or non-completion of assigned training, and inactivity for a significant duration, among other events.
7. Cost of Training
Internal enterprise training is imparted free of charge to employees. Organizations never ask employees to pay for learning content that is designed to upskill them or ensure compliance.
The case is different in the case of extended training. External strategic partners or customers can be persuaded to buy premium content that trains them on innovative ways to accomplish niche-specific goals. They can be influenced to buy certifications that attest to their expertise or superior skills in relevant domains.
For example, the selling partners of an organization engaged in eCommerce can offer curated paid courses on conversion funnel, upselling, cross-selling, taxation, volume pricing, etc. Such paid content must have the potential to empower partners with new techniques and tools to open up fresh streams of revenue generation.
8. Certifications for Completing Training
The internal learning management system is programmed to generate a certificate with the employee’s credentials upon successful completion of the assigned training. The certificate can be printed or saved in digital mode in popular file formats.
For external training, digital badges are usually provided to signify the completion of specific pieces of training. The recipient often displays this badge against his profile on social media, email communications, websites, and other digital touchpoints to showcase his proficiency and attract new customers.
The badge generally carries information about the enterprise training completed, the issuer organization’s name, date of training completion, badge expiration, and other relevant details in metadata. The badge can be used throughout one’s career.
Moving Ahead
Within the ever-changing field of corporate learning, internal and external strategies are essential for developing employees and promoting organizational progress. External learning adds a variety of viewpoints and areas of expertise to the learning process, while internal learning provides personalization and alignment with company goals.
Organizations can develop comprehensive learning strategies that foster creativity, adaptability, and long-term success in the current competitive environment by comprehending the differences between these methods and utilizing their unique advantages.
Hurix Digital delivers top-notch training content for your internal and external learning needs. With market-oriented solutions and strategic partnerships, we ensure engagement and success.
Summarize with:

Performance, Results, Growth, and Life-Long Learning define my professional life. I am passionate about making workplace learning planful, purposeful, and impactful. I take pride in partnering with clients and bringing them the best in learning design and creating solutions that address business challenges.
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful