
Level Up Patient Care with Gamification in Healthcare
Summarize with:
The last few years have seen the concept of gamification gain traction across industries. It is an engaging and innovative way to keep users engaged with brands, personalize offerings, and collect insightful data.
The healthcare industry, in particular, has recognized the importance of using gamification or game elements such as rewards, points, leaderboards, badges, and more to engage and encourage patients and be more involved in their health regimens.
The healthcare gamification market’s exponential growth, expected to exceed approximately $47,281.5 million by 2026 with a CAGR of 11.9%, is primarily attributed to high demand and technology adoption across the board.
In this post, we focus on gamification in healthcare and ways to use the concept.
Table of Contents:
- What is Gamification In Healthcare?
- Top 8 Ways to Use Gamification in the Healthcare Industry
- Benefits of Gamification in Healthcare
- Challenges and Limitations
- Simulation Training for Healthcare Professionals
- Benefits of Simulation in Healthcare
- Common Types of Simulation in Healthcare
- Impact of Simulation on Healthcare Training
- To Conclude
What is Gamification In Healthcare?
Gamification refers to the implementation of various game principles, elements, and techniques into non-game activities. Using gamification in healthcare apps enables better patient participation and interaction, making different health processes more exciting and engaging.
Some examples of gamification elements integrated into healthcare apps include the following:
- Levels and challenges
- Progress bars
- Simulation gaming
- Leaderboards
- Ratings
- Rewards and badges
In healthcare, gamification is primarily used to improve clinical outcomes of various diseases by encouraging or reinforcing healthy habits in patients. It also helps in various other aspects, such as disease prevention and following up with medical advice.
Overall, the key objective of incorporating gamification in healthcare is to personalize the patient’s healthcare journey, thereby improving patient engagement in the long run.
Some of the examples or use cases of gamification in healthcare are:
- Engaging patients suffering from diseases such as Alzheimer’s to perform specific tasks and improve dexterity.
- Sharing patient progress in fitness with other users
- Encouraging patients or users to perform specific exercises to treat ailments such as mobility impairments
- Using graphs, bars, and charts to help users track their progress in developing healthy habits.
- Completing specific milestones creates a sense of competition and a feeling of achievement among the patients/users.
Top 8 Ways to Use Gamification in the Healthcare Industry
Wondering how you can use gamification in healthcare effectively? Read on to know more:
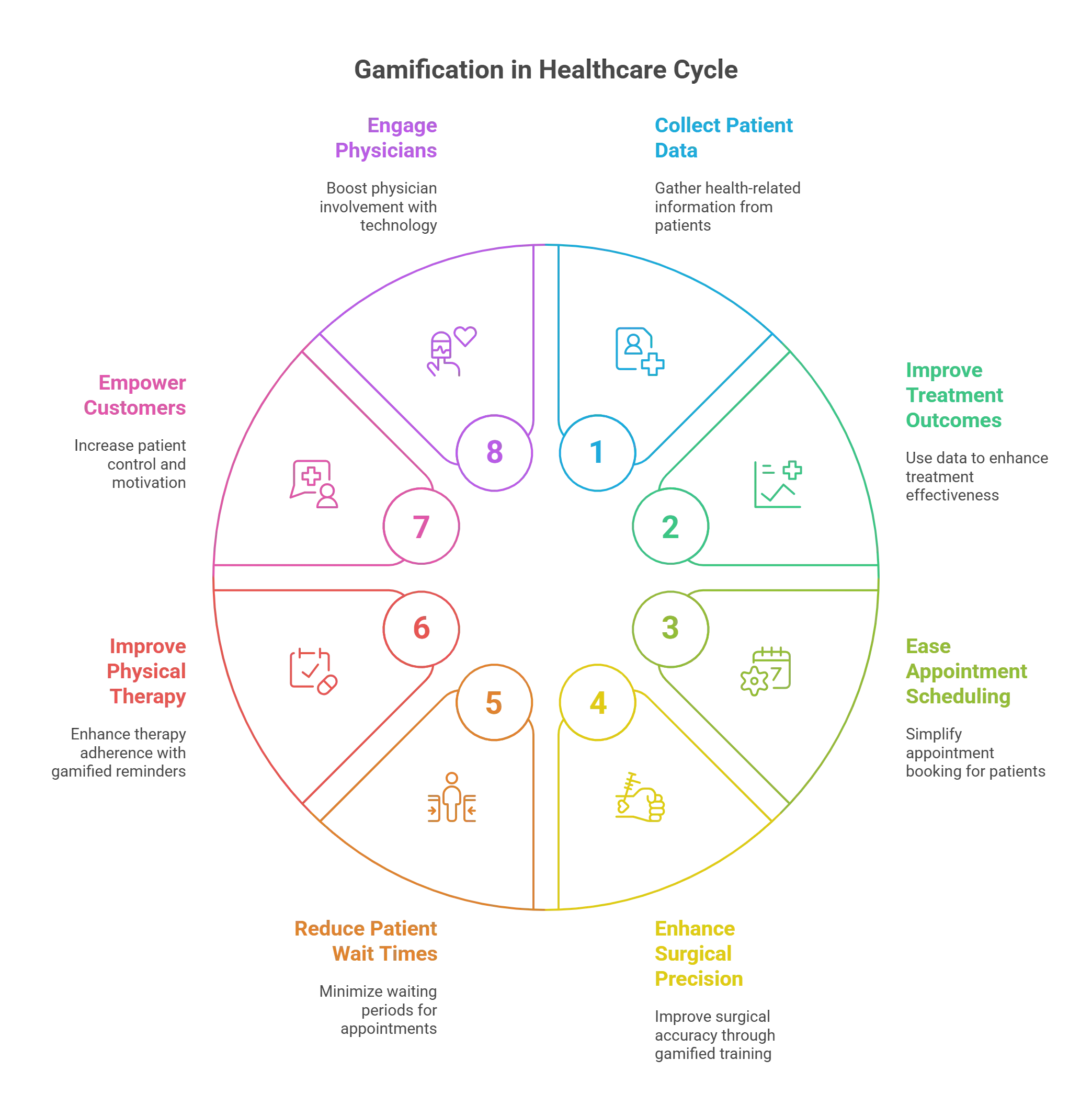
1. Better Treatment Outcomes
Gamification or gamified apps can be used for data collection (medication patients take, the food they consume, etc.) to give doctors and other medical practitioners more information to work with. This, in turn, helps in the overall effectiveness of the treatments they prescribe to their patients.
Various healthcare apps can also use gamification elements such as virtual points, rewards, or badges that patients can collect by completing specific tasks. This leads to improved healthcare outcomes and better customer retention in the long run.
2. Ease of Appointment Scheduling
One important aspect of managing patient engagement in healthcare is ensuring that patients or users have a smooth and hassle-free experience scheduling their appointments with doctors and other medical practitioners.
Gamification-based digitized health apps can be instrumental here as they use gaming techniques to help patients automatically schedule their appointments with doctors based on their specific symptoms or location.
Further, gamification strategies can also help engage patients even before they arrive at a hospital or healthcare center to lower their anxiety about possible health outcomes.
3. Enhanced Surgical Precision
Gamification in healthcare can also contribute to enhanced accuracy and improved precision in various surgical procedures.
A recent study also suggests that engaging in video games or other similar gamified elements allows healthcare professionals to better manage the movements of their surgical or laparoscopic devices.
4. Reduce Patient Wait Times
Another advantage of gamification in healthcare is reduced patient wait times. Healthcare practitioners can use various game elements to encourage good patient behavior and improve their chances of seeing them on time.
This ensures that patients who use a game (points, badges, simulation gaming, leaderboards, etc.) to make an appointment with a doctor have to wait less time than those who don’t.
5. Improved Physical Therapy
When it comes to dealing with cardiovascular diseases effectively, exercising is one of the ideal ways to combat the associated risks, especially for wheelchair patients/users.
Gamification apps such as the MedBridge Go interface are an excellent way of using game techniques in healthcare. These elements can help send patients automated reminders so they work on their exercises on time and use in-app messaging to reach their physical therapists easily.
6. Empowering Customers
Several digital tools available today in the healthcare industry use gamification techniques to encourage healthy behavior. These tools enable users to customize their treatment plans, adhere to discharge summaries, and more.
When patients feel more in control of the process, they become more motivated and are more likely to stick to their respective health goals. In addition, gamified healthcare apps with badges, points, and incentives give patients additional motivation and encouragement to follow and complete their health goals.
7. Engaging Physicians
Multiple technologies are used today in healthcare, such as patient population management tools that help plug directly into the electronic health record (EHR). These digital technologies are phenomenally changing how healthcare organizations function and track patient care management.
Adding gamification techniques and designs to these existing tools could further help significantly boost physician engagement in technology.
This, in turn, can be used to track patients more efficiently to keep them healthy and predict who is at greater risk with higher accuracy.
8. Better User Insights
The data that the patients and other users feed into the health apps can help healthcare providers and other stakeholders gain better insights into the data and consumer feedback.
This data can be instrumental in identifying specific customer needs, current healthcare trends, and other areas of improvement.
Benefits of Gamification in Healthcare
By incorporating gamification, healthcare providers can encourage patients to take an active role in their health, resulting in improved outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
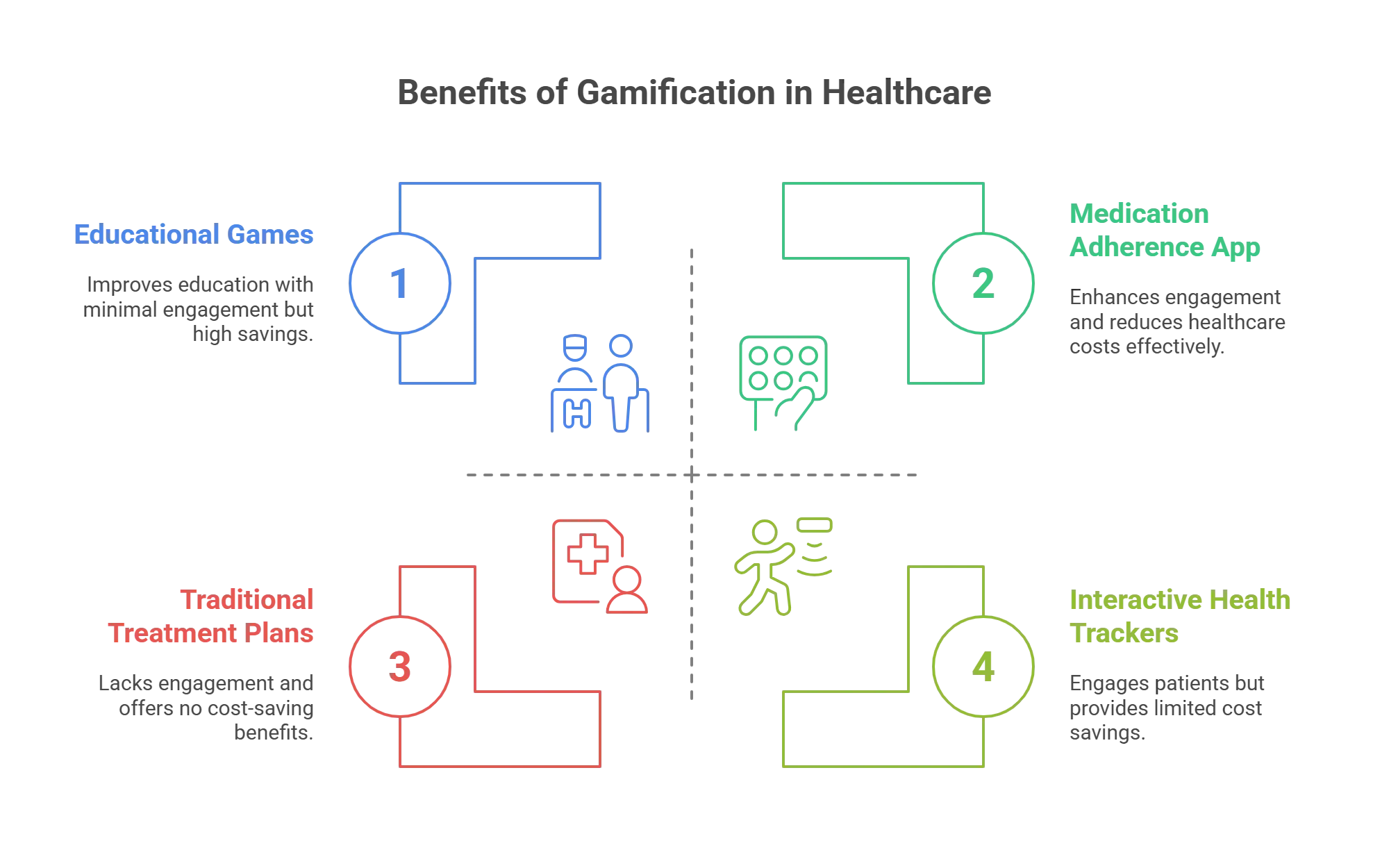
Gamification has the potential to revolutionize healthcare by making it more interactive, engaging, and effective. The following are some of the benefits of gamification in healthcare:
1. Increased Patient Engagement
Gamification can be a powerful tool for increasing patient engagement in healthcare. By adding game elements to the treatment process, patients can become more invested in their care and feel more motivated to stick to their medication plans.
Games can help patients track their progress, set goals, and receive rewards for achieving milestones. This can help create a sense of accomplishment and make the treatment process more enjoyable.
One framework that can be used to create engaging gamification experiences is Octalysis. Octalysis is a design framework that breaks down the elements of human motivation into eight key drivers: meaning, accomplishment, empowerment, ownership, social influence, unpredictability, avoidance, and scarcity.
By leveraging these drivers, healthcare providers can create a user journey that is as engaging as a live visit to a doctor.
A medication adherence app might use the octalysis framework to create a system where patients earn points for taking their medication on time.
This is one gamification in healthcare where social influence can be incorporated by allowing patients to compete with friends or join support groups for extra motivation.
By making the treatment process more fun and rewarding, patients are likely to stick to their medication plans and see better health outcomes.
2. Improved Patient Education
Gamification techniques have shown great potential for improving patient education in healthcare. By incorporating games and interactive apps, patients can become more engaged in their healthcare and better understand their health needs.
Healthcare organizations can use gamification to educate patients about healthy heart functions, nutrition, exercise, and other health-related topics through apps like CardioTeach and Decide.
Furthermore, as students pursue careers in healthcare, they can learn how to implement gamification techniques in the classroom or professional settings to educate patients or develop team members.
To effectively implement gamification, healthcare providers need to be technologically savvy, have strong teamwork and leadership skills, and be able to communicate with patients and troubleshoot issues.
Incorporating gamification in healthcare can help patients become care advocates for themselves and work collaboratively with providers to develop treatment plans.
Healthcare providers can also use gamification to educate patients about their health needs and promote healthy habits. Pursuing a degree in healthcare or a related field emphasizing technology and innovation can help students develop the necessary skills to implement gamification techniques effectively.
3. Increased Patient Adherence to Treatment
Research suggests that gamification can increase patient adherence to treatment by promoting patient motivation, self-efficacy, and enjoyment in medication management.
Gamification can also help patients develop a sense of accomplishment and provide a way to track progress toward treatment goals.
Gamification can potentially improve healthcare outcomes by reducing hospitalizations, improving disease management, and lowering healthcare costs by improving medication adherence.
However, there are still many knowledge gaps and inconsistencies in evidence regarding the effectiveness of gamification in medication adherence. Further research is needed to determine which gamification techniques are most effective and preferred by patients with chronic conditions.
In addition, incorporating patient involvement and co-design into the development of gamified medication management apps may improve patient engagement and treatment outcomes.
4. Cost Savings for Healthcare Providers
With the rising healthcare costs, providers are under pressure to provide quality care at lower prices. By using games and incentives to promote healthy behaviors and manage chronic conditions, healthcare providers can reduce the number of office visits and hospitalizations, resulting in significant cost savings.
Studies have shown that gamification can be effective in helping patients manage their conditions and avoid complications that could lead to hospital visits. For example, patients who used a game to manage their diabetes had fewer emergency room visits than those who did not use the game.
Additionally, gamification can help healthcare providers identify high-risk patients and provide targeted interventions to prevent complications and reduce costs. By using data from games and other digital tools, providers can track patient progress and provide personalized care that is more efficient and cost-effective.
Challenges and Limitations
One major challenge is the lack of consensus on what game elements are most effective in the promotion of behavior change in healthcare.
More research is needed to determine which specific game mechanics and design features are most effective for different patient populations and health conditions.
Another limitation is the potential for gamification to become a mere novelty that loses its effectiveness over time. Updating and improving the game design is pertinent to maintaining patient engagement.
Privacy concerns are another challenge associated with gamification in healthcare. Patient data must be kept secure and protected in compliance with regulatory requirements. Patients may also have concerns about their health data being collected and shared with third parties.
To address these challenges and limitations, healthcare providers and developers must prioritize patient engagement and data privacy. They should also involve patients in the development process to ensure that game design is patient-centered and aligned with patient needs and preferences.
Additionally, providers and developers should ensure that patient data is kept secure and comply with regulatory requirements such as HIPAA.
Healthcare providers and developers should also establish clear goals and metrics for gamification in healthcare so that the desired outcomes are achieved.
Finally, gamification initiatives should be integrated with other healthcare interventions, such as medication management programs and patient education, to maximize their impact on patient health outcomes.
Simulation Training for Healthcare Professionals
Simulation is a general term that involves an artificial representation of a real-world process, which enables knowledge and skill building via experiential learning. More specifically, simulation-based healthcare education is a learning tool that leverages simulation aids to recreate clinical scenarios.
According to a report published in 2010, simulation training is considered one of the most important value additions to the development of healthcare professionals.
First introduced into healthcare training in the 1960s, simulation training has significantly progressed and is expected to influence every field of healthcare in the future.
Benefits of Simulation in Healthcare
The ultimate aim of simulation training is to reduce errors and promote safety in the healthcare domain.
- This learning technique allows seasoned healthcare professionals to learn and grow their skills without repercussions on real-life patients. Hence, patient safety is prioritized.
- Freshers who have just graduated tend to be armed with theoretical knowledge. The introduction of simulation training into their curriculum enables them to build hands-on skills that help them become productive faster in the real world.
- Simulation training enables the customization of a range of learning scenarios, preparing professionals for various conditions and outcomes.
- Simulation in healthcare creates access to unlimited practice and is on-demand for professionals.
Common Types of Simulation in Healthcare
Let’s have a look at the most popular types of simulation in healthcare:
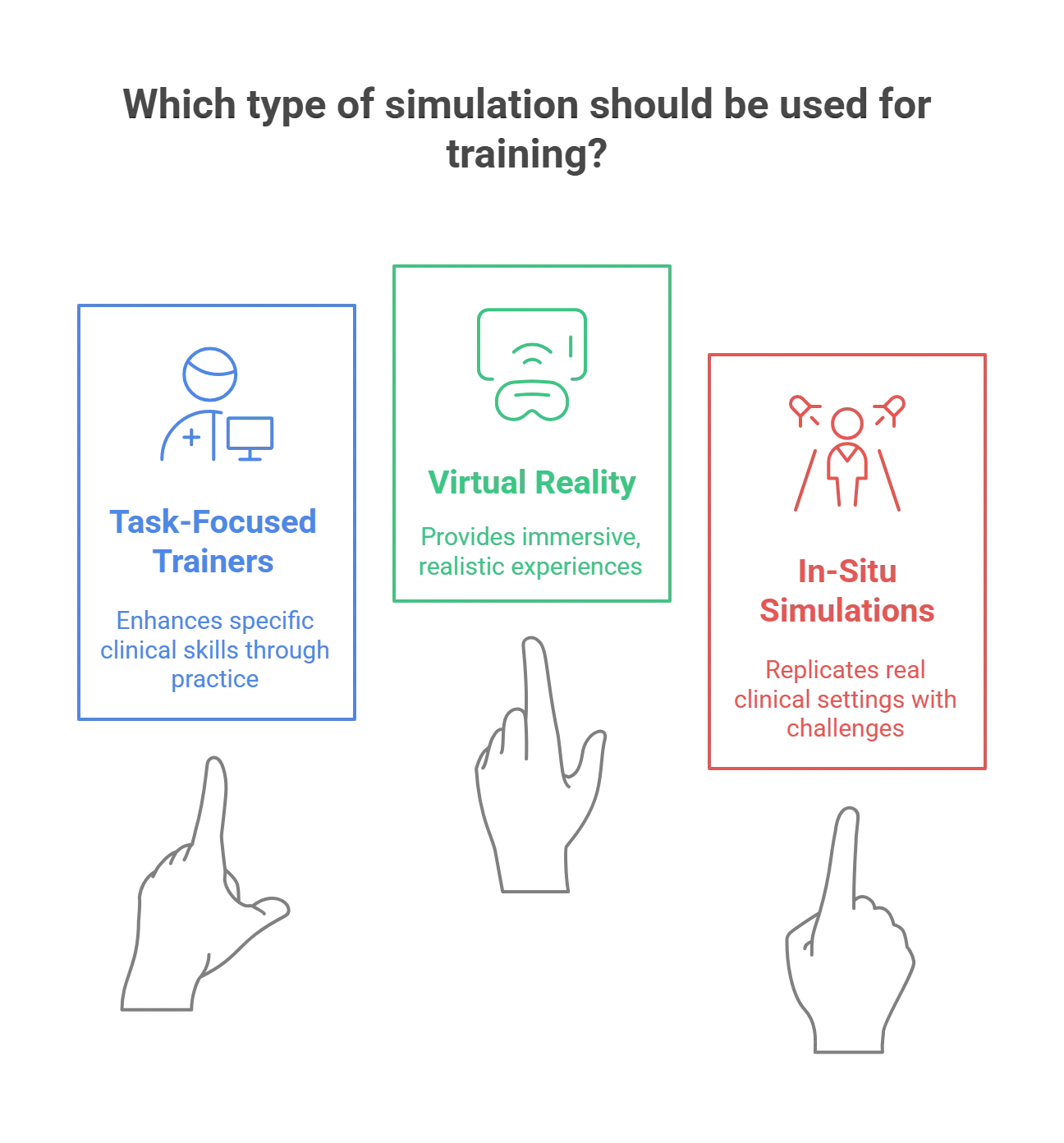
1. Task-Focused Trainers
These are customized training simulators, which enable learners to practice a specific type of task or even a partial aspect of a task.
For example, task trainers can be used to enhance basic clinical skills such as endotracheal intubation.
The more healthcare professionals practice, the more they are likely to perfect these basic skills before treating a real patient.
2. Use of Virtual Reality (VR)
To create a more immersive experience, the healthcare industry is introducing VR into simulations.
The use of VR replicates a more realistic experience in various scenarios, such as in the intensive care unit (ICU). It prepares healthcare professionals for all potential scenarios that occur in the real world.
It also enables interactions such as communication with a patient, which plays an important role in outcomes.
3. In-Situ Simulations
This type of simulation is executed in a real clinical setting, such as an operating room, with the participation of healthcare professionals.
They replicate real-life factors like limited resources, high stress, and complex medical scenarios. This helps healthcare professionals be prepared for the harsh realities of the healthcare domain.
Impact of Simulation on Healthcare Training
Simulation in healthcare is revolutionizing the teaching and learning methodology of the healthcare domain. Let’s understand the impact.
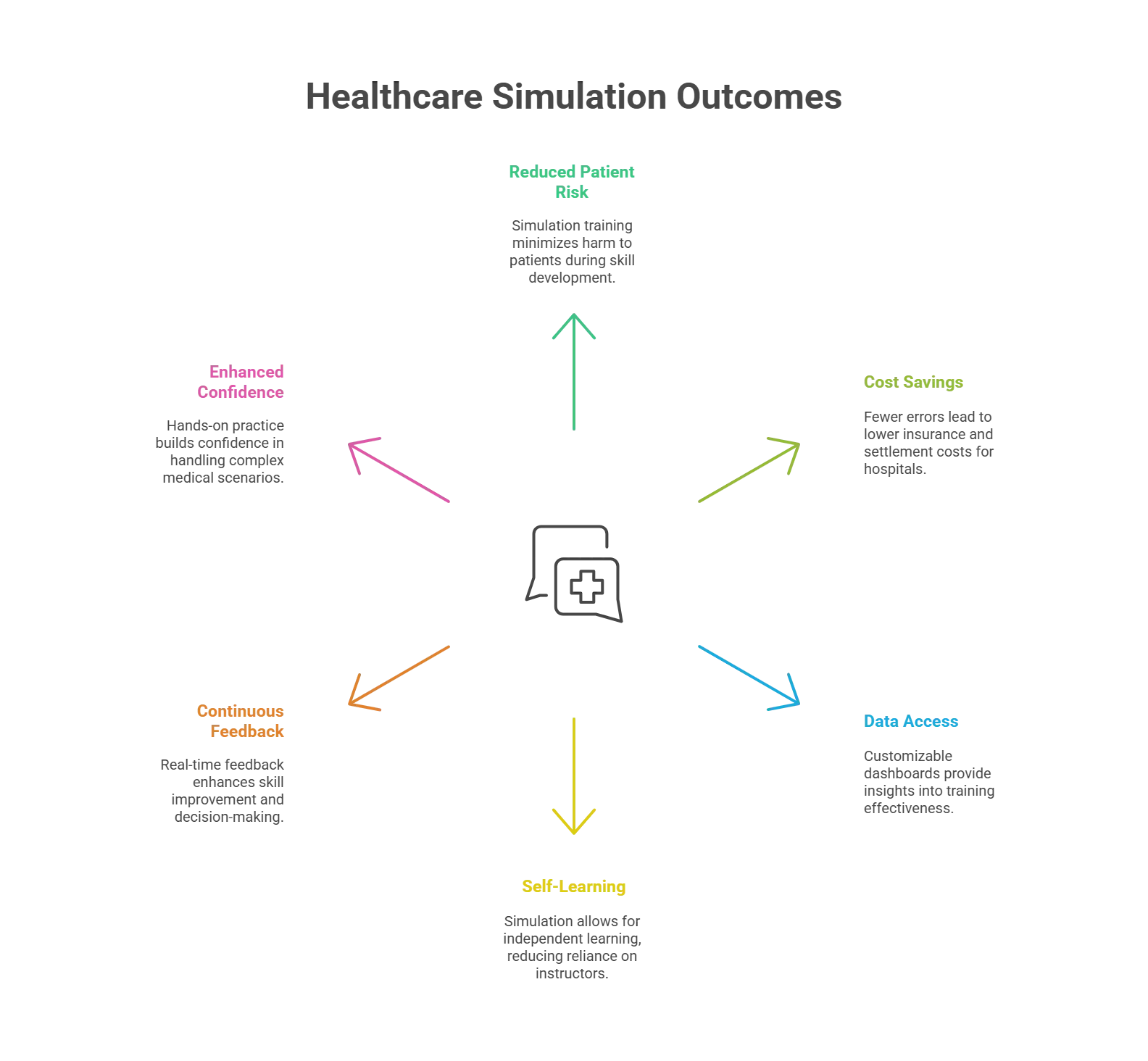
1. Reduced Patient Risk
Throughout history, healthcare practitioners have either had to practice on cadavers, which are hard to come by, or directly work with patients.
Simulation training has shifted this reality by enabling healthcare professionals to build skills, but not at the expense of patients.
Hence, increased patient safety is one of the top outcomes of this shift.
2. Reduced Payouts for Errors
Healthcare facilities such as hospitals face the risk of lawsuits, settlements, or damages costs of large ticket sizes. They invest large amounts in insurance to cover such costs.
Simulation training reduces the scope of error, which in turn helps healthcare facilities save on costs. These savings can go towards other, more pressing needs.
3. Access to Data
One of the most valuable aspects of simulation training for healthcare professionals is that it allows both learners and the training entities, such as hospitals, to access learner-related data.
Using customizable dashboards, they can detect trends, weaknesses, and strengths and determine where more training effort is needed.
4. More Self-Learning, Fewer Training Resources
Healthcare teaching has traditionally required the extensive expertise of established healthcare practitioners to teach students.
However, healthcare practices have limited time, as they are continuously engaged in patient care. The introduction of simulation in healthcare enables healthcare learners to invest in self-learning.
This reduces the burden on seasoned healthcare professionals.
5. Continuous Evaluation and Feedback
Healthcare professionals receive real-time and in-depth feedback for every simulated practice session, which is valuable for a healthcare professional’s growth journey.
6. Enhanced Confidence Levels
Hands-on training is an important aspect of training for healthcare professionals. Simulation training enables customized learning, which enables healthcare professionals to stay up to speed with the growing complexity of patient care.
They can practice on demand and continue to build new skills, which in turn, seeds confidence and an increased ability to make informed decisions, think on their feet, and stay highly productive.
To Conclude
Today’s healthcare system is going through a paradigm shift with an increased focus on patient-centered care and empowerment.
Gamification in healthcare is primarily utilized towards this goal in various health and wellness applications dealing with aspects such as self-management, medication adherence, disease prevention, and telehealth programs.
To help you navigate this better, we have shared some of the most effective ways gamification can be used in the healthcare industry for better patient outcomes and other significant benefits.
If you also wish to leverage the benefits of game-based learning in healthcare, Hurix Digital’s game-based learning solutions offer an apt solution for all your needs. Our solutions are easily customizable to your unique requirements and your specific healthcare challenges.
Get in touch with us to know more!
Summarize with:

Senior Vice President
Julia brings over 20 years of global experience in digital learning and business strategy. She specializes in client success, enterprise learning solutions, and driving growth through innovation, with a focus on AI, VR, and emerging technologies across diverse industry verticals.
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 



