Ravi Sharma
July 7, 2025
Smarter Business Decisions with the Right Analysis, Automation, and AI Alignment
Summarize with:
Table of Contents:
- What is Business Process Automation?
- Understanding AI and Data Analytics
- Business Process Automation Use Cases
- Understanding Key Business Analysis Methodologies
- Challenges in AI and Data Analytics Integration
- Top Strategies for Integration
- Top 10 Benefits of Business Process Automation
- Final Thoughts
What is Business Process Automation?
Business Process Automation refers to the use of advanced technology to automate complex processes with minimal human intervention. Simply put, it refers to shifting the responsibility of completing routine and repetitive tasks from humans to machines. Here, a business process refers to a series of actions or an activity undertaken to achieve a particular organizational objective. It can be anything from manufacturing a product to integrating fresh talent or engaging with prospective customers. By significantly reducing or eliminating manual intervention, BPA empowers you to standardize and streamline workflows, leading to amplified efficiency and cost savings. Due to this capability, BPA is often referred to as workflow automation.Understanding AI and Data Analytics
AI and data analytics form a potent combination, transforming business operations. Traditional analytics depends on human interpretation, whereas AI-powered analytics utilizes machine learning (ML) algorithms to process extensive data, identify patterns, and generate insights autonomously. Business data analytics involves examining raw data to answer questions, make predictions, and ultimately form better judgments. Combining this with AI makes the process more efficient and powerful, enabling deeper insights and more accurate predictions.Business Process Automation Use Cases
BPA finds extensive applications in various domains, including marketing and sales, human resources, finance, operations, customer service, data entry, supply chain management, and more. Generally, time-critical, high-volume, repetitive tasks that demand compliance, involve numerous stakeholders, and require audit trails are well-suited for digital process automation. The best part is that you can automate any rule-based business process, as machines excel in adhering to well-defined procedures. Some of the examples include:- Automate the onboarding process
- Invoice processing
- Document routing
- Expense reporting
- Transaction monitoring
- Automated helpdesk tools
- Automated marketing messages
- Automated shipment routing
Understanding Key Business Analysis Methodologies
Let us now take a look at some popular business analyst frameworks and methodologies that are widely used globally: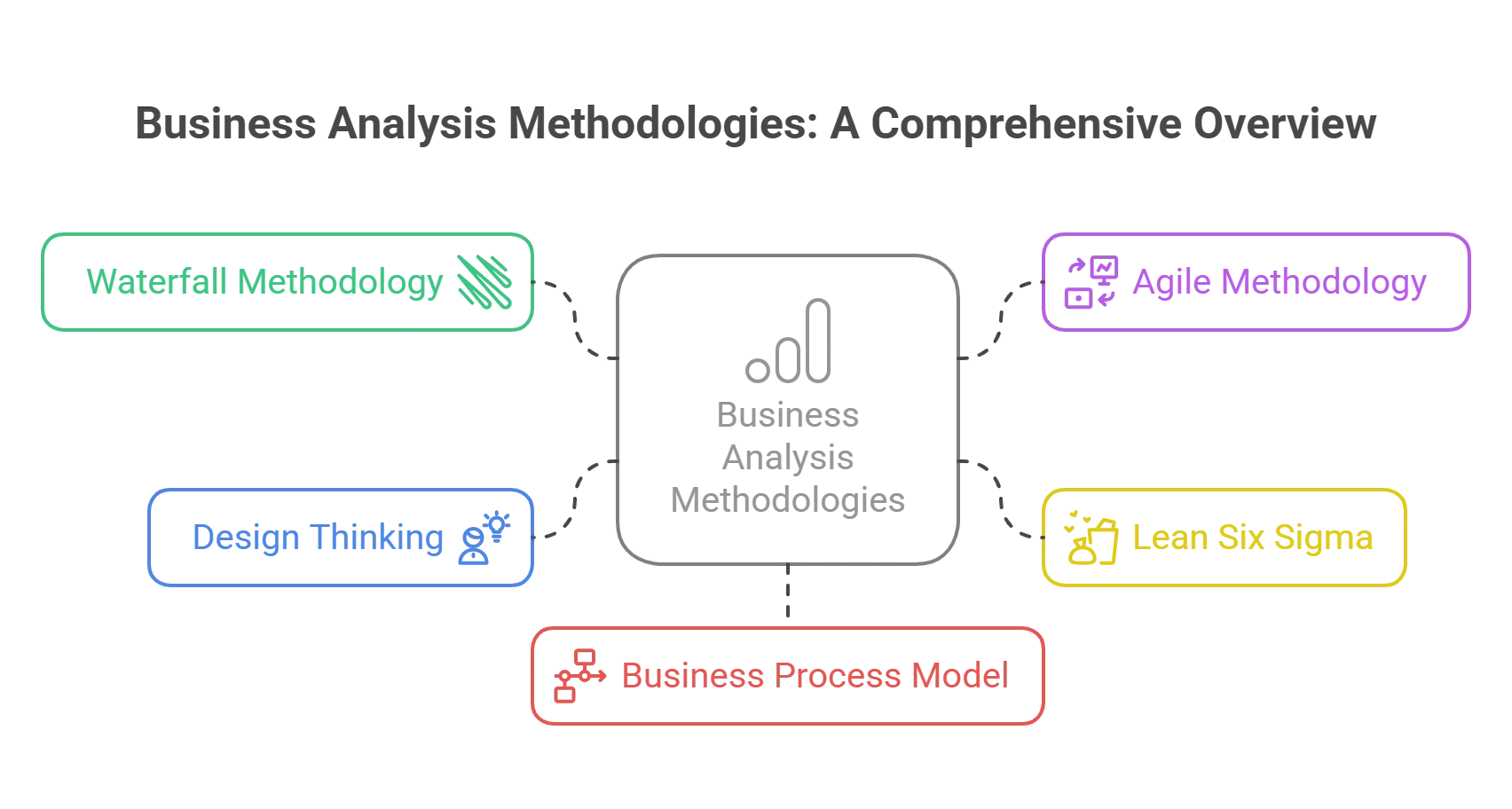
1. Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall methodology is one of the oldest and simplest approaches to software development and project management. Following this method, projects go through a series of sequential linear phases: requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Although the Waterfall methodology brings about orderliness and clarity, its rigidity becomes a hindrance, especially in changing business landscapes where requirements tend to change quickly.2. Agile Methodology
Agile is an adaptive set of software development practices that emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and customer feedback throughout the project life cycle. Instead of dividing the whole project into smaller parts, as the waterfall model does, the agile methodology divides it into small, manageable parts called sprints. Each sprint produces potentially shippable product increments. Agile methods like Scrum or Kanban favor responsiveness to change rather than adhering to a rigid plan. Thus, teams can respond quickly to evolving requirements while bringing more value to stakeholders.3. Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma combines the principles of Lean manufacturing and Six Sigma to eliminate waste, enhance quality, and simplify procedures. It focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities that drive variation and streamlining workflow. Business analysts use Lean Six Sigma tools such as value stream mapping, root cause analysis, process optimization, etc, to determine requirements and steer continuous improvement programs in organizations.4. Design Thinking
Design thinking is a user-centric innovation approach that prioritizes empathy, experimentation, and creativity. It involves understanding user needs, generating ideas, prototyping solutions, and testing them with real users to refine the product or service iteratively. By empathizing with users and involving them in the design process, organizations can develop products and services that truly meet their needs. Business analysts exploit design thinking methods to unearth hidden customer needs and prove assumptions while co-creating answers with key stakeholders.5. Business Process Model
Business process models are used to visualize an organization’s processes, understand how they work, identify inefficiencies, and suggest improvements. They often use techniques such as flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and business plan models and scripts (BPMN) to model business processes. Business analysts use process modeling to document current-state processes, analyze challenges, and develop future-state processes that align with organizational goals and objectives. This streamlines the organization’s operations, reduces costs, and increases customer satisfaction.Challenges in AI and Data Analytics Integration
While the benefits of integrating AI and data analytics are substantial, several challenges must be addressed: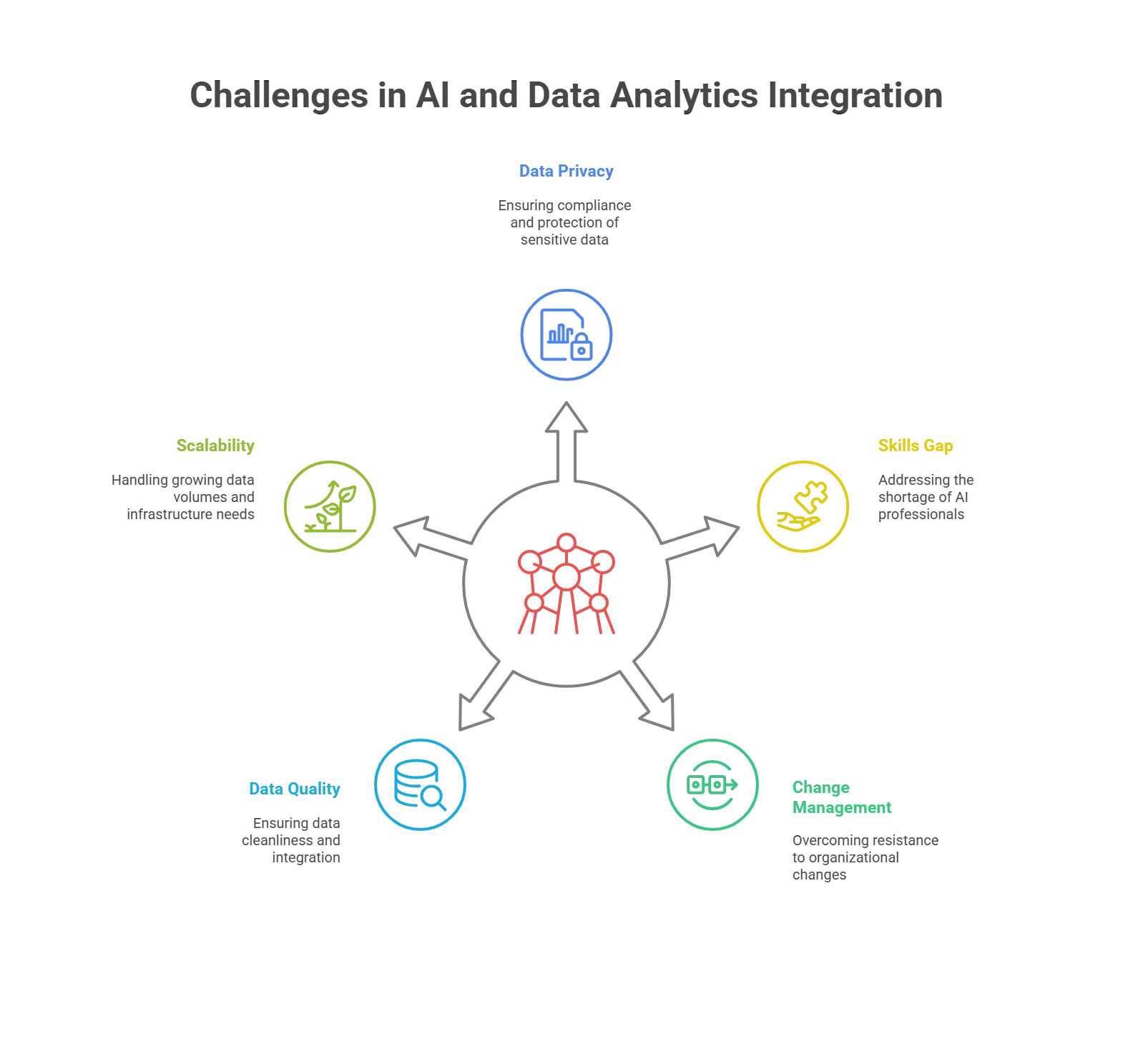
1. Data Privacy and Security
When adopted, AI and data analytics solutions can create data privacy and security issues. Adhering to data protection regulations and protecting sensitive data requires strong measures, which can also be intricate and time-consuming.2. Skills Gap
The shortage of AI and data analytics professionals is a significant hurdle. It is hard and costly to attract and retain individuals possessing knowledge in predictive modeling and machine learning, which might affect the pace of AI projects.3. Change Management
AI and analytics implementation usually means that many changes should be made to the existing organizational framework. Change management, resistance to change, and managing employees’ fears of losing their jobs to automation require keen planning and implementation.4. Data Quality and Integration
AI and data analytics efficiency are highly dependent on data quality and availability. Most organizations face the problem of data isolation and the variability of formats within the organization. Applying data modernization to ensure data cleanliness and integration involves various lengthy processes.5. Scalability and ROI
As AI and analytics needs grow, scaling infrastructure to handle increasing data volumes can be challenging. Additionally, justifying the significant investments required for these initiatives, especially when benefits are not immediately tangible, can be difficult.Top Strategies for Integration
To successfully integrate AI and data analytics into your business, consider these key strategies: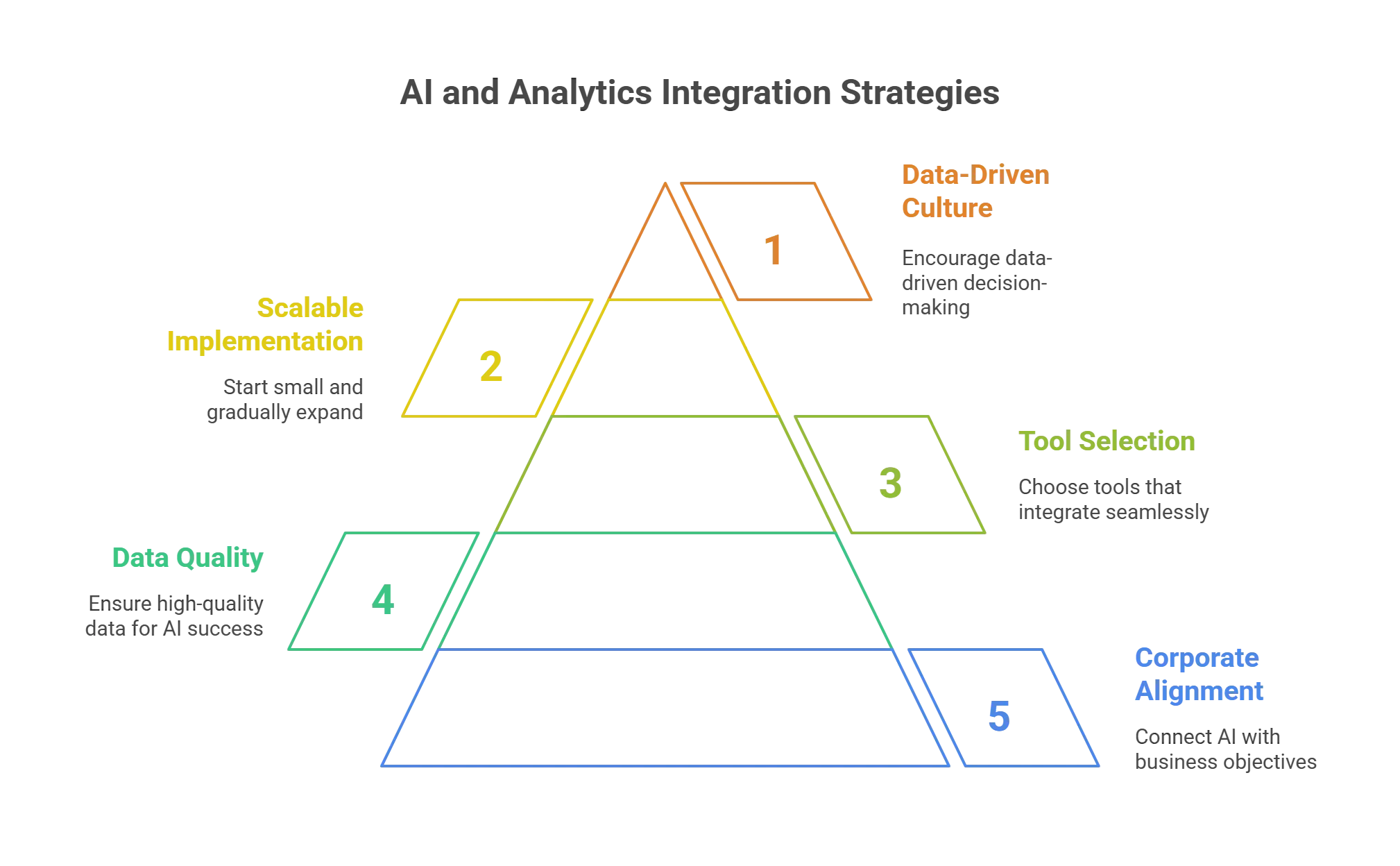
Tip 1: Comply with Corporate Objectives
Make sure your company’s goals are closely connected to your AI and analytics activities. This alignment aids in concentrating efforts and proving value to stakeholders. First, determine your main business problems and how analytics and AI can help you solve them.Tip 2: Invest in Quality Data
The quality of input data is very essential for the success of AI and analytics. Therefore, you should apply proper data management procedures to enhance your data sets’ quality, integrity, and utility. It may be useful to implement data modernization measures to increase the quality and usability of data.Tip 3: Choose the Right Tools
Select AI and analytics tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. Consider factors like ease of use, scalability, and specific analytics needs. Tools like Microsoft’s Power BI or cloud-based solutions can provide powerful analytics capabilities.Tip 4: Start Small and Scale
Begin with small-scale projects to test and refine your approach. This strategy allows for controlled experimentation and helps build a foundation for larger implementations. Gradually expand your AI and analytics initiatives as you gain experience and demonstrate success.Tip 5: Foster a Data-Driven Culture
Encourage data-driven decision-making across all levels of your organization. Offer resources to educate workers on how to implement AI and analytics within the scope of their jobs. This cultural shift is important for getting the most out of your AI and analytics solutions.Top 10 Benefits of Business Process Automation
If you wish to grow your roster of delighted customers, prioritizing process excellence becomes important. BPA is a simple yet powerful strategy for starting on that path. From increased compliance and productivity to better performance and customer experience, BPA benefits spread to every facet of the organization.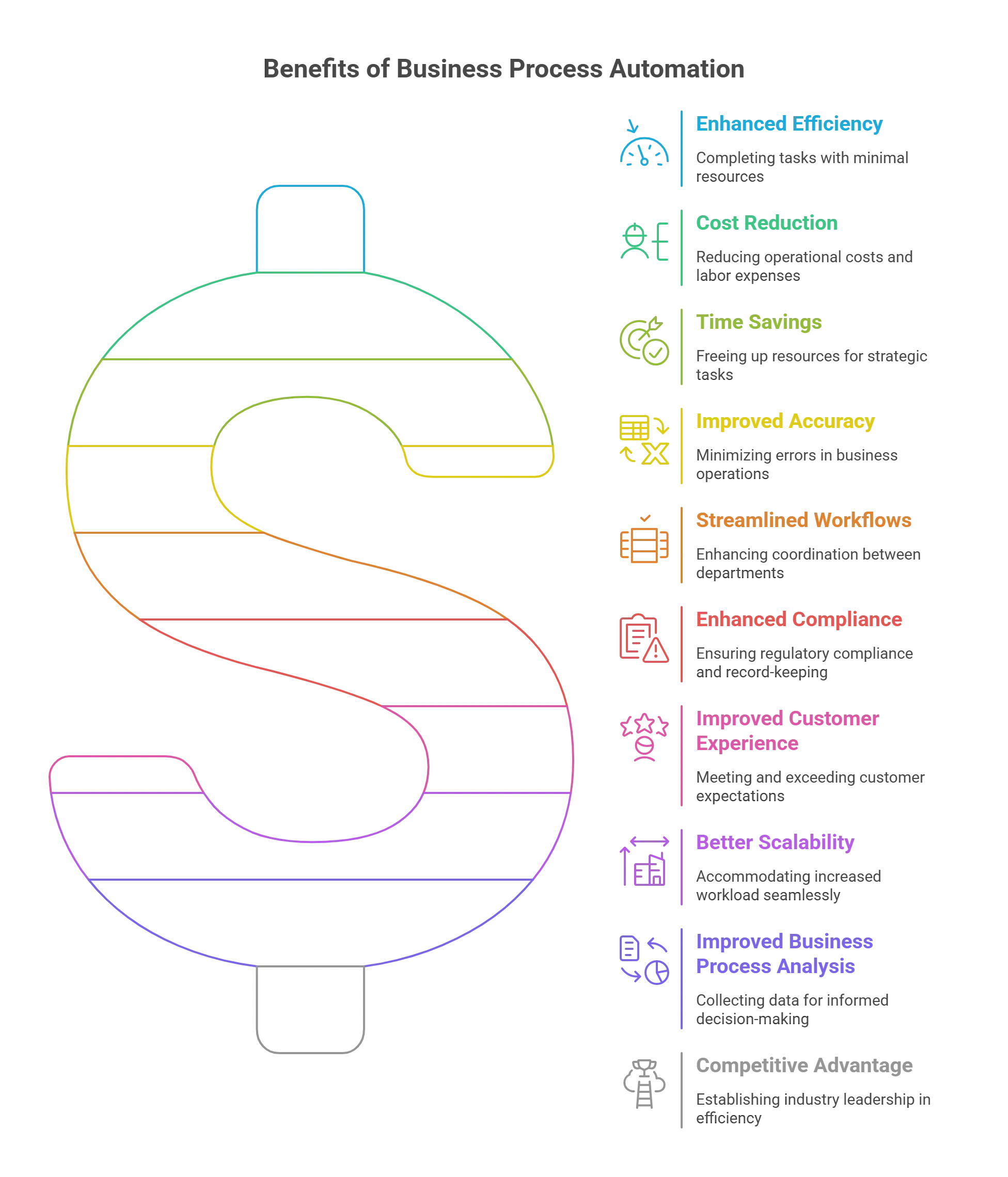 Here are ten compelling reasons for investing in BPA:
Here are ten compelling reasons for investing in BPA:
1. Enhanced Efficiency
With BPA, you can complete arduous tasks with minimal resources. It delivers quicker and more reliable results at reduced costs, leading to improved overall efficiency. Furthermore, delegating mundane tasks to machines results in higher productivity and increased profits. By leveraging technologies to aid in certain tasks, employees can amplify their productivity within the same timeframe and spend more time on activities that add value to their customers.2. Cost Reduction
BPA helps reduce operational costs by reducing the need for extensive human resources. It also minimizes the occurrence of errors that might lead to financial setbacks. Approximately 31% of business executives report decreased labor expenses as a result of process automation. Companies enjoy cost reductions because of the reduced labor demands. By efficiently using time, you can either boost production without scaling your workforce or trim payroll expenses while sustaining current output levels.3. Time Savings
Automating time-consuming tasks frees up resources, enabling employees to work smarter, not harder. About 74% of engineering and IT leaders believe process automation saves almost 30% of the time. By charging machines with performing rule-based, recurrent tasks, your staff can focus on more strategic and creative endeavors that drive business growth.4. Improved Accuracy
Even highly skilled and capable employees can make mistakes due to absent-mindedness, lack of attention, or multitasking. But unlike humans, machines never get distracted or tired. BPA minimizes the risk of errors that can have detrimental effects on your business outcomes. It ensures a higher level of accuracy and consistency in business operations.5. Streamlined Workflows
BPA streamlines complex workflows, enabling smoother coordination between various departments. This leads to enhanced collaboration and communication within the organization. Transparent accountability, tailored notifications, insightful analytics, and faster turnaround periods facilitate the elimination of wasteful activities. This enables employees to focus on improving tasks that add significant value.6. Enhanced Compliance
BPA helps in ensuring regulatory compliance by implementing standardized processes. This minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties and legal repercussions. Furthermore, BPA maintains a meticulous record of each aspect of a business process. These comprehensive details can be showcased during audits to demonstrate compliance.7. Improved Customer Experience
Customer satisfaction is a key differentiator in any industry. Focusing on operational and process excellence helps you effortlessly surpass customer expectations. By expediting response times and streamlining customer-facing processes, BPA contributes to an improved customer experience. When you consistently meet promised standards, you increase customer satisfaction and loyalty. Consequently, customers are more likely to develop a preference for your business.8. Better Scalability
Manual procedures lack scalability and can readily impede business expansion. For instance, manually invoicing a hundred clients demands significantly more resources than invoicing just ten, thereby placing a strain on companies. BPA, on the other hand, enables businesses to scale operations seamlessly. Machines can simultaneously execute multiple tasks at a considerably faster rate than humans. They help you accommodate increased workload and evolving business demands without compromising efficiency or quality.9. Improved Business Process Analysis
With BPA, you can collect and analyze valuable data for business impact analysis. It also enables you to monitor the progression of a business process. This makes it easier to refine processes for superior and swifter business results. Furthermore, it helps you make informed decisions and implement strategies for continuous improvement.10. Competitive Advantage
BPA helps organizations establish themselves as industry leaders in operational excellence. Leveraging BPA provides a competitive edge by enabling you to deliver products and services more efficiently.Final Thoughts
Performance evaluation systems and processes provide valuable guidelines and tools for collecting and evaluating requirements. Integrating AI and data analytics into your business processes is necessary for staying competitive. By following these strategies and addressing potential challenges, you can harness the power of AI and data analytics to drive innovation, improve decision-making, and achieve your business goals. At Hurix Digital, we provide a wide range of solutions tailored to meet your specific needs. With our expertise, you can streamline your requirements gathering and analysis processes and ensure that your projects are delivered successfully, on time, and within budget. Connect with us now!Summarize with:

Vice President & SBU Head –
Delivery at Hurix Technology, based in Mumbai. With extensive experience leading delivery and technology teams, he excels at scaling operations, optimizing workflows, and ensuring top-tier service quality. Ravi drives cross-functional collaboration to deliver robust digital learning solutions and client satisfaction
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful