Why is 508 Compliance Necessary for Accessible EdTech Content?
Summarize with:
Educational Technology (EdTech) has progressed considerably in recent history and accessibility is now mandatory to make education available for everyone. A significant 15% of the world’s population lives with disabilities, and making education readable and perceivable for this demographic is essential.
Did you know that 21 percent of undergraduate students reported having a disability in 2019-20? This large portion of students emphasizes the critical importance for all higher education eLearning platforms to fully comply with WCAG 508. With such accessibility, students with physical and cognitive disabilities would have similar educational opportunities.
Understanding accessibility compliance for edTech can save your company a lot of time as it can save you from civil lawsuits. Let us learn what 508 compliance rules are, how you can create a 508-compliant website, and how such a website can impact the teaching of your edTech content.
Table of Contents:
- Understanding WCAG 508 Compliance
- Key Components of WCAG 508 Compliance
- Best Practices for WCAG Compliance in Higher Education
- What are the EdTech Content Accessibility Standards?
- Why is Accessibility in Educational Technology Important?
- Top Ways an Accessible 508 Compliant Website Impacts EdTech Content
- Tools and Resources for Enhancing Accessibility
- Case Studies: Success Stories in Education
- Final Words
Understanding WCAG 508 Compliance
WCAG 508 compliance is a conformance that meets the accessibility guidelines covered under Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act for Web Content.
It stipulates that all the electronic and information technology used by federal agencies be available to people living with disabilities. This compliance in higher education is critical as it gives all students access to digital content and enables them to relate well.
Today’s accessibility standards were first generated in 1998 through the original Section 508, which was intended to make federal technology accessible. The committee later conformed it to the more encompassing WCAG developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) to ensure a global standard.
WCAG 2.0, released in 2008, and its updates, like WCAG 2.1 in 2018, developed this framework further to include more disabilities, such as cognitive, auditory, and visual impairments.
Key Components of WCAG 508 Compliance
WCAG 508 compliance remains anchored on four core principles of making digital content accessible to any user, including the disabled. If one is considering building an inclusive eLearning platform in higher education, take into account these most important principles:
- Perceivable: Information and user interface components must be presented in ways all users can perceive. This includes providing text alternatives for non-text content and incorporating audio descriptions in videos.
- Operable: Interface components and navigation must be operable by everyone. This includes enabling all the functionalities with a keyboard and ensuring that users get sufficient time to read and use content.
- Readable and Understandable: Interface information should be legible and understandable. Information provided through text should be easy to read, and web pages should be predictable in appearance and interaction.
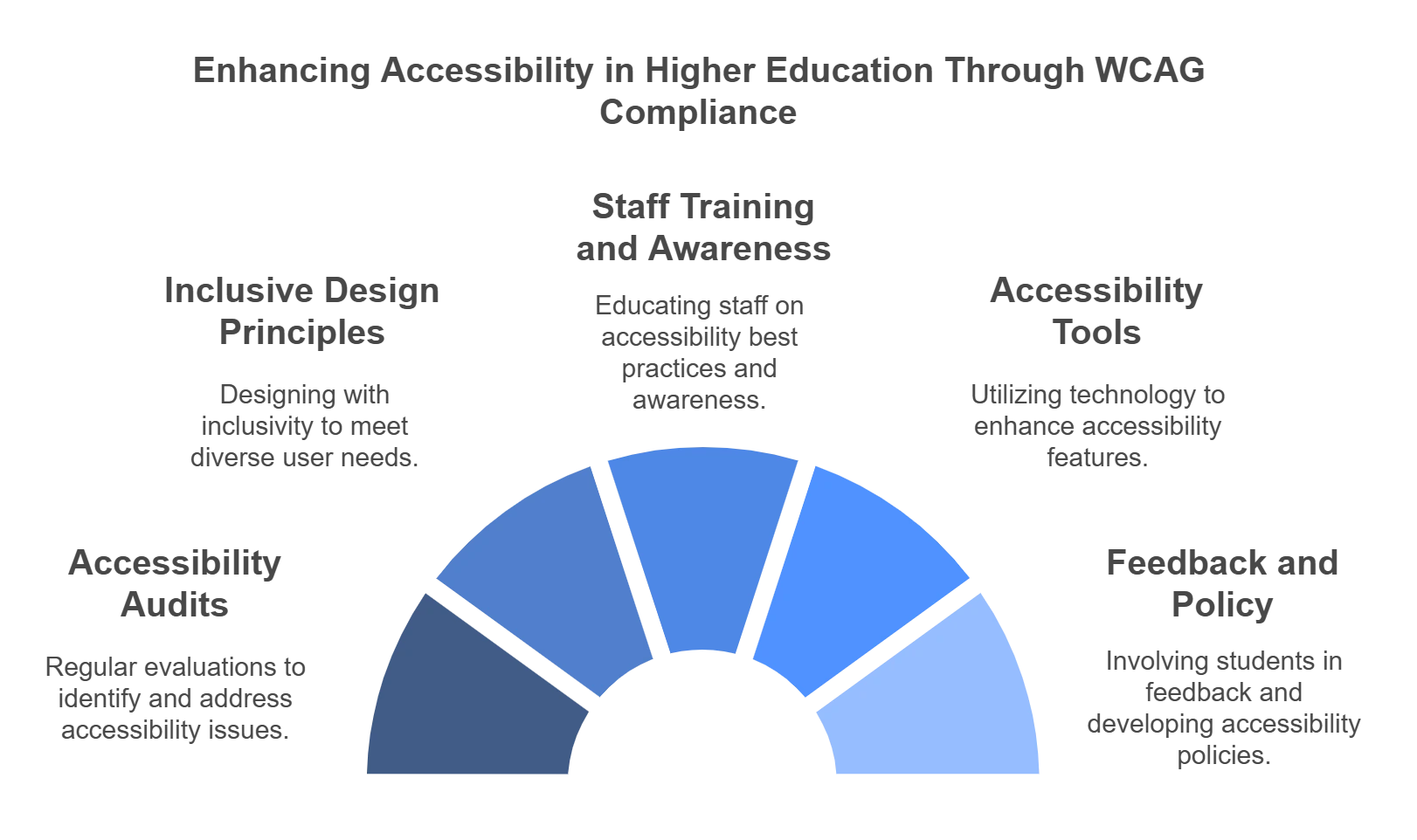
Best Practices for WCAG Compliance in Higher Education
Adhering to WCAG 508 compliance in higher education is essential to meeting legal standards and fostering an inclusive learning environment. Implementing these best practices ensures that students, particularly those with disabilities, have equal access to educational resources.
1. Accessibility Audits
- Regular Review: Institutions must conduct periodic reviews of their eLearning platforms to identify and rectify compliance gaps.
- Engage Experts: Involve accessibility experts to provide deeper insights into the effectiveness of present practices and what could be improved.
2. Principles of Inclusive Design
- Universal Design: Implement universal design principles in developing courses so that learning materials are accessible to all students.
- Responsive Design: eLearning content needs to be designed to be usable on all devices and through different assistive technologies to enhance flexibility for students with diverse needs.
3. Training and Awareness of Staff
- Regular Training Sessions: Educate faculty and IT support staff about WCAG, focusing on why it is important and how it applies to daily work.
- Awareness Promotion: Help people realize the challenges that students with disabilities face in their pursuit of education and the role of accessibility in dealing with such challenges.
4. Use of Accessibility Tools and Technologies
- Use Technology: Use the latest tools and technologies to create and test accessible digital content. These include screen readers, text-to-speech software, and accessibility-checking browser plugins like WAVE or AXE.
- Latest Updates: Keep technology and software updated continually to maintain consistency with new accessibility standards and practices.
5. Student Feedback and Participation
- Interact with Students with Disabilities: Frequently take input from students with disabilities on their experience and implement improvements to accessibility based on that feedback.
- Inclusive Decision Making: Include students with disabilities in eLearning’s content development and platform development.
6. Documentation and Policy Development
- Clear Policies: Develop clear and documented policies on accessibility that are harmonious with the WCAG 508 standards.
- Accessibility Statement: Post an accessibility statement on the eLearning platform that conveys your commitment to accessibility and the resources available to students.
Engaging in these best practices meets legal mandates and also improves the educational experience for everyone involved. Institutions that improve accessibility may experience higher levels of student satisfaction and retention and improved academic outcomes.
Institutions that adhere to WCAG standards enhance their reputation as inclusive communities, attract a broader student base, and may secure improved funding opportunities.
What are the EdTech Content Accessibility Standards?
Section 508 compliance guidelines were established by the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Congress amended these compliance guidelines again in 1998 and added Section 508 standards for all federal agencies and companies to create electronic and information technology (EIT) accessible to all individuals, irrespective of disabilities.
During this update, they included digital content to cater to the needs of disabled people. The act was revised in 2017 again and the law now requires all information and communication technology (ICT) to be accessible to disabled people.
This last update included telecommunication equipment for enhanced accessibility at every digital step. Such laws indicate how crucial it is to form an accessible 508-compliant website for your EdTech content so you can make education available to all.
Why is Accessibility in Educational Technology Important?
Educational institutions must adhere to 508 compliance guidelines to avoid civil lawsuits. Complying with these guidelines is crucial to making space for every individual in education.
Technology has become a significant game changer in education, with 51% of students feeling they can concentrate better. Thus, making space for disabled people in digital learning spaces becomes more important than ever. Creating clear and concise websites makes navigation easy, and this can increase the number of people benefitting from the website.
With enhanced ease, new and existing students can go through study materials on a 508-compliant website much more quickly to perform better academically. EdTech can benefit educators by giving them a platform that students are enthusiastic about, which can increase their effectiveness as educators.
Let us see how accessibility compliance for EdTech can significantly impact teachers and students alike.
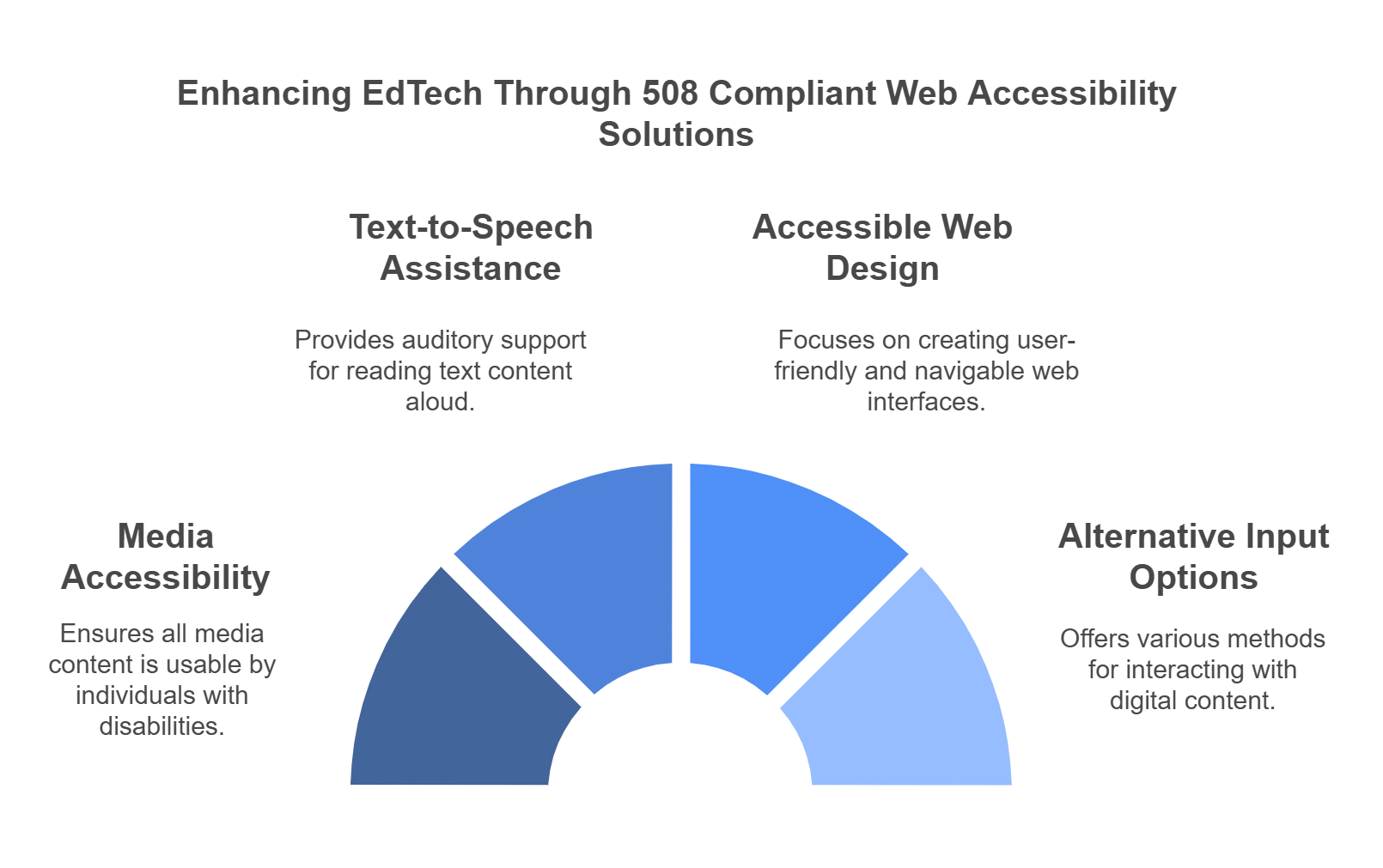
Top Ways an Accessible 508 Compliant Website Impacts EdTech Content
The global educational technology market stood at $142.37 billion in 2023, which is expected to grow exponentially over the coming years. So, it only makes sense to integrate accessibility into this evolving digital educational landscape.
Here are four ways 508 compliance benefits educators and learners with accessible EdTech content:
1. Media Accessibility
Using visuals is a great way to enhance the learning process because around 65% of the population are visual learners. Using videos, images, and animations can make your EdTech content more engaging for students, and it can become more informative with accessibility enhancement.
Use alt texts for every visual, as well as captions and headings so readers can see them. Try to use a clear and large font for captions for videos and images so readers can read them and understand the visuals. Large and clear fonts for captions are great for people with hearing impairments who cannot use text-to-speech or screen readers for 508-compliant websites.
If you want to make educational videos accessible, write descriptive captions that give readers an idea about what the video is. This way, visually impaired individuals can benefit from the descriptions they hear with screen readers.
2. Text-to-Speech Assistance
28% of students have an absolute visual impairment, while 72% are partially sighted. Thus, inclusive EdTech content becomes essential, and text-to-speech assistance is the right solution. As the name suggests, this tool converts text to speech for students with visual impairments.
The tool has several options to increase or decrease voice speed and lower or increase volume. Text-to-speech tools now make documents, business websites, and other written text accessible for people with any visual impairment. For enhanced readability, try to create documents in PDF or Word format that are easily detectable by screen readers.
For a better performing 508 compliant website, consider adding alt texts to images so the reader also describes images to every reader.
3. Accessible Web Design
Creating inclusive online EdTech content begins with creating an accessible web design. Consider breaking text into several paragraphs and using headings and bullet points. Integrating such practices makes the text easy to scan and can help students with ADD, ADHD, and dyslexia.
Choose your font carefully. Choose a clear and large font that readers find easy to scan. Choose a dark font color so it is easy for readers with visual impairments to read and understand what is written.
Include adequate white spacing between lines and keep the entire page or document clean so people do not fumble too much while reading it. Use meaningful headings so readers know what you are about to write next, and add captions with every visual.
4. Alternative Input Options
Using Universal Design is one of the best EdTech accessibility solutions for enhanced readership. Approximately 39 million adults in the U.S. have motor impairments, and such individuals can find it difficult to use traditional input devices like the mouse.
Make your EdTech content accessible by making it navigable with the help of keyboards and trackpads. Integrate assistive technology like voice command, which allows readers to use voice to navigate to certain portions of the page or to different pages.
The practices mentioned above can make your EdTech content accessible to everyone, making it easy for learners across the globe to read and learn from it.
Tools and Resources for Enhancing Accessibility
Implementing the right tools and technologies can really make a difference for educational institutions committed to WCAG 508 compliance. These resources help develop accessible eLearning content, ensuring all students can benefit from digital learning platforms regardless of their abilities.
1. Key Tools for Accessibility
- Screen Readers: These include JAWS, NVDA, and VoiceOver. For students with visual impairment, they convert text into speech, enabling them to hear the content being presented to them.
- Accessibility-Checking Tools: WebAIM’s WAVE and Lighthouse by Google can quickly provide feedback on WCAG compliance and thus pinpoint probable issues on a webpage.
- Online Transcription and Captioning Services: Companies such as Rev and Amara provide captioning services for multimedia content. This is crucial for ensuring that students with hearing impairments have access to video captions.
2. Effective Integration Tips
Make the best use of those tools with these strategic integration tips:
- Embed Early in Design: Embedding accessible features into the design of eLearning materials from the start prevents the need for costly and often ineffective retrofitting later on.
- Ongoing Training: All content creators and IT staff should be updated on how to use these tools effectively and trained in the latest accessibility standards.
- Regular Testing: Test regularly with real people, including those with various disabilities, to ensure the tools facilitate accessibility.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Education
Several higher education institutions have set benchmarks in implementing WCAG 508 compliance, creating more inclusive and accessible learning environments. These case studies highlight the successful integration of accessibility standards and their tangible benefits.
1. University of Michigan
The University of Michigan undertook a campus-wide audit to identify accessibility gaps and implemented a phased strategy for WCAG compliance. Post-implementation, the university saw an increase in engagement from students with disabilities. The inclusive design also improved the overall user experience for all students, demonstrating the universal benefit of accessible design.
2. California State University
The California State University integrated a comprehensive training program for faculty and IT staff focused on creating accessible course materials and utilizing accessibility tools. The initiative increased course completion rates among students with disabilities. Faculty feedback highlighted an enhanced understanding of accessibility issues, leading to better instructional strategies across the board.
Final Words
Creating a 508-compliant website is not complicated if you understand the rules your eLearning platform needs to follow. Opening up edTech for everyone benefits both educators and learners because everyone adapts quickly to such easy websites.
Understanding where your website is lacking and integrating accessible practices in those gaps can help create a website that is perceivable by all. Want to invest in a powerful website with the best edTech accessibility solutions? Hurix Digital‘s expert editorial team provides clear and concise content.
With our high-technology accessibility solutions, you can take your educational journey to new levels of reach with an easy-to-use website that everyone can use effortlessly. To get the most out of accessibility, call us today!
Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful