
Gokulnath B
July 8, 2025
Understanding the European Accessibility Act 2025 and What It Means for Your Digital Presence
Summarize with:
Table of Contents:
- Understanding the European Accessibility Act (EAA)
- What is the Web Accessibility Directive? (WAD)
- What are Web Content Accessibility Guidelines? (WCAG)
- The European Accessibility Act 2025 and WCAG: The Common Grounds and Differences
- What is the Scope and Impact of the EAA?
- The Importance of Accessibility Training
- Reasons for Accessibility Compliance in Europe
- Steps Your Organization Can Take to Observe EAA
- Best Practices to Maintain Compliance with EAA
- 3 Compelling Reasons to Act Now in Keeping with The European Accessibility Act
- In Conclusion
Understanding the European Accessibility Act (EAA)
The European Accessibility Act is a transformative directive that draws inspiration from the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities. Adopted in April 2019, the EAA was designed to harmonize accessibility rules across the European Union member states. By adhering to European Union Laws, the EAA complements the EU’s Web Accessibility Directive, creating a more inclusive society for all citizens. The EAA sets forth accessibility requirements for a wide range of key products and services that are fundamental to people’s daily lives. The act covers areas such as websites, e-commerce platforms, computers, operating systems, smartphones, TV equipment, telephony services, banking services, and eBooks. By establishing accessibility standards for these products and services, the EAA aims to break down barriers and enhance access for individuals with disabilities and the elderly.What is the Web Accessibility Directive? (WAD)
Just like the European Accessibility Act, the Web Accessibility Directive is another digital inclusion law passed by the European Union. This directive was passed on 22 December 2022 with the sole purpose of making websites and mobile applications accessible to people with disabilities. However, the directive is only limited to public sector entities like transportation, public administration, education, healthcare, etc. Under the web accessibility act, web platforms must follow three major directives. First and foremost, all platforms must issue an accessibility statement stating all accessible and non-accessible content. Alternatives should follow the non-accessible content. Secondly, all websites must have a feedback mechanism in place that users can use to raise requests and complaints about non-accessible content. Lastly, the state members must regularly monitor all these public web pages and apps and report the results to the commission every three years.What are Web Content Accessibility Guidelines? (WCAG)
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are technical web accessibility standards developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The first set of guidelines, WCAG 1.0, was introduced on 5 May 1999. They have been revised multiple times since then to ensure comprehensiveness in the accessibility guidelines. WCAG 2.0 was published on 11 December 2008, followed by WCAG 2.1 on 5 June 2018. The WCAG 2.2 guidelines were finalized in August 2023 and will be released soon. The Web Accessibility Directive (WAD) and the digital aspects of the European Accessibility Act (EAA) have to follow the WCAG 2.1 guidelines to ensure standardized accessible digital content globally. Other countries and their digital inclusion laws are also expected to follow the WCAG guidelines for the responsible implementation of accessibility mechanisms.The European Accessibility Act 2025 and WCAG: The Common Grounds and Differences
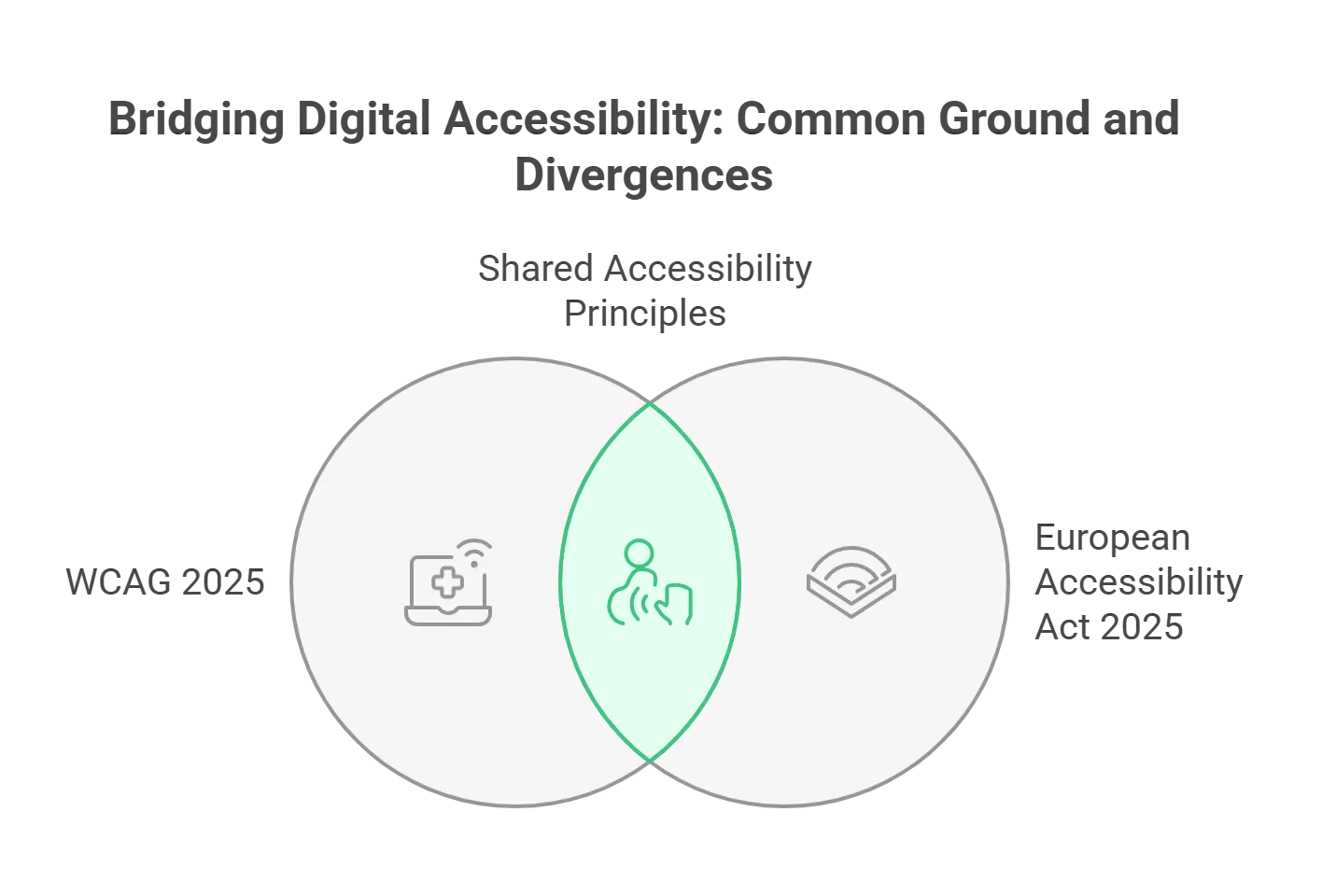
1. The Common Grounds
Both WCAG 2025 and the European Accessibility Act 2025 are accessibility frameworks that aim to make digital products and services inclusive. The European Union requires all member states to abide by WCAG 2.1 recommendations for EAA accessibility. They are both formed on the same four principles that say that the products and services must be:- Perceivable
- Operable
- Understandable
- Robust
2. The Differences
The EU Accessibility Act 2025 is a law, and WCAG is a recommendation. This means that EAA can be enforced, and WCAG can only be suggested. The EU Accessibility Act 2025 is formed by the government and is applicable only to the European Union, whereas WCAG is an international standard created by a group of individuals and organizations. WCAG 2025 focuses mainly on accessibility for websites, whereas EAA extends to all digital products. WCAG does not contain specific directives and rules; EAA does. If you want to learn more, you can read the complete text of WCAG 2.2 here and the EAA here.What is the Scope and Impact of the EAA?
The scope of the European Accessibility Act is comprehensive, addressing both digital and physical aspects of accessibility. Let’s explore the key areas covered by the EAA:- Digital Accessibility: Websites and digital platforms are crucial channels for communication, information dissemination, and e-commerce. Ensuring that these platforms are accessible to everyone is a fundamental aspect of the EAA. The act emphasizes adherence to the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which provides guidelines for creating accessible websites and digital content.
- Assistive Technologies: The EAA recognizes the importance of assistive technologies in facilitating accessibility. It calls for the compatibility of digital devices and software with various assistive tools, such as screen readers, magnifiers, and voice recognition software.
- Electronic Communication: Telephony services, including smartphones and telecommunication devices, play a central role in modern communication. The EAA aims to ensure that these services are accessible to all individuals, including those with disabilities.
- Audiovisual Media Accessibility: The act also addresses audiovisual media, ensuring that TV equipment and services offer features like closed captions and audio descriptions for individuals with hearing and visual impairments.
- Accessible Banking Services: Financial inclusion is a key aspect of the EAA. It emphasizes the need for accessible banking services, allowing individuals with disabilities to manage their finances independently.
The Importance of Accessibility Training
First and foremost, including accessibility in L&D programs is just the right thing to do. Every individual can learn, grow, develop, and contribute their ideas and perspectives.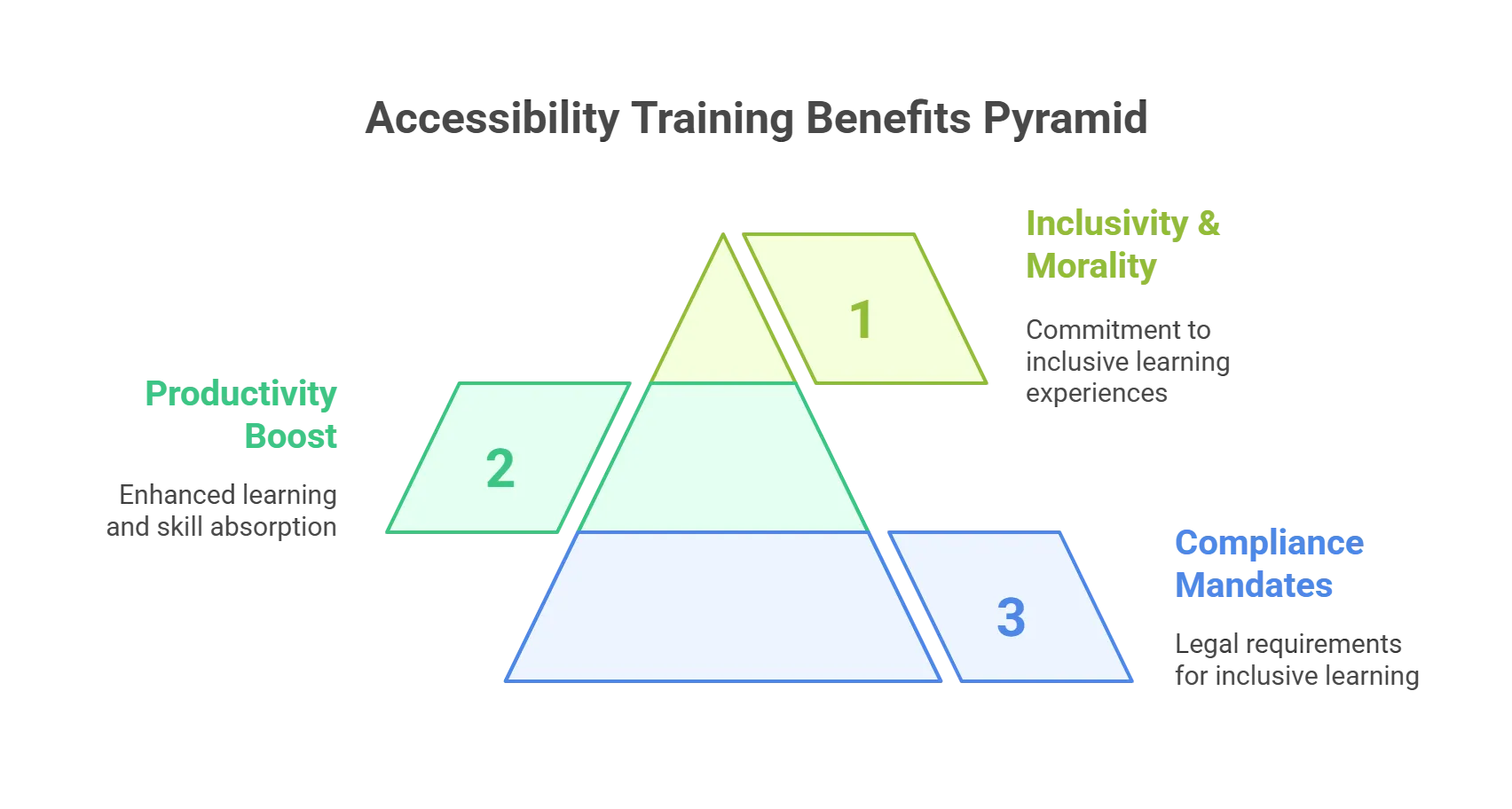 However, even when you look beyond the moral landscape, there are several benefits to making digital content as accessible as possible, from boosting productivity to regulatory mandates.
However, even when you look beyond the moral landscape, there are several benefits to making digital content as accessible as possible, from boosting productivity to regulatory mandates.
1. The Rise of Accessibility Compliance Mandates
Avoiding penalties and lawsuits is the best motivator for keeping L&D resources more accessible. Moreover, legislation such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the EAA mandates organizations make learning inclusive for all individuals. For companies looking to avoid lawsuits and fines, the W3C WAI Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) mandate that all training resources should be built on these four key design principles:- Perceivable
- Operable
- Understandable
- Robust
2. Boosts Productivity & Training Outcomes
Amidst all the legal and moral barriers to accessibility training, it’s easy to miss the basic principle behind it. Accessibility training ensures that all individuals complete their L&D programs and engage with, absorb, and learn new skills. A McKinsey study indicates that the demand for online learning is rising, and good training design and delivery significantly impact individuals’ performance and productivity.3. Inclusivity Keeps Morality at the Heart of Digital Training
Adhering to accessibility guidelines isn’t just about keeping the lawmakers happy – it’s about showcasing that you genuinely care about individuals’ learning experiences. It’s a linear and thoughtful commitment to inclusivity that speaks to your organization’s brand voice, and all employees will appreciate your effort in this matter. After all, accessibility training doesn’t just benefit people with disabilities – it also helps people with temporary impairments like:- Situational conditions like bright or noisy environments
- Broken Bones
- Age-related barriers
- Challenges due to low internet bandwidth
Reasons for Accessibility Compliance in Europe
Organizations must prioritize accessibility when developing their digital solutions. This should be a fundamental consideration to ensure that the needs of all users are met.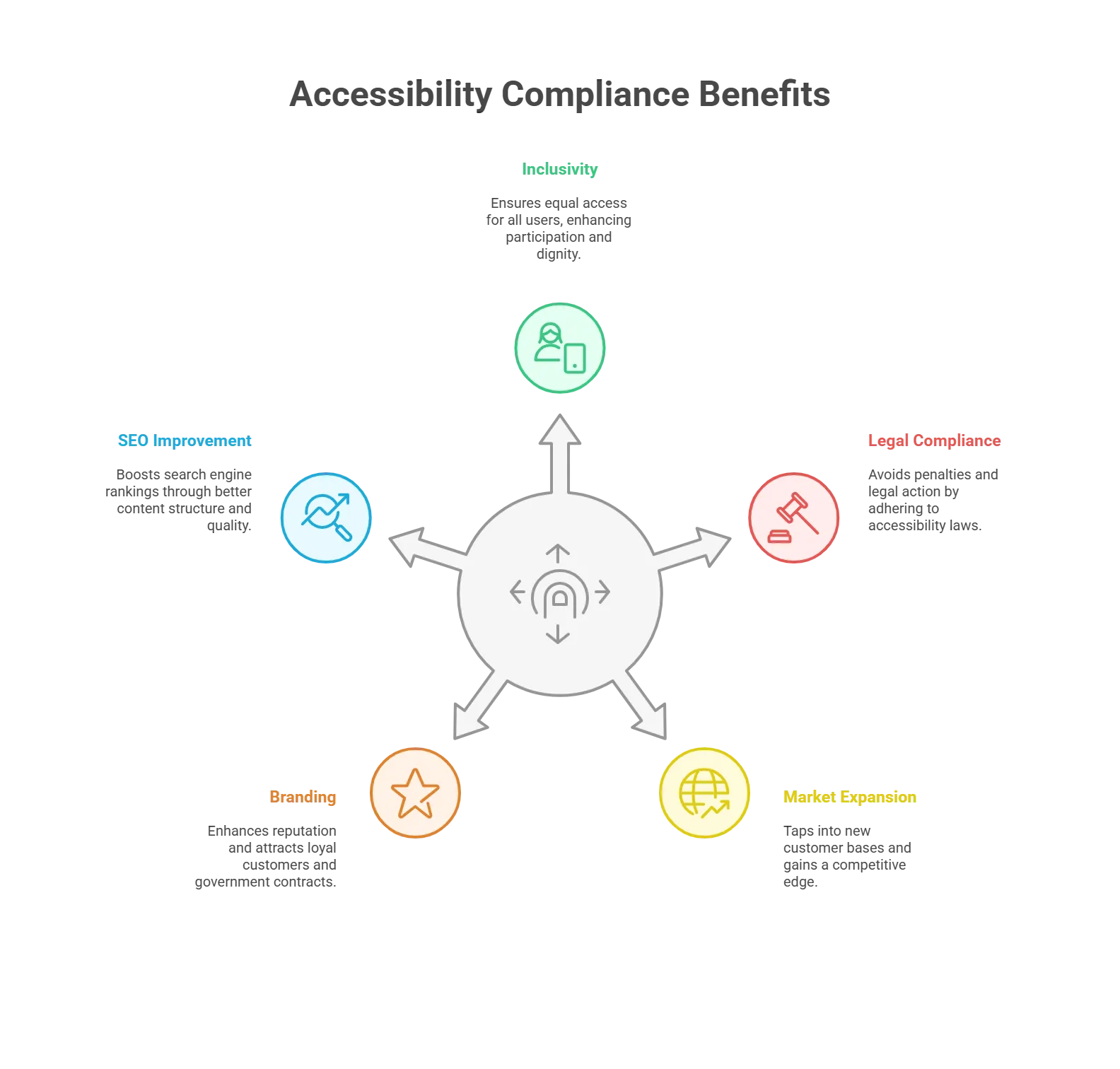 Let’ see why accessibility compliance is necessary in Europe:
Let’ see why accessibility compliance is necessary in Europe:
1. Inclusivity and Equal Access
Inclusivity and equal access are the primary reasons digital platforms and applications strive to comply with accessibility guidelines. Often, individuals with disabilities like visual or cognitive impairments find it difficult to access critical information and other relevant resources. This is a major hassle in their everyday lives and hampers their employment and learning. Consequently, website accessibility ensures that all individuals, with or without disabilities, can equally participate in all kinds of online activities and leverage their full potential. Ensured participation goes a long way in providing every individual with a dignified and independent living environment. Additionally, website accessibility guidelines are also helpful for people in their old age or those facing circumstantial injury-induced disability.2. Legal Requirements
Websites and digital platforms that do not adhere to accessibility guidelines will be subject to heavy penalties and strict legal action. The European Accessibility Act 2025 has presented an important deadline for all countries in the European Union that have yet to implement the guidelines. By 28 June 2025, they must ensure that all administrative digital provisions adhere to strict and robust inclusivity guidelines. Platforms that miss this deadline will face severe legal consequences. Customers and users can also file complaints against them with the national court and other relevant authorities.3. Market Expansion
Once websites have incorporated accessibility guidelines, they will automatically be able to expand their reach and market by tapping into a previously unexplored customer base. These positive steps towards inclusivity will also provide the platform with a competitive edge. With the advancement in digital technology, the marketplace has become increasingly crowded and competitive. By offering accessible products and services, customers will begin to prioritize the platform, thus demonstrating their loyal commitment. This gradual market expansion can eventually increase a company’s global reach. With a well-established customer base, it becomes easy for organizations to enter the international market and diversify.4. Branding and Reputation
Another important benefit of adhering to accessibility standards is a positive reputation and inclusive branding. By enabling all customers to have a great user experience, positive publicity will automatically follow via social media platforms, word-of-mouth, online testimonials, and more. A positive brand image and reputation go a long way in attracting loyal customers. Apart from customers, a positive reputation regarding accessibility and inclusiveness will also attract government contracts and tenders. Governments are constantly looking for businesses that promise equal rights and opportunities to all citizens of the country. To leverage these stakeholder relationships, conduct a digital accessibility audit to ensure your services are up to the accessibility mark.5. Boosting SEO
Implementing accessibility standards automatically improves content structure and quality. Factors like clear and easy-to-understand content, proper use of headings & sub-headings, keyword usage, etc., lead to positive search engine optimization. There are numerous other overlapping features between website accessibility and search engine optimization. Mentioned here are some examples:- Faster loading time
- User-friendly design interface and layout
- Mobile-friendly design
- Alternative text for audio and videos
- Broader audience reach
- Compliance with technical standards like HTML AND CSS3
Steps Your Organization Can Take to Observe EAA
To conform to EAA, organizations must adopt these step-by-step approaches toward making their platforms more accessible to persons with disabilities:- Accessibility Audit: Perform an overall accessibility review of your website and try to identify the need to remove all access barriers.
- Alternate Text of Images: Ensure alternative texts for images so that visually impaired users who are reliant on readers can have accessible content based on their descriptions for images.
- Keyboard Availability: Ensure that your website is usable by keyboard navigation for disabled people who may not have the ability to use a mouse.
- Easy Navigation for People with Cognitive Disabilities: Ensure that your web app is user-friendly and easy to navigate for people with cognitive disabilities.
- Compatibility with Assistive Technologies: Your website must support assistive technologies like screen readers and magnifiers.
- Accessibility at Every Stage of Development: Involve accessibility considerations at every level of your website’s design and development process
- Update Regularly: Don’t forget that a website has to be updated regularly. The older a website is, the fewer chances it will have at its next web accessibility audit.
Best Practices to Maintain Compliance with EAA
Here are some key strategies that organizations must follow to comply with EAA: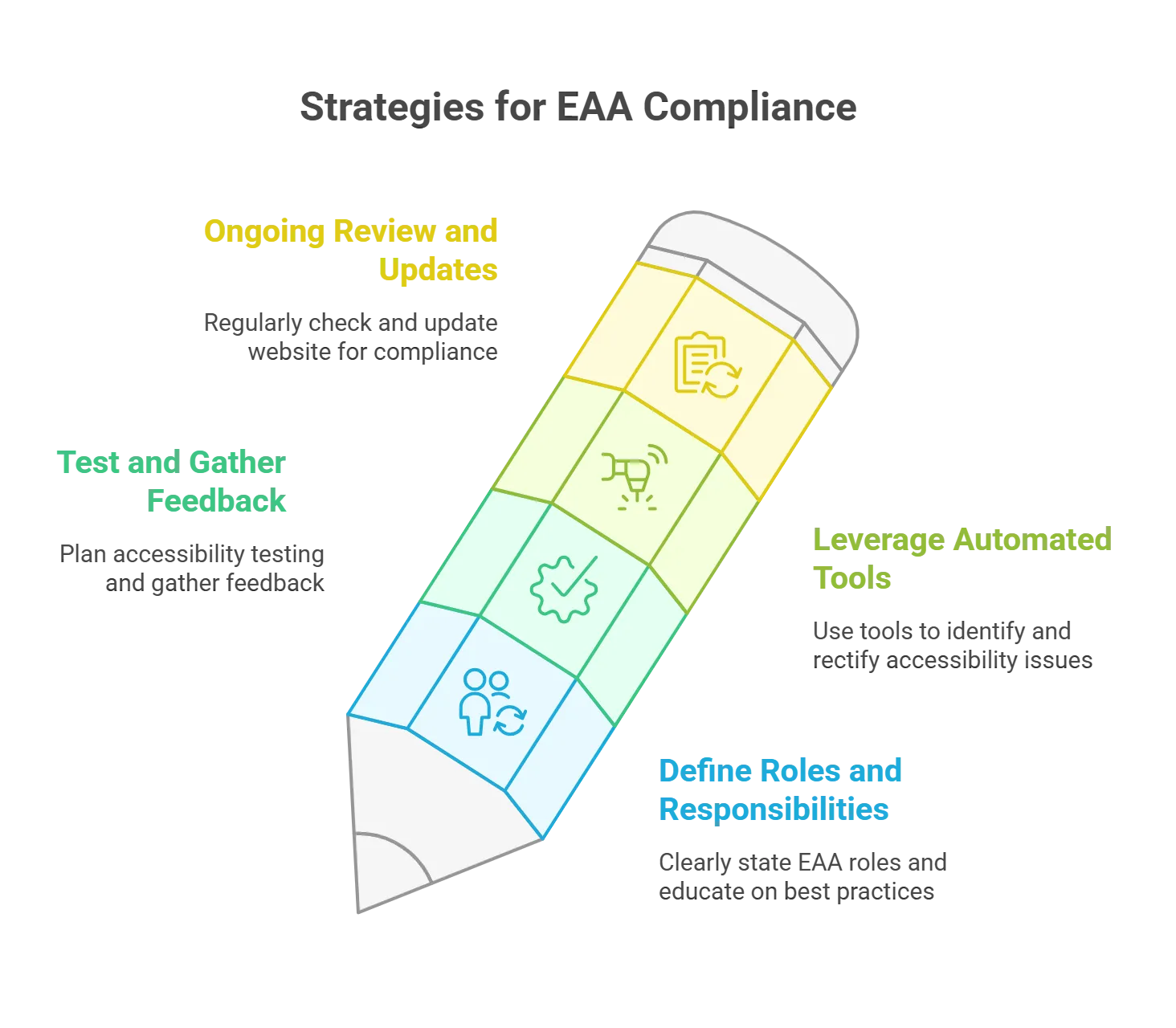
1. Clearly Define Roles and Responsibilities
State the EAA to everyone, from design and development to content authors. Educate on best practices and tools. It will help you achieve consistent adherence to the EAA standards throughout your organization.2. Test Frequently and Gather Feedback
Plan accessibility testing at various points during development and gather feedback during the process. Allocate an accessibility lead to handle compliance questions, provide direction on accessibility needs, and help the project stay on track with issues.3. Leverage Automated Tools for Accessibility
There are automating tools that can facilitate your activities of identifying and rectifying accessibility issues on your digital platforms, giving you more opportunities to address them promptly and track them permanently. A clear accessibility policy should explain the steps you are taking to comply with relevant standards and be circulated to employees, customers, and other stakeholders.4. Ongoing Review and Updates
To maintain compliance with accessibility standards, one must regularly check and update their website concerning ever-changing accessibility standards. This means responding to the problems that emerge immediately, but also ensuring your platform is current with all the latest best practices and guidelines.3 Compelling Reasons to Act Now in Keeping with The European Accessibility Act
The European Union implements the European Accessibility Act, which obliges a wide range of products and services, including digital platforms that feature e-commerce and banking, to become accessible.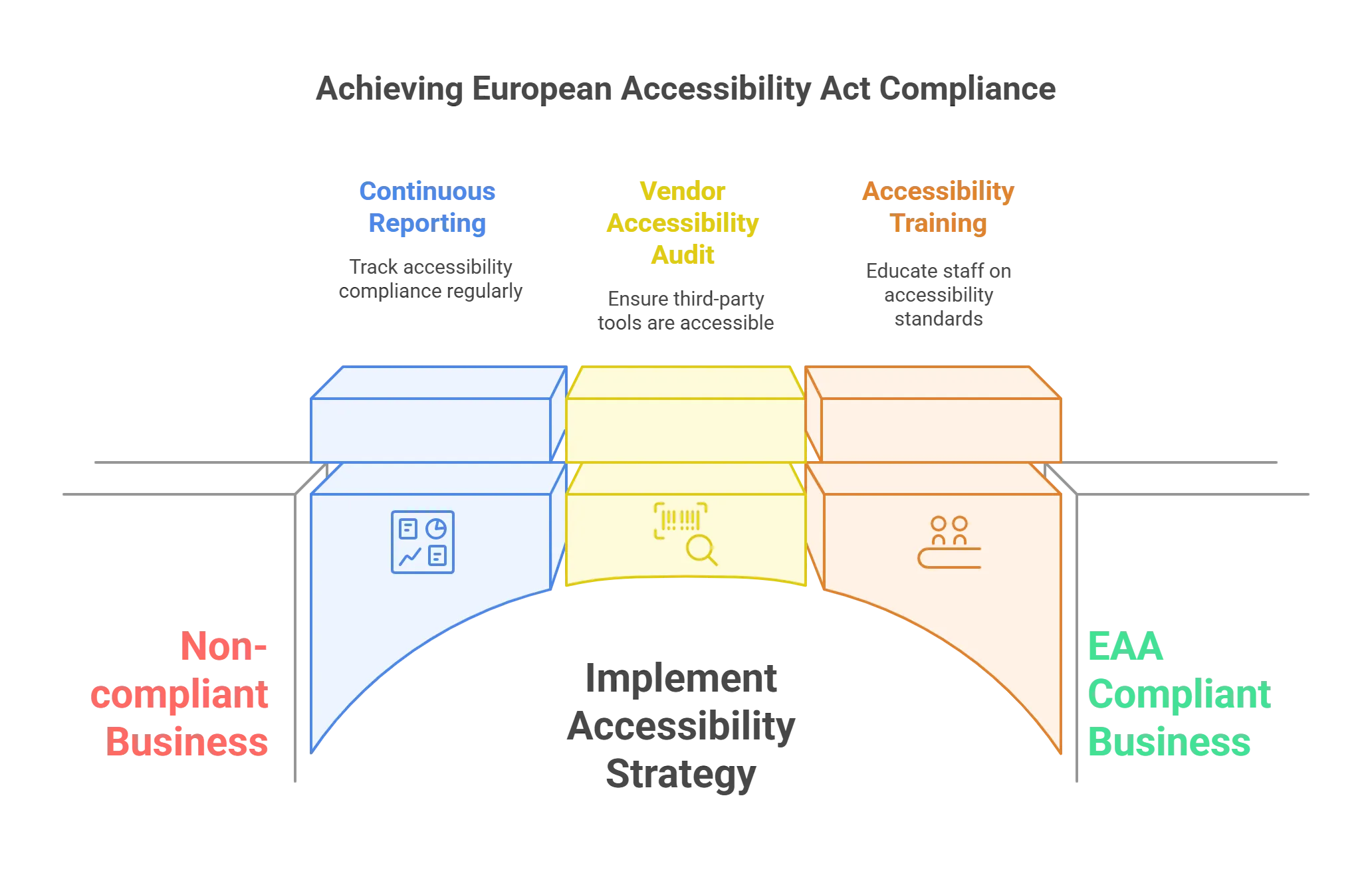 If your business sells its products and services to consumers within the EU, regardless of your location, you need to adhere to the EAA. Here are three key reasons why you need to start preparing now:
If your business sells its products and services to consumers within the EU, regardless of your location, you need to adhere to the EAA. Here are three key reasons why you need to start preparing now:
1. Why Compliance Extends Beyond Correcting Accessibility Issues
Organizations are wrong in the assumption that accessibility compliance is an event rather than a process. In other words, it involves technical audits, fixing issues, and purchasing compliance with standards such as EN 301 549, which means maintaining compliance with WCAG 2.1 A and AA as well as with WCAG 2.2. Compliance with the EAA also involves sustainable processes such as continuous reporting, regular monitoring, and ongoing accessibility training. Early starts give you time to create a long-term accessibility strategy that will ensure compliance over time and help minimize the risks of introducing new barriers through updates later on.2. Participation from Third-Party Vendors
The EAA applies to your digital products and third-party tools and services integrated into your platform. For example, if your site uses a chatbot or payment gateway from a third-party provider, then their products should also be accessible. Assuring this with your vendors early will save you from a delay and avoid non-adherence. Accessibility should be a non-negotiable requirement in the procurement of new products.3. Severe Punishment for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with the EU Accessibility Act on enforcement dates can lead your organization to severe financial and legal risks. The European Union nations will track and enforce compliance, and in some cases, they may suspend business operations as a possible fine. In some countries, such as Ireland, organizations that are not compliant can even face jail time. Non-accessibility also comes with a heavy opportunity cost. Based on the statistics, one in every four adults in the European Union suffers from disability, making this an essential market that businesses that are not compliant risk missing out on. For that reason, there is a need to begin preparations now so as not to face risks and ensure that the business continues as usual.In Conclusion
As technology and digital tools continue to develop rapidly, it becomes important to foster digital inclusivity via accessible platforms. By embracing inclusivity guidelines, each user can unlock a world of opportunities. Consequently, all countries are implementing inclusive digital strategies to ensure an equitable and resourceful society. Now that you have found your answer to why digital accessibility is important and want to implement accessibility guidelines for your digital platform, we have got you covered. Visit us at Hurix Digital and benefit from our vast list of disability laws and accessibility services. We also offer other digital services like robotic process automation, customer software development, e-commerce solutions, and more. Reach out to our expert team now and get started.Summarize with:

Vice President – Content Transformation at HurixDigital, based in Chennai. With nearly 20 years in digital content, he leads large-scale transformation and accessibility initiatives. A frequent presenter (e.g., London Book Fair 2025), Gokulnath drives AI-powered publishing solutions and inclusive content strategies for global clients
 A Space for Thoughtful
A Space for Thoughtful 