Why Mobile App Accessibility Matters and How to Improve It?
Summary
This blog explores why mobile accessibility matters, its impact on inclusivity, and key accessibility remediation strategies. Learn how mobile web accessibility, usability best practices, and assistive technologies can make your app seamless for all users. Keep reading to discover how an inclusive mobile experience can give you a competitive edge!
In the age of mobile computing, phones and tablets have become essential devices, acting as our crucial resources for using the Internet. On the other hand, inaccessible mobile app solutions that lack ADA compliance standards can pose significant obstacles for over 1.3 billion individuals with disabilities.
It has been demonstrated that inclusively designed apps enhance everyday active users, improve retention, and broaden their audience. Providing mobile app solutions that are accessible to consumers with disabilities can boost app customer retention by 36%. Building for accessibility entails improving the experience for all your clientele, so making an effort is worth it.
This blog covers the intricacies of mobile app accessibility remediation to create an inclusive app experience and the reasons why it improves your business. Let’s dispel the ambiguity surrounding accessibility, explore its benefits, and close the gaps in digital experiences. Keep reading to discover how being inclusive can give you a competitive edge!
Table of Contents:
- Understanding Mobile Accessibility
- Why is Mobile App Accessibility Significant?
- The Impact on User Experience and Inclusivity
- Mobile Web Accessibility & Mobile Usability
- 6 Steps to Accessibility Remediation for Apps
- Strategies for Creating Seamless Mobile User Experiences
- Conclusion
Understanding Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility involves designing and developing mobile interfaces that focus on inclusivity and user accessibility. It centers around recognizing users’ diverse needs and capabilities, including those with visual impairments, hearing loss, motor disabilities, or cognitive challenges. In essence, it’s about ensuring that every individual can interact effortlessly with mobile technology, irrespective of their unique abilities.
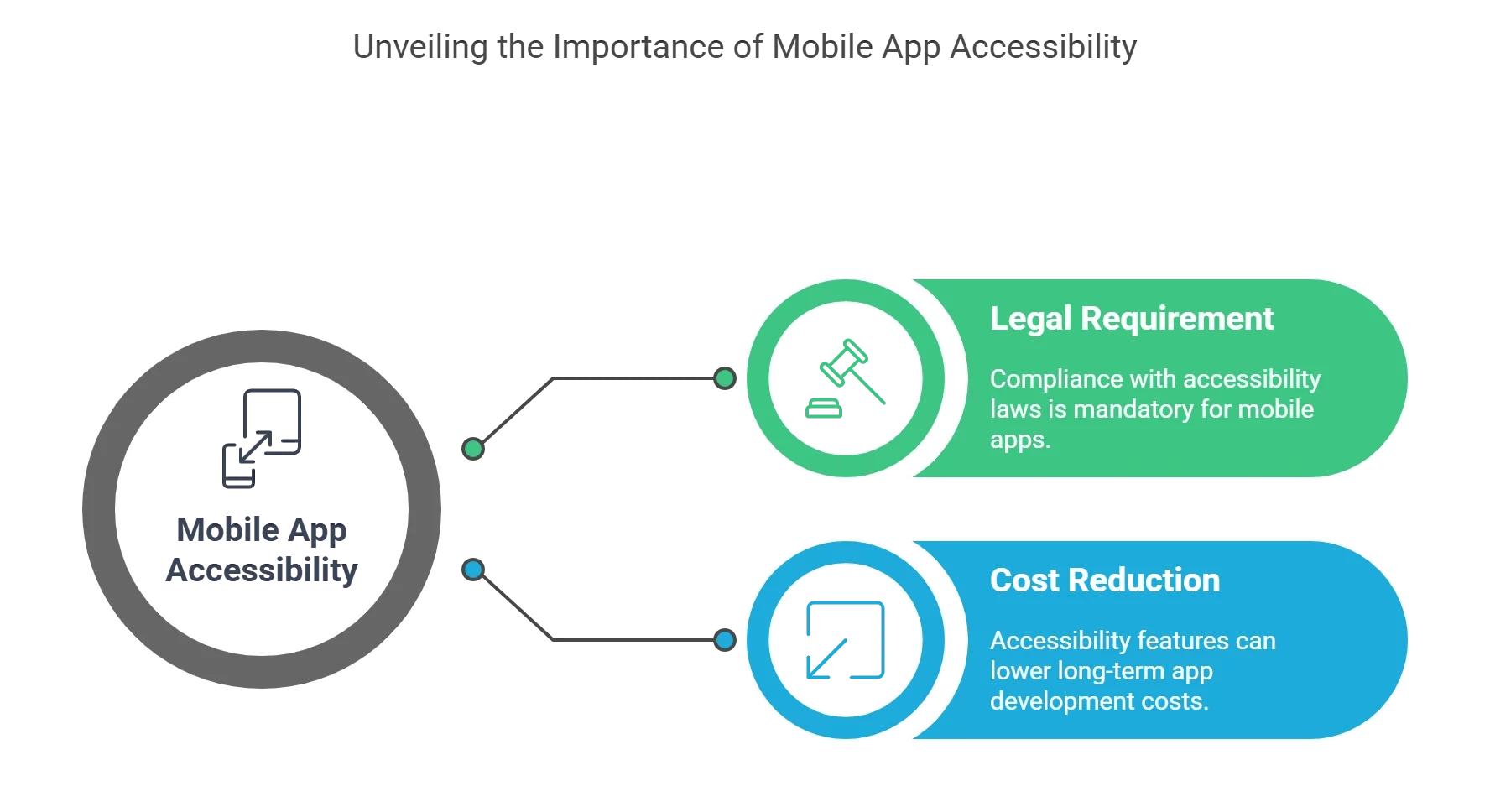
Why is Mobile App Accessibility Significant?
Apps with accessible mobile design can cater to a wider range of people. Businesses can create online experiences that are accessible to everyone by anticipating the needs of individuals with disabilities.
However, here are the two basic and crucial requirements for making apps ADA-compliant:
1. It is a Stringent Legal Requirement
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) mandates that all businesses must provide accessible online content. Organizational leaders are devoting additional funds to technological compliance, even as the number of lawsuits related to ADA web accessibility rises annually.
However, in addition to being necessary for websites, Title III of the ADA also mandates accessibility for mobile apps.
As stated differently, all organizations are legally required to ensure that their mobile apps are accessible. Of course, there are other benefits to being accessible, but for many companies, ensuring proper accessibility remediation for ADA compliance is a persuasive case.
2. Reduces the Cost of Developing Mobile Apps
ADA compliance for mobile apps helps emphasize the advantages of inclusive design when developing an accessible mobile app.
The widely accepted international norms for digital accessibility are the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which also serve as an outstanding basis for enhancing adherence to other non-discrimination regulations and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Despite being a technical manual, the WCAG doesn’t severely restrict mobile app developers; on the contrary, it strengthens industry standard practices.
You can connect with a wider audience and lower your service’s long-term expenditures by adhering to WCAG guidelines for mobile:
- WCAG requires accurate semantic markup. When its semantics are right, your app will function on a greater variety of platforms and be easier to upgrade and add new functions to.
- WCAG demands responsive content design. Setting reflow as a top priority is essential because non-responsive mobile app content will not function consistently across various screens.
- When a feature needs pointer gestures, WCAG mandates that the feature be able to be used with just one pointer and no path-based gesture. Adhering to this stipulation guarantees that the content functions for a wider spectrum of users.
The Impact on User Experience and Inclusivity
Prioritizing mobile accessibility results in user experiences that are inclusive, efficient, and delightful for all. An accessible mobile interface allows individuals with disabilities to independently access information, communicate, and engage with mobile apps and websites. It fosters inclusivity, empowering everyone to participate fully in the digital world.
When entering the world of mobile design, understanding and applying mobile accessibility guidelines becomes paramount. Mobile interface design isn’t just about creating visually appealing layouts; it’s about crafting inclusive user experiences that accommodate your audience’s diverse needs and abilities. Incorporating mobile accessibility guidelines into your mobile design ensures that every user can seamlessly interact with your mobile interface, regardless of their unique capabilities.
This means designing with empathy, considering touch and gesture interactions, responsive layouts, and clear content presentation. By embracing these principles, you’re not only enhancing the accessibility of your mobile design but also fostering a more inclusive digital landscape for all.
Did You Know? Over 15% of the world’s population lives with some form of disability, highlighting the importance of inclusive design to accommodate a diverse user base.
Mobile Web Accessibility & Mobile Usability
One critical aspect of mobile accessibility is mobile web accessibility. It demands that websites and web applications accessed through mobile devices are designed to be accessible. This entails ensuring compatibility with screen readers, adequately labeled form elements, high color contrast, and easy navigation for touch-based interactions.
Mobile usability complements accessibility by focusing on user-friendliness. It is concerned with crafting intuitive, efficient, and convenient interfaces for interaction on smaller screens. The goal is to make mobile technology a seamless part of users’ lives, regardless of their abilities.
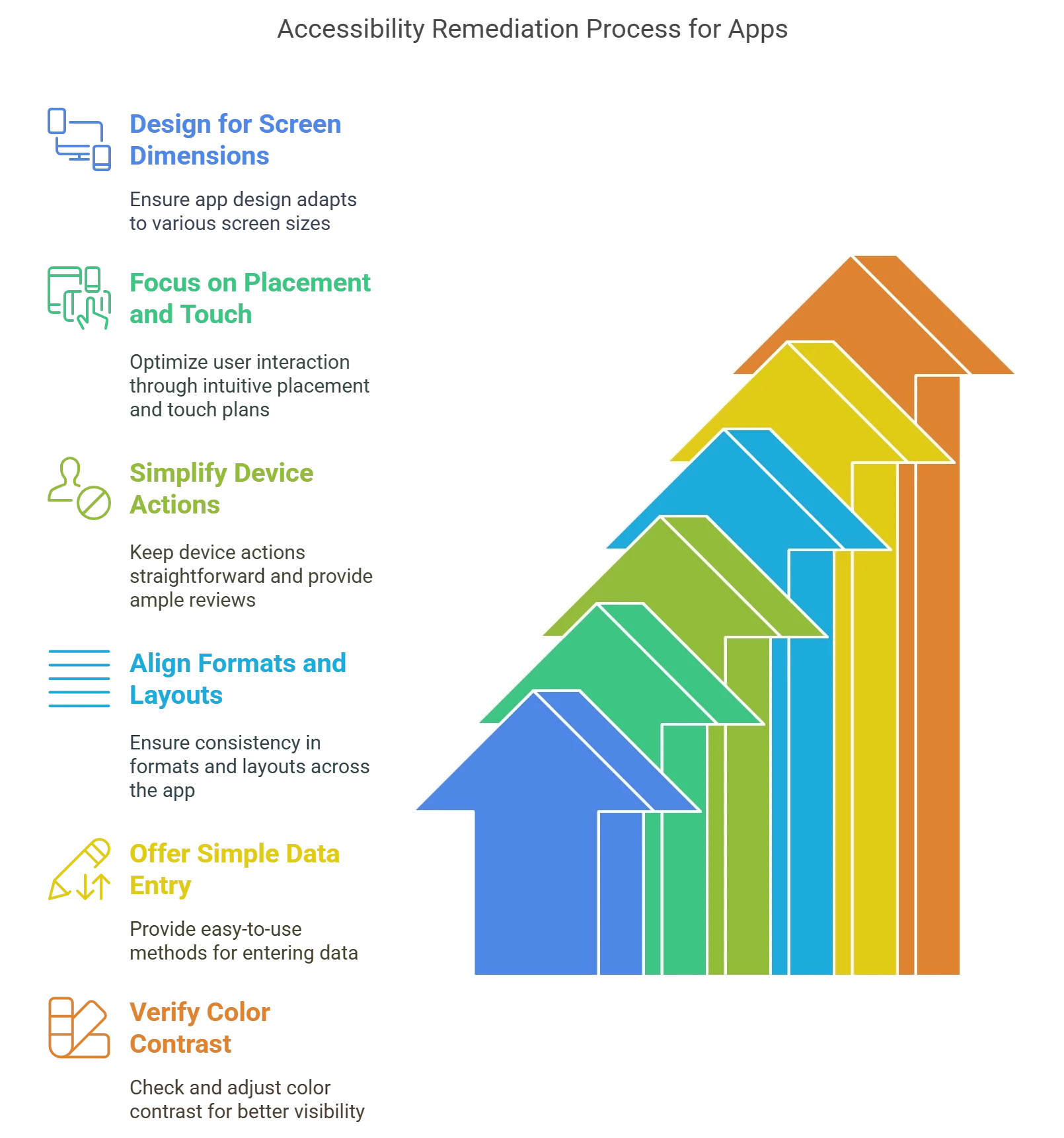
6 Steps to Accessibility Remediation for Apps
Six inclusive accessibility remediation strategies for mobile native apps are outlined here. These are the most important components a native app creator or developer must consider to guarantee accessibility and usability.
1. Design for an Array of Screen Dimensions
Mobile devices are characterized by smaller display sizes and unique aspect ratios, which developers must consider when creating native apps. A less extensive screen reduces the amount of data that users can process at once, particularly when they are using it to enlarge content because of low vision.
Here are a few accessibility app development tips to enhance the user interface for small screens:
- Reducing the volume of data on every page by offering a mobile-specific website or using a mobile-friendly design
- Providing touch controls and information with a suitable default size will reduce the necessity for consumers with low vision to zoom in and out
- The link text dimension is adjusted to the viewport breadth
- Form fields should be positioned beneath their labels instead of alongside them.
2. Concentrate on Placement and Touch Plans
Mobile devices with higher resolutions enable the simultaneous presentation of multiple interactive features on a small screen. However, for users to aim for these components with their fingertips, they need to be sufficiently big and far apart.
An app’s tap targets must be large enough to allow users to engage confidently and precisely, even when they are rushing through tasks.
Touch target size: optimal procedures include:
- Creating touch targets with a minimum height and width of 9 mm
- Increasing the amount of inactive space around smaller touch targets
The interactive components on mobile applications should also be well-positioned so that users can easily access them no matter how the device is held. Designers should take into account the possibility that a button that is intuitive for certain individuals may be challenging for others to navigate.
Here are some pointers for placing touch targets:
- Place the buttons in a convenient location
- Give every interactive aspect unlimited operational status
3. Maintain Device Actions Basic and Offer Plenty of Reviews
The majority of mobile devices are made mainly for use with touchscreen actions. These motions can be as straightforward as tapping with one fingertip or as complicated as using several fingers, pressing using several taps, and drawing patterns.
Mobile app control gestures should be as simple for users as possible. Those with motor or skill disabilities may find complicated gesture control especially difficult. Provide substitutes that enable basic swipe or tap actions instead of complicated ones.
4. Ascertain Formats and Layouts are in Tandem
In a mobile application, elements that are displayed repeatedly on different pages must have a uniform structure. Pages with specific dimensions and positioning should have in-line placement of navigational elements and repeating features according to a responsive layout, which arranges components depending on device size and display orientation.
5. Offer Simple Techniques for Entering Data
Another crucial feature of mobile devices is multi-modal data entry, which allows individuals to input data using a variety of methods, such as speech, a displayed keyboard, and a Bluetooth keypad.
For certain users, typing can be laborious and challenging; however, alternative methods of information entry can take priority. Provide checkboxes, toggle switches, or select listings to minimize the volume of text entry needed. You can also have known data (like the date, time, and location) filled in automatically.
6. Verify Color Contrast
The majority of users can follow the general color contrast ratios outlined by WCAG, but mobile apps and devices require special consideration.
Mobile device use is more common outside, where sunlight may make it difficult to focus on the screen. For all users, employing good contrast is essential, as poor contrast can exacerbate the difficulties individuals with low vision have while using mobile devices.
Strategies for Creating Seamless Mobile User Experiences
Design for Touch and Gestures: Mobile interfaces heavily rely on touch interactions and gestures. The importance here lies in ensuring that touch targets, such as buttons and links, are appropriately sized and spaced to prevent accidental taps. Familiar gestures and clear visual feedback enhance the user experience.
- Responsive and Flexible Layouts: Responsive layouts ensure content adapts to different screen sizes and orientations. This allows users with diverse abilities to access and interact with the interface comfortably.
- Clear and Concise Content: The use of clear headings, straightforward language, and well-structured content aids comprehension. Breaking down information into smaller, scannable sections makes it more digestible for all users.
- Provide Accessibility Features: Incorporate accessibility features specific to mobile devices, such as screen magnification, text-to-speech, and closed captioning options. These features empower individuals with disabilities to access and engage with content effectively.
- Support Assistive Technologies: Compatibility with assistive technologies, like screen readers and alternative input methods, is crucial. Properly labeling form elements, providing descriptive alt text for images, and offering skip-navigation options contribute to a more accessible experience.
- Test and Iterate: Thorough testing with users of diverse abilities, gathering feedback, and making iterative improvements ensures continuous enhancement of the overall user experience.
Conclusion
Performance is driven by accessibility; however, the advantages of accessibility testing for mobile go beyond just performing well.
Making sure your app is usable by people with different abilities is a moral duty and a smart business move for mobile app developers. An accessible mobile experience expands your app’s user base, fosters client retention, and improves your company’s perception.
Mobile Accessibility is not merely an option but a necessity. It ensures that people with disabilities can effortlessly navigate and engage with mobile interfaces, making the digital world a more inclusive place. By implementing strategies like mobile web accessibility, touch and gesture-friendly designs, and support for assistive technologies, we can create mobile experiences that are both user-friendly and inclusive.
If you are looking for mobile app accessibility remediation, get in touch with Hurix Digital. Our accessibility specialists have laid the groundwork for an effective methodology-based assessment. In addition, we certify your products and provide WCAG audit reports to help with your marketing and sales initiatives.

Vice President – Digital Content Transformation. He is PMP, CSM, and CPACC certified and has 20+ years of experience in Project Management, Delivery Management, and managing the Offshore Development Centre (ODC).